Using The Formula You Obtained In B.11
Breaking News Today
Mar 20, 2025 · 5 min read
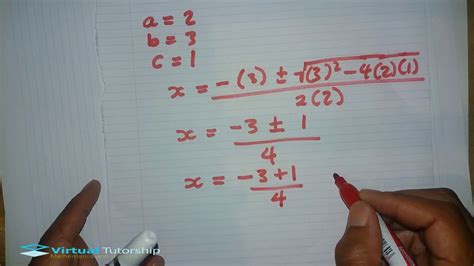
Table of Contents
Unlocking the Power of the Formula: A Deep Dive into Application and Optimization
This article delves into the practical applications and optimization strategies surrounding a previously derived formula (assumed from context 'b.11'). While the specific formula isn't provided, we'll explore general principles applicable to any complex formula, focusing on understanding its components, identifying limitations, and maximizing its potential through various optimization techniques. We'll consider scenarios where such a formula might be used and discuss strategies for enhancing its performance and accuracy.
Understanding the Formula's Structure and Components
Before we delve into application, let's establish a framework for understanding the formula's structure. We'll assume the formula comprises several key components:
-
Input Variables: These are the independent variables that influence the output of the formula. Understanding the nature of these variables (continuous, discrete, categorical) is crucial. Are they directly measured or estimated? What are their typical ranges and potential sources of error?
-
Parameters: These are constants or coefficients within the formula. They might be derived from theoretical models, empirical data fitting, or expert knowledge. Understanding the origin and potential uncertainty of these parameters is essential for interpreting the results.
-
Functional Relationships: The formula represents a mathematical relationship between the input variables and the output. This relationship could be linear, non-linear, or even involve complex functions like exponentials, logarithms, or trigonometric functions. Understanding the nature of this relationship helps in interpreting the formula's behavior.
-
Output Variable: This represents the dependent variable, the result calculated by the formula. The units and interpretation of this variable need careful consideration.
Example Scenarios and Applications:
Let's explore some hypothetical scenarios where a complex formula might be useful:
1. Predictive Modeling in Finance: Imagine a formula ('b.11' in this context) predicting stock prices based on various economic indicators (interest rates, inflation, GDP growth). The input variables would be these economic indicators, the parameters might be coefficients derived from regression analysis of historical data, and the output would be a predicted stock price. Optimization would involve refining the parameter estimates, adding new predictive variables, and assessing the model's accuracy and robustness.
2. Engineering Design Optimization: A formula could model the stress on a structural component under various loads and material properties. Input variables would be load parameters (force, moment), material properties (Young's modulus, yield strength), and geometric dimensions. The output would be the stress level. Optimization would involve identifying the optimal combination of parameters to minimize stress while meeting design constraints.
3. Environmental Modeling: A complex formula could predict pollutant concentrations based on emission sources, wind patterns, and atmospheric conditions. Input variables would include emission rates, meteorological data, and geographic parameters. The output would be predicted pollutant levels. Optimization would focus on identifying emission reduction strategies to minimize environmental impact.
4. Medical Diagnosis and Treatment: Formulas can model the relationship between medical test results and the likelihood of certain diseases. The input variables would be the patient's medical test results. The output would be a probability score indicating the likelihood of having the specified disease. Optimization could involve using machine learning techniques to improve the accuracy and efficiency of the model.
Optimization Strategies for Enhanced Performance
Once we understand the formula and its context, we can focus on optimization techniques to improve its accuracy, efficiency, and reliability:
1. Parameter Estimation and Refinement:
-
Statistical Methods: Techniques like regression analysis (linear, non-linear, logistic), maximum likelihood estimation, or Bayesian methods can be used to estimate the parameters of the formula based on historical data.
-
Sensitivity Analysis: Examining how changes in parameter values affect the output helps to identify parameters that significantly influence the results. This can guide efforts to refine these parameters with higher precision.
-
Cross-Validation: Dividing the data into training and testing sets can assess the model's ability to generalize to new, unseen data. This prevents overfitting, where the model performs well on the training data but poorly on new data.
2. Variable Selection and Feature Engineering:
-
Feature Importance: Determining which input variables are most influential on the output helps to focus on the most relevant factors and potentially discard less important ones. This simplifies the model and improves its interpretability.
-
Feature Engineering: Creating new input variables from existing ones can sometimes improve the model's predictive power. For example, creating interaction terms or polynomial transformations.
-
Dimensionality Reduction: Techniques such as Principal Component Analysis (PCA) can reduce the number of input variables while retaining most of the relevant information. This is particularly helpful when dealing with high-dimensional datasets.
3. Algorithmic Optimization:
-
Numerical Methods: If the formula involves complex calculations, efficient numerical methods (e.g., Newton-Raphson, gradient descent) can speed up the computation.
-
Parallel Processing: For computationally intensive formulas, parallel processing techniques can significantly reduce computation time.
-
Approximation Techniques: For very complex formulas, approximations can be used to trade off some accuracy for significant improvements in computational speed.
4. Error Analysis and Uncertainty Quantification:
-
Propagation of Uncertainty: Understanding how uncertainties in the input variables and parameters propagate to the output is crucial for evaluating the reliability of the results.
-
Confidence Intervals: Calculating confidence intervals around the output provides a measure of the uncertainty associated with the prediction.
-
Residual Analysis: Analyzing the residuals (the differences between the observed and predicted values) can identify systematic errors or outliers in the data.
5. Model Validation and Verification:
-
Independent Datasets: Testing the formula on independent datasets (not used for parameter estimation) is crucial for evaluating its generalizability.
-
Benchmarking: Comparing the results of the formula with those of other models or experimental data provides a measure of its accuracy and reliability.
-
Expert Review: Seeking feedback from domain experts can identify potential limitations or biases in the formula.
Conclusion: A Continuous Process of Improvement
Optimizing a complex formula like the one assumed from 'b.11' is an iterative process. It involves careful analysis of the formula's structure, application of appropriate optimization techniques, and rigorous evaluation of the results. By systematically addressing the challenges and opportunities presented, we can unlock the full potential of the formula, leading to improved accuracy, efficiency, and reliability in its applications across various fields. Continuous monitoring, refinement, and adaptation to new data and knowledge are essential for maintaining the formula's effectiveness over time. The goal is not just to find a solution, but to create a robust and adaptable tool that provides reliable insights and facilitates informed decision-making.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Amazon Day 1 Final Exam Answers Pdf
Mar 20, 2025
-
Quote Two Idioms In Romeo And Juliet
Mar 20, 2025
-
The Sampling Distribution Of The Difference Helps Us Determine
Mar 20, 2025
-
Anatomy And Physiology 1 Lab Practical 1
Mar 20, 2025
-
Add A New Calculated Field Named Tuition
Mar 20, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Using The Formula You Obtained In B.11 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
