What Factor Can Increase Blood Pressure Quizlet
Breaking News Today
Mar 17, 2025 · 5 min read
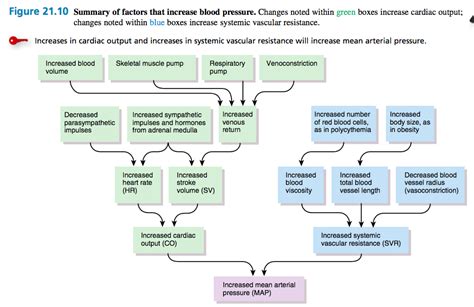
Table of Contents
What Factors Can Increase Blood Pressure? A Comprehensive Guide
High blood pressure, or hypertension, is a serious health concern affecting millions worldwide. Understanding the factors that contribute to its development is crucial for prevention and management. This comprehensive guide explores the various elements that can elevate blood pressure, drawing on established medical knowledge and research. We'll delve into lifestyle choices, underlying health conditions, and genetic predispositions, providing you with a thorough understanding of this complex issue.
Understanding Blood Pressure
Before exploring the factors that increase blood pressure, it's essential to understand what blood pressure actually is. Blood pressure is the force of your blood pushing against the walls of your arteries. It's measured in two numbers:
- Systolic Pressure: The top number, representing the pressure when your heart beats.
- Diastolic Pressure: The bottom number, representing the pressure when your heart rests between beats.
High blood pressure is generally defined as a reading consistently above 140/90 mmHg. However, individual thresholds may vary depending on factors like age and overall health.
Lifestyle Factors Contributing to High Blood Pressure:
Several lifestyle choices significantly impact blood pressure levels. Modifying these behaviors can often effectively manage or prevent hypertension.
1. Diet:
- High Sodium Intake: Excessive salt consumption is a major culprit. Sodium causes the body to retain water, increasing blood volume and subsequently blood pressure. Reducing processed foods, fast food, and restaurant meals, which are often high in sodium, is crucial. Opt for fresh fruits, vegetables, and whole grains instead.
- Unhealthy Fats: Saturated and trans fats found in fried foods, processed snacks, and red meat can raise LDL ("bad") cholesterol levels, contributing to plaque buildup in arteries and increasing blood pressure. Substituting these with healthier fats, like those found in olive oil, avocados, and nuts, is beneficial.
- Lack of Potassium: Potassium helps balance sodium levels in the body. A potassium-deficient diet can exacerbate the effects of high sodium intake. Increasing potassium intake through fruits and vegetables like bananas, spinach, and potatoes can be helpful.
- Excessive Alcohol Consumption: Regular, heavy alcohol consumption directly impacts blood pressure. Moderate alcohol intake, if any, is recommended.
2. Physical Inactivity:
Regular exercise is vital for maintaining healthy blood pressure. Physical activity strengthens the heart, improves blood vessel function, and helps regulate blood pressure. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise per week, along with muscle-strengthening activities twice a week.
3. Obesity:
Excess weight, particularly around the abdomen, puts extra strain on the heart and blood vessels, leading to elevated blood pressure. Weight loss, even a modest amount, can significantly lower blood pressure. A combination of diet and exercise is the most effective approach for weight management.
4. Stress:
Chronic stress can trigger the release of hormones like adrenaline and cortisol, temporarily increasing blood pressure. Prolonged stress can lead to sustained high blood pressure. Effective stress management techniques, such as yoga, meditation, deep breathing exercises, and spending time in nature, can be immensely beneficial.
5. Smoking:
Smoking damages blood vessels, narrows arteries, and increases heart rate, all contributing to high blood pressure. Quitting smoking is one of the most significant steps towards improving cardiovascular health and lowering blood pressure.
Underlying Health Conditions Contributing to High Blood Pressure:
Certain medical conditions can significantly increase the risk of developing hypertension.
1. Chronic Kidney Disease:
Damaged kidneys are less effective at filtering waste and excess fluid from the blood, leading to increased blood volume and pressure.
2. Sleep Apnea:
This sleep disorder, characterized by repeated pauses in breathing during sleep, can lead to oxygen deprivation and trigger hormonal changes that raise blood pressure.
3. Diabetes:
High blood sugar levels damage blood vessels over time, increasing the risk of hypertension. Managing blood sugar levels effectively is crucial for preventing or managing high blood pressure in individuals with diabetes.
4. Thyroid Disorders:
Both hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid) and hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid) can impact blood pressure.
5. Primary Aldosteronism:
This rare endocrine disorder involves the adrenal glands producing excessive aldosterone, a hormone that regulates sodium and potassium levels. This excess can lead to high blood pressure.
6. Cushing's Syndrome:
This condition, resulting from prolonged exposure to high levels of cortisol, can contribute to hypertension.
Genetic Predisposition and Family History:
Family history is a significant risk factor for high blood pressure. A genetic predisposition can make individuals more susceptible to developing hypertension, even if they adopt healthy lifestyle choices. While you can't change your genes, understanding your family history allows for proactive monitoring and preventative measures.
Other Factors Influencing Blood Pressure:
Several other factors can influence blood pressure levels:
- Age: Blood pressure tends to rise with age.
- Race: Certain racial groups, such as African Americans, have a higher prevalence of hypertension.
- Sex: Men tend to have higher blood pressure than women before menopause, after which the risk equalizes.
- Medication Side Effects: Some medications, such as oral contraceptives and certain pain relievers, can elevate blood pressure.
Managing and Preventing High Blood Pressure:
Managing and preventing high blood pressure involves a multifaceted approach:
- Lifestyle Modifications: Adopting a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, maintaining a healthy weight, quitting smoking, and managing stress are crucial.
- Medical Intervention: If lifestyle changes are insufficient, your doctor may prescribe medication to lower blood pressure. Several types of medications are available, each targeting different mechanisms that regulate blood pressure.
- Regular Monitoring: Regular blood pressure checks are essential, both at home and during doctor visits. This allows for early detection and prompt management of any increase in blood pressure.
Conclusion:
High blood pressure is a complex condition influenced by a multitude of factors. While some factors, such as genetics, are beyond our control, many others, like lifestyle choices, can be modified to significantly reduce the risk of developing or worsening hypertension. By understanding these factors and adopting a proactive approach towards health, you can significantly improve your chances of maintaining healthy blood pressure and overall cardiovascular well-being. Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider are vital for early detection and effective management of high blood pressure. Remember that this information is for educational purposes and should not replace advice from a qualified healthcare professional. Consult your doctor for personalized guidance regarding your blood pressure and overall health.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Cdl Combination Test Questions And Answers Pdf
Mar 18, 2025
-
Life Insurance Exam Questions And Answers Pdf
Mar 18, 2025
-
The Direct Carry Is Used To Transfer A Patient
Mar 18, 2025
-
The Emancipation Proclamation Of January 1 1863 Quizlet
Mar 18, 2025
-
These Cards Will Get You Drunk Quizlet
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Factor Can Increase Blood Pressure Quizlet . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
