USGS: Multiple Earthquakes Shake Hayward
Breaking News Today
Feb 14, 2025 · 5 min read
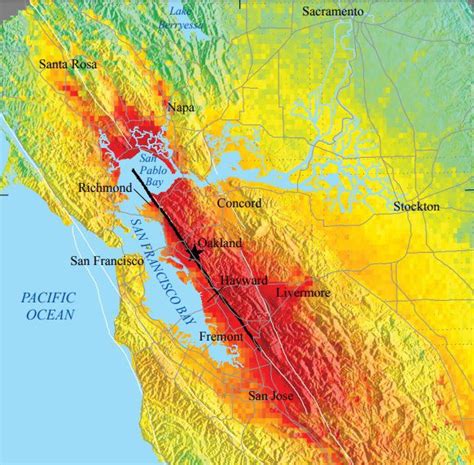
Table of Contents
USGS: Multiple Earthquakes Shake Hayward - A Deep Dive into Seismic Activity
The Hayward Fault, a major geological feature running through the heart of the San Francisco Bay Area, is infamous for its potential to unleash devastating earthquakes. Recent seismic activity, as reported by the United States Geological Survey (USGS), has once again highlighted this risk, with multiple earthquakes shaking Hayward and surrounding communities. This article will delve into the details of these recent tremors, explore the geological context of the Hayward Fault, examine the potential for future earthquakes, and discuss the importance of preparedness in earthquake-prone regions.
Understanding the Recent Earthquake Swarm
The USGS reported a series of earthquakes in the Hayward area, with magnitudes ranging from minor tremors barely perceptible to residents to more significant events felt across a wider region. These events, often occurring in close temporal proximity, are characteristic of what seismologists refer to as an earthquake swarm. Earthquake swarms differ from earthquake sequences – which typically begin with a larger mainshock followed by aftershocks – in that there isn't a clear dominant mainshock. Instead, the seismic activity is more diffuse, with a number of events of comparable magnitude.
Analyzing the Data: Magnitude, Depth, and Location
Precise data regarding the location, magnitude, and depth of each earthquake are crucial for understanding the overall seismic activity. The USGS provides this information in real-time through its website and various mobile applications. Examining the precise locations of these events can help seismologists pinpoint the specific areas of stress along the fault line. The depth of the earthquakes is also vital; shallower earthquakes generally cause greater damage at the surface than deeper ones, even if they have the same magnitude. Detailed analysis of this data is essential for refining earthquake hazard models and improving earthquake early warning systems.
The Role of the USGS in Monitoring Seismic Activity
The USGS plays a critical role in monitoring earthquake activity across the United States, including the highly active Hayward Fault zone. Its dense network of seismic sensors provides real-time data on earthquake occurrences. This data is then analyzed to determine the magnitude, location, and depth of each event. This rapid and accurate information is vital for public safety, enabling emergency response teams to react quickly and efficiently. The USGS also conducts extensive research to better understand earthquake processes and improve prediction models.
The Hayward Fault: A Geological Overview
The Hayward Fault is a major active fault, part of the larger San Andreas Fault system. It runs approximately 74 kilometers (46 miles) through densely populated areas of the East Bay region, including cities like Hayward, Fremont, and Oakland. The fault's location within a highly populated area makes it a significant source of earthquake risk. Geologists estimate the Hayward Fault has the potential to produce earthquakes of up to magnitude 7.0 or greater, capable of causing widespread devastation.
Understanding Fault Movement and Seismic Risk
The Hayward Fault is a strike-slip fault, meaning the movement along the fault is primarily horizontal. The two sides of the fault move past each other in opposite directions. This movement is not continuous but rather occurs in fits and starts, with periods of relative inactivity punctuated by sudden, dramatic slips that generate earthquakes. The accumulated stress along the fault over time eventually exceeds the strength of the rocks, leading to a rupture and the release of energy in the form of an earthquake. This cyclical process highlights the inevitability of future seismic events along the Hayward Fault.
Historical Earthquakes and Seismic Records
Historical records provide valuable insights into the past behavior of the Hayward Fault. While complete records are not available for the entire history of the fault, existing data reveal a pattern of significant earthquakes occurring at intervals of hundreds of years. Understanding the recurrence intervals of past earthquakes is critical for assessing the likelihood of future events and for developing effective mitigation strategies. The study of paleoseismology, which involves examining geological evidence of past earthquakes, helps to extend the historical record and improve our understanding of the fault's long-term behavior.
Preparedness: Mitigating Earthquake Risks
Given the significant seismic risk posed by the Hayward Fault, preparedness is crucial. This involves a multi-faceted approach encompassing individual actions, community initiatives, and government policies.
Individual Preparedness: What You Can Do
Individuals can take several steps to prepare for a potential earthquake along the Hayward Fault. These include:
- Developing an emergency plan: This should outline communication strategies, evacuation routes, and meeting points.
- Creating an emergency kit: This kit should include essential supplies such as food, water, medications, a first-aid kit, and a flashlight.
- Securing your home: This involves identifying and securing potential hazards such as heavy objects that could fall during an earthquake.
- Learning earthquake safety procedures: Knowing what to do during and after an earthquake can significantly improve your chances of survival.
Community and Government Initiatives
Effective earthquake preparedness requires collaboration between individuals, communities, and government agencies. Communities can organize earthquake drills and awareness campaigns to educate residents about earthquake risks and safety procedures. Government agencies play a critical role in enforcing building codes, developing emergency response plans, and providing resources for earthquake preparedness. Investing in infrastructure improvements designed to withstand seismic events is also crucial.
Conclusion: Living with the Hayward Fault
The recent earthquake swarm near Hayward serves as a stark reminder of the ever-present seismic risk in the San Francisco Bay Area. While the precise timing of future large earthquakes along the Hayward Fault remains unpredictable, the inevitability of such events is undeniable. Through a combination of scientific monitoring, comprehensive risk assessment, and a dedicated approach to preparedness, communities can mitigate the potential impacts of future earthquakes and build resilience in the face of this ongoing geological reality. The USGS continues to play a vital role in monitoring seismic activity, providing crucial data and insights that guide our efforts to understand and prepare for the next significant event. Staying informed and actively engaging in preparedness measures is essential for everyone living in the vicinity of the Hayward Fault.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
People Who Benefit From Its Philanthropy Are All
Mar 12, 2025
-
What Do You Call The Demarcation Point For Fiber Technologies
Mar 12, 2025
-
Which Statement Best Describes The Circular Flow Model
Mar 12, 2025
-
Trac Nghiem Kinh Te Chinh Tri Chuong 6
Mar 12, 2025
-
A State Function Is Best Described As
Mar 12, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about USGS: Multiple Earthquakes Shake Hayward . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
