What Are The Largest Wires In The Automostive Electrical Sustem
Breaking News Today
Mar 17, 2025 · 6 min read
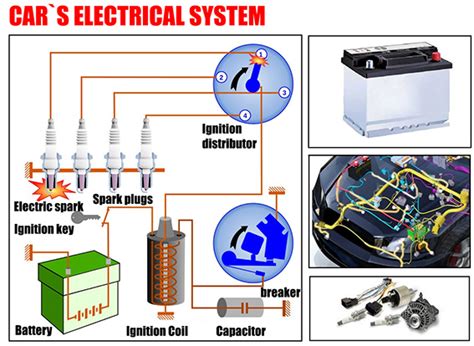
Table of Contents
What Are the Largest Wires in the Automotive Electrical System?
The automotive electrical system, a complex network powering everything from the headlights to the engine control unit (ECU), utilizes a wide range of wire gauges. Understanding the largest wires and their roles is crucial for diagnosing electrical issues, performing repairs, and appreciating the intricate design of modern vehicles. This comprehensive guide delves into the thickest conductors within your car, explaining their function, location, and the implications of damage or failure.
Identifying the Heavy Hitters: Gauges and Ampacity
Before we pinpoint the largest wires, let's establish a common understanding of wire gauge and ampacity. Wire gauge is a standardized system that inversely measures wire diameter. Smaller gauge numbers indicate thicker wires, capable of carrying higher amperage (amps). Ampacity refers to the maximum current a wire can safely carry without overheating or causing damage. The largest wires in your car will naturally have the lowest gauge numbers and the highest ampacity ratings.
Why are large gauge wires necessary? High-amperage components, such as the starter motor, alternator, and battery, demand substantial current flow. Using insufficiently thick wires would lead to excessive resistance, heat generation, and potentially catastrophic failure. Overheating could melt insulation, causing short circuits and even fires.
The Top Contenders for Largest Wires
Several components consistently utilize the largest wires in an automotive electrical system. These are typically located in high-current areas, often near the battery and engine compartment. Precise gauge sizes may vary depending on the vehicle's make, model, and year, but the general principles remain the same.
1. The Battery Cables: The Heavyweight Champions
Undoubtedly, the largest wires in your car are the battery cables. These thick, heavy-duty conductors connect the battery to the starter motor and alternator. They handle the immense current surges required to crank the engine and charge the battery. You'll find these cables are usually made of robust materials designed for high-current applications and often feature substantial insulation for protection against short circuits. Expect to see thick gauge wires, often in the range of 0 gauge (0 AWG) or even larger, depending on the engine size and vehicle type. These are truly the powerhouses of the system.
Identifying Battery Cables: These are easy to locate. Look for the thick cables directly connecting the battery's positive (+) and negative (-) terminals to their respective points on the starter motor and alternator. They are typically red (positive) and black (negative).
Consequences of Damage: Damaged or corroded battery cables are a significant concern. They can lead to a weak or no-start condition, poor charging, and potentially even fire hazards.
2. Starter Motor Cable: Powering Up the Engine
The cable connecting the battery's positive terminal to the starter motor is a crucial component in the starting process. The starter motor demands an enormous amount of current to turn the engine's crankshaft and initiate combustion. This high current draw necessitates a very large wire gauge, often comparable to or even larger than the main battery cable. You'll notice a strong, thick wire attached directly to the starter motor's positive terminal.
Identifying the Starter Cable: This is usually a thick, red wire emanating from the battery's positive terminal and directly connecting to the starter motor's positive terminal.
Consequences of Damage: A damaged starter cable can prevent the engine from starting altogether, due to insufficient current reach. Poor connections cause high resistance, resulting in sluggish cranking or even failure to crank.
3. Alternator Output Cable: Sustaining the Power Supply
The alternator is responsible for generating electricity to charge the battery and power various accessories while the engine is running. The cable linking the alternator's output to the battery's positive terminal carries significant amperage, particularly during charging. While not as thick as the starter cable (due to the constant rather than surge current), it's still one of the largest wires in the system. This is because the alternator outputs a substantial amount of current to maintain the electrical needs of the car.
Identifying the Alternator Output Cable: This cable is typically red and runs from the alternator's positive terminal to the battery's positive terminal or a distribution point.
Consequences of Damage: A damaged or compromised alternator output cable can lead to insufficient charging, resulting in a dead battery and eventual failure of the electrical system.
4. Ground Cables: Completing the Circuit
Don't underestimate the importance of ground cables! While not always the largest in terms of gauge, these thick conductors play a critical role in completing the electrical circuits. They provide a low-resistance path for current to return to the battery's negative terminal. Their size is essential for ensuring efficient current flow. Several significant ground cables, typically black, are strategically placed throughout the vehicle.
Identifying Ground Cables: These are often found attached to the engine block, chassis, and body panels, connecting to the battery's negative terminal. Look for thick, black wires.
Consequences of Damage: Poor ground connections can lead to various electrical problems, including dimming lights, erratic operation of components, and increased risk of corrosion.
Other Potentially Large Wires: Beyond the Basics
While the battery, starter, and alternator cables typically hold the title of "largest," other components may utilize surprisingly thick wires in certain vehicle configurations:
- High-Power Audio Systems: Vehicles equipped with high-powered aftermarket sound systems often use large-gauge wiring to accommodate the substantial current demand of amplifiers and subwoofers. This is especially true for systems with multiple amplifiers.
- Electric Motors (Hybrid/Electric Vehicles): Hybrid and fully electric vehicles have even larger wiring harnesses to handle the high current required for the electric motors. These wires are typically specially designed to withstand intense heat and vibration.
- Heavy-Duty Accessories: Vehicles with heavy-duty accessories, such as winches or power inverters, may require larger-gauge wiring to support their high current draw. These accessories are commonly associated with off-road vehicles, construction equipment and similar applications.
Diagnosing Problems with Large Wires
Identifying issues with large gauge wires often involves visual inspection and testing.
Visual Inspection: Look for signs of:
- Corrosion: White, green, or bluish deposits on the terminals or wire ends indicate corrosion.
- Damage to Insulation: Cracks, cuts, or melting in the insulation can compromise the wire's integrity and cause short circuits.
- Loose Connections: Loose or poorly crimped terminals can lead to high resistance and heat generation.
- Broken Wires: A physically broken wire will completely interrupt the circuit.
Testing: A multimeter is useful to test:
- Voltage Drop: Excessive voltage drop across a wire indicates high resistance, possibly due to corrosion or damage.
- Continuity: A continuity test verifies that the wire is intact and not broken.
- Amperage: Measuring amperage flowing through a wire helps assess whether it's carrying too much current.
Safety Precautions
Working with large automotive wires requires caution.
- Always disconnect the battery's negative terminal before working on any electrical components.
- Wear appropriate safety glasses and gloves.
- Never attempt to repair a damaged wire without proper training and tools. Improper repairs can create significant fire hazards.
- Use proper crimping tools for connecting terminals.
Conclusion
Understanding the largest wires in your vehicle’s electrical system is essential for both maintenance and troubleshooting. The battery cables, starter cable, alternator output cable, and ground cables typically represent the thickest wires, handling the most significant current demands. Recognizing their location and function will allow you to identify potential issues and ensure the safe and reliable operation of your vehicle. Always prioritize safety when working with high-amperage wiring.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
If An Individual Is Heterozygous For A Particular Trait
Mar 18, 2025
-
If You Add More Enzyme The Reaction Will
Mar 18, 2025
-
The Purpose Of A Hazcom Program Is To Ensure That
Mar 18, 2025
-
Describe The Continuous Nature Of The Physical Fitness Concept
Mar 18, 2025
-
High Levels Of Cholesterol Can First Lead Directly To
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Are The Largest Wires In The Automostive Electrical Sustem . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
