Using Budgeting Assumptions When Preparing The Master Budget
Breaking News Today
Mar 17, 2025 · 7 min read
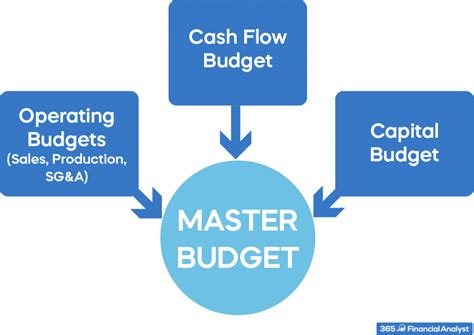
Table of Contents
Using Budgeting Assumptions When Preparing the Master Budget
The master budget is the cornerstone of any successful organization's financial planning. It's a comprehensive document that brings together all the individual budgets into a unified whole, providing a roadmap for the upcoming fiscal period. However, the accuracy and usefulness of the master budget hinge heavily on the underlying budgeting assumptions. These assumptions, which are essentially educated guesses about the future, directly impact every aspect of the budget, from sales forecasts to production plans and ultimately, the organization's financial health. This article delves deep into the crucial role of budgeting assumptions in preparing a robust and reliable master budget.
Understanding the Master Budget and its Components
Before exploring budgeting assumptions, let's briefly review what a master budget entails. It's not just a single document; rather, it's a collection of interconnected budgets that provide a holistic view of the organization's financial projections. Key components often include:
-
Sales Budget: This is the foundation upon which all other budgets are built. It forecasts sales revenue based on anticipated demand, pricing strategies, and market conditions.
-
Production Budget: Based on the sales budget, this outlines the quantity of goods to be produced, considering factors like inventory levels and production capacity.
-
Direct Materials Budget: This details the cost of raw materials needed for production, factoring in material costs, wastage, and desired inventory levels.
-
Direct Labor Budget: This budget estimates the labor costs required for production, encompassing wages, benefits, and overtime.
-
Manufacturing Overhead Budget: This covers all indirect manufacturing costs, including factory rent, utilities, and depreciation.
-
Selling and Administrative Expense Budget: This outlines the expenses associated with selling and marketing products, as well as administrative costs.
-
Cash Budget: This projects the organization's cash inflows and outflows, ensuring sufficient liquidity.
-
Capital Expenditure Budget: This details planned investments in fixed assets, such as property, plant, and equipment.
-
Pro Forma Financial Statements: These projected financial statements (income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement) summarize the overall financial impact of the master budget.
The Critical Role of Budgeting Assumptions
The accuracy of each of these individual budgets, and consequently the master budget as a whole, relies heavily on a set of realistic and well-defined budgeting assumptions. These assumptions are not arbitrary guesses; they should be based on thorough research, market analysis, historical data, and expert opinions. Failing to carefully consider these assumptions can lead to significant discrepancies between the budgeted figures and actual results, rendering the entire budgeting process ineffective.
Key Categories of Budgeting Assumptions
Budgeting assumptions can be categorized in several ways, depending on the specific context of the organization. However, some common categories include:
1. Sales Assumptions:
-
Market Demand: This is arguably the most crucial assumption. It forecasts the overall demand for the organization's products or services. Factors to consider include market size, growth rate, competition, economic conditions, and consumer trends. This requires careful analysis of market research data, industry reports, and competitor analysis.
-
Sales Price: The assumed selling price significantly impacts revenue projections. Factors influencing price include cost structure, competition, market positioning, and pricing strategies.
-
Sales Mix: This refers to the proportion of different products or services sold. Fluctuations in sales mix can impact revenue and profitability, making accurate assumptions crucial.
-
Sales Growth Rate: Forecasting the rate of sales growth is fundamental. This requires analyzing historical sales data, considering market trends, and assessing potential growth opportunities.
2. Production Assumptions:
-
Production Capacity: This defines the maximum amount of goods or services that can be produced within a given timeframe. It considers factors like available equipment, labor force, and production efficiency.
-
Production Efficiency: This assumes a certain level of efficiency in the production process. Factors such as machine downtime, labor productivity, and waste reduction need to be considered.
-
Inventory Levels: Decisions regarding desired inventory levels (raw materials, work-in-progress, finished goods) are critical assumptions that affect both production and cash flow.
3. Cost Assumptions:
-
Direct Material Costs: These assumptions involve forecasting the cost of raw materials, considering factors like commodity prices, supplier contracts, and potential price fluctuations.
-
Direct Labor Costs: This involves projecting labor costs, accounting for wages, benefits, and potential changes in labor rates or workforce size.
-
Manufacturing Overhead Costs: This includes estimating indirect costs like rent, utilities, and depreciation. Changes in these costs should be factored in based on expected changes in production levels or operational adjustments.
-
Selling and Administrative Expenses: Forecasting these costs requires analyzing historical data and projecting future expenses based on anticipated sales volumes, marketing campaigns, and administrative changes.
4. Financial Assumptions:
-
Interest Rates: These assumptions are crucial for calculating interest expenses on loans and the return on investments.
-
Tax Rates: Accurate assumptions about applicable tax rates are vital for calculating income tax expense.
-
Exchange Rates: For organizations engaged in international trade, fluctuating exchange rates must be carefully considered.
-
Inflation Rates: The anticipated inflation rate impacts various costs and revenues and should be factored into the budget.
5. External Environmental Assumptions:
-
Economic Conditions: Assumptions about economic growth, unemployment rates, and consumer confidence can significantly impact sales forecasts and overall budget performance.
-
Government Regulations: Changes in government regulations, such as new environmental laws or tax policies, need to be considered and integrated into the budget.
-
Competition: Assumptions about competitor actions, such as new product launches or pricing strategies, are vital for creating a realistic sales forecast.
-
Technological Advancements: Rapid technological changes can disrupt markets and impact production processes. The potential for technological advancements must be considered.
-
Natural Disasters/Unforeseen Events: While difficult to predict accurately, the potential for unexpected events that impact operations should be at least qualitatively considered.
The Process of Developing Budgeting Assumptions
The development of sound budgeting assumptions is an iterative process that requires collaboration across different departments and levels of management. The steps typically involved include:
-
Data Gathering and Analysis: Begin by gathering relevant historical data, market research reports, industry benchmarks, and expert opinions. This stage involves thorough analysis to identify trends and potential risks.
-
Scenario Planning: Develop multiple scenarios based on different possible outcomes (e.g., optimistic, pessimistic, most likely). This approach helps to assess the sensitivity of the budget to different assumptions.
-
Consultation and Collaboration: Involve key stakeholders from different departments to ensure that the assumptions reflect the collective knowledge and expertise within the organization.
-
Documentation and Review: Document all assumptions clearly and concisely, explaining the rationale behind each one. Regularly review and update the assumptions throughout the budget period as new information becomes available.
-
Sensitivity Analysis: Conduct a sensitivity analysis to understand how changes in key assumptions (e.g., sales volume, material costs) impact the overall budget. This provides insights into potential risks and opportunities.
The Consequences of Poor Budgeting Assumptions
Using inaccurate or poorly developed budgeting assumptions can have severe consequences, including:
-
Inaccurate Financial Projections: The entire master budget will be unreliable, leading to poor decision-making.
-
Insufficient Resources: Underestimating costs or overestimating revenue can lead to a shortage of resources, hindering operations.
-
Missed Opportunities: Underestimating market demand or potential growth can lead to missed opportunities for expansion and increased profitability.
-
Financial Losses: Overestimating revenue or underestimating costs can result in significant financial losses.
-
Damaged Credibility: Repeated inaccuracies in the budget can damage the credibility of the financial planning process and undermine trust in management.
Conclusion
The master budget is a powerful tool for financial planning and control, but its effectiveness depends entirely on the accuracy and realism of the underlying budgeting assumptions. By carefully considering the key categories of assumptions, employing a rigorous development process, and regularly reviewing and updating the assumptions, organizations can create a robust master budget that serves as a reliable guide for achieving their financial objectives. Remember, a well-developed master budget, built on sound assumptions, is not just a financial projection; it's a strategic roadmap for success. The effort invested in crafting realistic and informed assumptions will yield significant returns in terms of improved financial performance and better decision-making.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Describe The Continuous Nature Of The Physical Fitness Concept
Mar 18, 2025
-
High Levels Of Cholesterol Can First Lead Directly To
Mar 18, 2025
-
True Or False Professional And Technical Communication Is Research Oriented
Mar 18, 2025
-
Which Best Describes The Terrorist Planning Cycle
Mar 18, 2025
-
Cdl Combination Test Questions And Answers Pdf
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Using Budgeting Assumptions When Preparing The Master Budget . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
