What Happens In The Condition Called Mitral Valve Prolapse Quizlet
Breaking News Today
Mar 18, 2025 · 6 min read
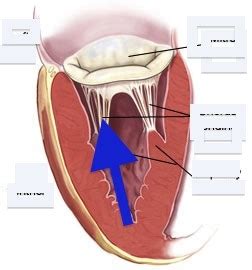
Table of Contents
What Happens in the Condition Called Mitral Valve Prolapse? A Comprehensive Guide
Mitral valve prolapse (MVP), also known as mitral regurgitation, is a common heart condition affecting the mitral valve, one of the four valves in your heart. Understanding what happens in MVP is crucial for managing the condition and improving your overall heart health. This comprehensive guide will delve into the mechanics of MVP, its symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and potential complications.
Understanding the Mitral Valve and Its Function
Before understanding MVP, it's essential to grasp the function of the mitral valve. This valve is located between the heart's two left chambers: the left atrium and the left ventricle. Its primary role is to prevent the backflow of blood from the left ventricle (the powerful pumping chamber) back into the left atrium (the receiving chamber) during ventricular contraction (systole). The mitral valve consists of two leaflets or cusps that open and close precisely with each heartbeat, ensuring unidirectional blood flow.
The Mechanism of Mitral Valve Prolapse
In MVP, one or both leaflets of the mitral valve bulge or prolapse backward into the left atrium during ventricular contraction. This abnormal movement disrupts the valve's ability to close completely, leading to mitral regurgitation—the backflow of blood from the left ventricle to the left atrium. The severity of regurgitation varies, ranging from mild to severe, impacting the extent of blood backflow and the overall workload on the heart.
Causes and Risk Factors of Mitral Valve Prolapse
The exact cause of MVP isn't always clear. While some cases are inherited (familial MVP), others develop due to various factors, including:
1. Connective Tissue Disorders:
MVP is frequently associated with connective tissue disorders like Marfan syndrome and Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. These genetic conditions affect the body's connective tissues, including the heart valves, leading to structural abnormalities.
2. Myxomatous Degeneration:
This condition involves the degeneration of the mitral valve's connective tissue, making it abnormally floppy and prone to prolapse. It's often the underlying cause of non-familial MVP.
3. Rheumatic Fever:
Although less common nowadays, rheumatic fever, a severe inflammatory condition following a streptococcal infection, can damage the heart valves, including the mitral valve, leading to prolapse.
4. Other Factors:
Other potential contributing factors include:
- Age: MVP is more common in older individuals.
- Gender: It's slightly more prevalent in women.
- Infective endocarditis: Bacterial infection of the heart valves can damage the mitral valve.
Symptoms of Mitral Valve Prolapse
Many individuals with MVP are asymptomatic, meaning they experience no noticeable symptoms. However, some individuals may experience various symptoms, which can vary in severity and presence:
1. Palpitations:
A common symptom is palpitations, which are feelings of a rapid, fluttering, or irregular heartbeat. This is often related to the heart's attempt to compensate for the regurgitation.
2. Shortness of Breath (Dyspnea):
Shortness of breath, especially during exertion, may occur as the heart works harder to compensate for the backflow of blood.
3. Chest Pain:
Some individuals may experience chest pain or discomfort, although this is less common and may not be directly related to the MVP itself.
4. Lightheadedness or Dizziness:
Reduced blood flow to the brain due to decreased cardiac output can lead to lightheadedness or dizziness.
5. Fatigue:
The increased workload on the heart can result in fatigue and reduced energy levels.
6. Atrial Fibrillation:
In some cases, MVP can lead to atrial fibrillation, an irregular heartbeat originating in the atria.
It's important to note that these symptoms are not exclusive to MVP and can be present in other heart conditions. Accurate diagnosis requires a thorough medical evaluation.
Diagnosing Mitral Valve Prolapse
Diagnosing MVP involves a combination of physical examination, electrocardiogram (ECG), echocardiogram, and other tests.
1. Physical Examination:
During a physical examination, the doctor will listen to the heart using a stethoscope to detect any murmurs indicative of mitral regurgitation.
2. Electrocardiogram (ECG):
An ECG records the heart's electrical activity. While it may show some abnormalities in individuals with MVP, it's not always diagnostic.
3. Echocardiogram:
An echocardiogram, commonly referred to as an echo, is the most crucial diagnostic tool for MVP. This ultrasound test produces detailed images of the heart's chambers and valves, visualizing the prolapse of the mitral valve leaflets and the degree of regurgitation. A transthoracic echocardiogram (TTE) is typically performed initially; if more detailed images are needed, a transesophageal echocardiogram (TEE) may be used.
4. Other Tests:
In some cases, additional tests like a chest X-ray or cardiac catheterization may be conducted to assess overall heart function and rule out other conditions.
Treatment and Management of Mitral Valve Prolapse
Treatment for MVP depends on the severity of the regurgitation and the presence of symptoms. Many individuals with mild MVP require no specific treatment beyond regular monitoring. However, more severe cases may necessitate medical or surgical interventions:
1. Medical Management:
For individuals with mild to moderate symptoms, medical management focuses on managing symptoms and preventing complications. This may include:
- Medication: Medications like beta-blockers or ACE inhibitors may be prescribed to help manage symptoms like palpitations or reduce the workload on the heart.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is essential. This includes regular exercise, a balanced diet, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding excessive alcohol consumption and smoking.
2. Surgical Intervention:
Surgical intervention is considered for individuals with severe mitral regurgitation, significant symptoms, or progressive heart failure. Surgical options may include:
- Mitral Valve Repair: This procedure aims to repair the damaged valve, restoring its proper function. It is generally preferred over valve replacement when feasible.
- Mitral Valve Replacement: In cases where repair is not possible, a damaged mitral valve may be replaced with a prosthetic valve. The type of prosthetic valve (mechanical or biological) depends on factors like age and overall health.
Potential Complications of Mitral Valve Prolapse
While many individuals with MVP experience no major complications, some potential risks exist, particularly with more severe regurgitation:
1. Heart Failure:
Over time, severe mitral regurgitation can lead to heart failure, where the heart's ability to pump blood efficiently is compromised.
2. Atrial Fibrillation:
MVP can increase the risk of atrial fibrillation, an irregular heartbeat that can lead to blood clots and stroke.
3. Infective Endocarditis:
Individuals with MVP are at a slightly increased risk of infective endocarditis, an infection of the heart valves. Prophylactic antibiotics may be recommended before certain medical procedures.
4. Stroke:
As mentioned above, atrial fibrillation associated with MVP can increase the risk of stroke.
5. Sudden Cardiac Death:
In rare cases, severe MVP can lead to sudden cardiac death, although this is less common.
Living with Mitral Valve Prolapse
Living with MVP often involves regular monitoring and adherence to a healthy lifestyle. Regular check-ups with your cardiologist are crucial to monitor the condition's progression and identify any potential complications early. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, a balanced diet, and stress management, can contribute to improved heart health and overall well-being.
It's essential to understand that MVP is not a death sentence. Many individuals with MVP live long and fulfilling lives with proper management and monitoring. Open communication with your healthcare provider, adhering to their recommendations, and making healthy lifestyle choices are key to managing the condition effectively.
Disclaimer: This information is for educational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Always consult with a qualified healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment of any medical condition. This article does not provide any medical advice or diagnosis. It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional for any health concerns.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
If An Individual Is Heterozygous For A Particular Trait
Mar 18, 2025
-
If You Add More Enzyme The Reaction Will
Mar 18, 2025
-
The Purpose Of A Hazcom Program Is To Ensure That
Mar 18, 2025
-
Describe The Continuous Nature Of The Physical Fitness Concept
Mar 18, 2025
-
High Levels Of Cholesterol Can First Lead Directly To
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Happens In The Condition Called Mitral Valve Prolapse Quizlet . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
