What Alterations Are Recommended For Resuscitation Drug Administration
Breaking News Today
Mar 22, 2025 · 6 min read
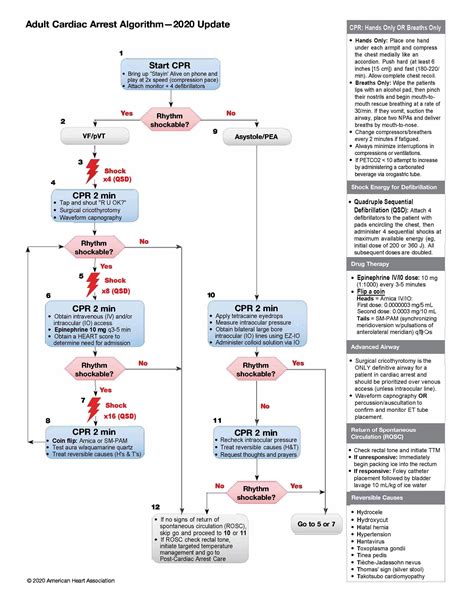
Table of Contents
Recommended Alterations for Resuscitation Drug Administration: Optimizing Outcomes in Emergency Situations
The administration of drugs during resuscitation is a critical aspect of emergency medical care. The goal is swift, effective intervention to restore vital functions and improve patient outcomes. However, the standard approach isn't always optimal, and several alterations can significantly enhance the efficacy and safety of resuscitation drug administration. This article explores key recommendations for altering existing practices, emphasizing evidence-based strategies to improve patient care.
I. Optimizing Drug Selection and Dosing
A. Tailoring Drug Choices to Specific Conditions
The "one-size-fits-all" approach to resuscitation drugs is outdated. Individualized drug selection based on the specific etiology of arrest, patient characteristics (age, weight, comorbidities), and presenting symptoms is crucial. For example, the choice of vasopressor in septic shock might differ from that in cardiogenic shock. Similarly, the dosage of certain drugs needs adjustment based on renal or hepatic function. This necessitates a thorough understanding of the pathophysiology driving the arrest and a nuanced approach to pharmacotherapy.
B. Re-evaluating Standard Doses and Intervals
Traditional drug dosing regimens may not be ideal for all patients. Studies suggest that adjustments based on patient-specific factors, such as body mass index (BMI) and underlying diseases, can lead to improved outcomes. For instance, obese patients may require higher doses of certain medications to achieve the desired therapeutic effect due to increased volume of distribution. Similarly, adjusting the interval between drug administrations based on real-time monitoring of vital signs can improve efficacy and reduce the risk of adverse events.
C. Considering Alternative Drug Delivery Routes
Intraosseous (IO) access remains a valuable alternative to intravenous (IV) access, particularly in situations where immediate vascular access is challenging. This is particularly relevant in pediatric resuscitation and in situations where peripheral IV access is difficult to establish quickly. While IO administration offers a rapid route, careful attention must be paid to the potential for extravasation and complications. Similarly, endotracheal administration may be considered in extreme circumstances, though its efficacy is often debated and requires precise dosage adjustments.
II. Enhancing Drug Administration Techniques
A. Optimizing Infusion Rates and Techniques
The rate of drug infusion significantly impacts its efficacy and the risk of adverse effects. Utilizing infusion pumps ensures precise delivery of drugs, minimizing the potential for errors in dosage and infusion rate. Moreover, carefully monitoring the patient's response to the drug during infusion allows for real-time adjustments, optimizing treatment and reducing the risk of complications. Close attention to the compatibility of drugs when co-infusing through a single line is also vital.
B. Utilizing Advanced Monitoring Techniques
Real-time monitoring of vital signs, including electrocardiogram (ECG), blood pressure, and oxygen saturation, is paramount during resuscitation. These parameters provide valuable feedback on the efficacy of the administered drugs and allow for immediate adjustments. Advanced monitoring techniques, such as transthoracic echocardiography or point-of-care ultrasound, can offer additional insights into the hemodynamic status of the patient, guiding further therapeutic decisions.
C. Integrating Targeted Temperature Management
Hypothermia, particularly after cardiac arrest, can significantly impact drug metabolism and distribution. Therefore, implementing targeted temperature management (TTM) protocols may necessitate adjustments to drug dosages and administration frequencies. Understanding the pharmacokinetic alterations induced by hypothermia is crucial for optimizing drug effectiveness during this phase of post-arrest care.
III. Improving Safety Protocols and Preventing Errors
A. Implementing Double-Checking Procedures
Human error is a significant concern in emergency situations. Rigorous double-checking procedures for drug selection, dosage, and administration route are essential to minimizing the risk of medication errors. Clear communication protocols among healthcare providers, alongside standardized checklists and labeling systems, significantly enhance safety.
B. Utilizing Barcoded Medication Administration (BCMA) Systems
The integration of BCMA systems can improve the safety of drug administration by automatically verifying the selected drug, dose, and patient. These systems minimize the risk of human error and provide an electronic record of drug administration, facilitating improved accountability and analysis of medication errors.
C. Promoting Continuous Education and Training
Regular training and education for healthcare professionals on current guidelines and best practices in resuscitation drug administration are crucial. This includes simulations and hands-on practice to hone skills and improve teamwork. Staying updated on the latest research and evidence-based guidelines ensures that healthcare providers are equipped to make informed decisions during critical situations.
IV. Addressing Specific Drug-Related Challenges
A. Vasopressor Administration
The choice of vasopressor and the optimal dosing strategy remain areas of ongoing research. Careful consideration of the underlying cause of shock, patient comorbidities, and hemodynamic response are essential when selecting and administering vasopressors. Close monitoring of blood pressure, heart rate, and rhythm is vital to prevent adverse events.
B. Electrolyte Management
Electrolyte disturbances are frequently encountered during resuscitation. Careful monitoring of serum potassium, magnesium, and calcium levels is crucial, with prompt correction of any imbalances. Appropriate electrolyte replacement can significantly influence the efficacy of other resuscitation drugs.
C. Acid-Base Balance
Acidosis is commonly observed during resuscitation. Addressing acidosis with appropriate bicarbonate administration, when indicated, can improve the effectiveness of other resuscitation efforts. However, indiscriminate use of bicarbonate should be avoided due to potential adverse effects.
V. The Role of Technology and Future Directions
A. Smart Infusion Pumps and Drug Delivery Systems
Advanced infusion pumps with built-in safety features, such as drug library alerts and dose-limit settings, are playing an increasingly important role in enhancing the safety and efficacy of drug administration. Future developments in smart pumps and drug delivery systems promise to further optimize drug administration, minimize errors, and improve patient outcomes.
B. Pharmacogenomics and Personalized Medicine
The field of pharmacogenomics holds significant promise for individualizing drug therapy based on a patient's genetic makeup. This approach can help predict drug responses, optimize dosages, and minimize adverse drug reactions. Further research in this area may lead to significant advancements in resuscitation drug administration.
C. Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Resuscitation
AI algorithms are being developed to assist in the real-time analysis of patient data during resuscitation, guiding drug selection and dosage adjustments based on individual patient characteristics and response. This technology has the potential to significantly improve the efficiency and effectiveness of resuscitation drug administration.
VI. Conclusion: A Multifaceted Approach to Improvement
Improving resuscitation drug administration requires a multifaceted approach encompassing optimized drug selection, refined administration techniques, enhanced safety protocols, and the integration of advanced technologies. By addressing each of these aspects, we can strive towards more effective and safer resuscitation practices, ultimately leading to improved patient outcomes and a higher survival rate in emergency situations. Continuous research, education, and a commitment to evidence-based practice are crucial in achieving this goal. The future of resuscitation drug administration is likely to be shaped by advanced technologies, personalized medicine, and a deeper understanding of the complex interplay between drug pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and patient physiology. This necessitates a collaborative effort among healthcare professionals, researchers, and technology developers to ensure that every patient receives the best possible care during life-threatening emergencies.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Sickle Cell Disease Is Caused By Quizlet
Mar 23, 2025
-
What Is Included In A Business Plan Quizlet
Mar 23, 2025
-
Which Factors Increase The Risk Of Breast Cancer Quizlet
Mar 23, 2025
-
How Does Hiv Harm The Body Quizlet
Mar 23, 2025
-
Common Causes Of Acute Psychotic Behavior Quizlet
Mar 23, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Alterations Are Recommended For Resuscitation Drug Administration . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
