What Is An Action Of Growth Hormone Quizlet
Breaking News Today
Mar 18, 2025 · 5 min read
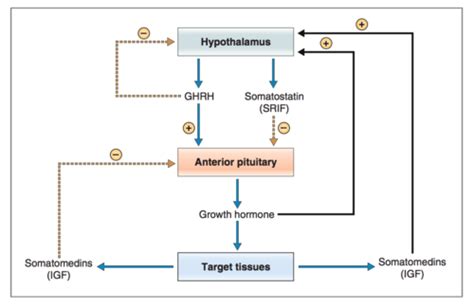
Table of Contents
- What Is An Action Of Growth Hormone Quizlet
- Table of Contents
- What is the Action of Growth Hormone? A Comprehensive Guide
- The Diverse Actions of Growth Hormone: Beyond Height Increase
- Direct Actions of Growth Hormone:
- Indirect Actions of Growth Hormone: The Role of Insulin-like Growth Factor 1 (IGF-1)
- Factors Affecting Growth Hormone Secretion
- Pulsatile Secretion:
- Nutritional Factors:
- Exercise:
- Stress:
- Age:
- Sleep:
- Gender:
- Clinical Significance of Growth Hormone: Deficiency and Excess
- Growth Hormone Deficiency (GHD):
- Growth Hormone Excess (Acromegaly):
- Conclusion: A Holistic Understanding of Growth Hormone's Action
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
What is the Action of Growth Hormone? A Comprehensive Guide
Growth hormone (GH), also known as somatotropin, is a potent peptide hormone synthesized and secreted by the somatotroph cells within the anterior pituitary gland. Its primary function is to stimulate growth and cell reproduction in humans and other animals. However, its actions are far more nuanced and widespread than simply increasing height. Understanding the multifaceted actions of GH is crucial for comprehending its physiological roles and the implications of its dysregulation in various clinical conditions. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricate mechanisms and diverse effects of growth hormone.
The Diverse Actions of Growth Hormone: Beyond Height Increase
While the association between GH and increased height is well-known, its effects extend far beyond linear growth. GH exerts its influence through a complex interplay of direct and indirect mechanisms, impacting various tissues and metabolic processes.
Direct Actions of Growth Hormone:
-
Stimulation of Protein Synthesis: GH directly promotes protein synthesis within cells. It achieves this by increasing the uptake of amino acids into cells, enhancing the translation of messenger RNA (mRNA) into proteins, and reducing the breakdown of existing proteins. This anabolic effect is crucial for tissue growth and repair.
-
Lipogenesis and Lipolysis: GH has a dual role in lipid metabolism. While it can promote the synthesis of fatty acids (lipogenesis) in certain contexts, it predominantly stimulates the breakdown of fats (lipolysis), releasing fatty acids into the bloodstream for energy utilization. This contributes to the overall energy balance of the body.
-
Regulation of Carbohydrate Metabolism: GH exhibits a diabetogenic effect, meaning it can lead to elevated blood glucose levels. It achieves this by decreasing glucose uptake by cells and increasing glucose production by the liver (gluconeogenesis). This effect counteracts the action of insulin.
Indirect Actions of Growth Hormone: The Role of Insulin-like Growth Factor 1 (IGF-1)
The majority of GH's effects are mediated indirectly through the production of Insulin-like Growth Factor 1 (IGF-1), also known as somatomedin C. IGF-1 is a potent growth-promoting peptide produced primarily in the liver in response to GH stimulation. This explains why GH deficiency can present with significantly impaired growth, even if protein synthesis is stimulated directly by GH in other cells.
-
IGF-1's Role in Linear Growth: IGF-1 is the principal mediator of GH's effects on linear growth. It stimulates chondrocyte proliferation and differentiation in the epiphyseal growth plates of long bones, leading to bone elongation. This process is crucial during childhood and adolescence. Once the epiphyseal plates fuse, linear growth ceases, even with high levels of GH and IGF-1.
-
IGF-1's Systemic Effects: IGF-1's influence extends far beyond bone growth. It promotes protein synthesis and cell proliferation in various tissues, including muscle, liver, and other organs. It plays a crucial role in maintaining tissue homeostasis and facilitating repair processes.
-
Feedback Regulation: The relationship between GH, IGF-1, and the hypothalamus forms a negative feedback loop. High levels of circulating IGF-1 inhibit GH secretion from the anterior pituitary, preventing excessive growth and maintaining hormonal balance.
Factors Affecting Growth Hormone Secretion
Several factors influence the secretion of growth hormone, leading to variations in its levels throughout the day and across different life stages.
Pulsatile Secretion:
GH is not released continuously but rather in a pulsatile manner, with peaks and troughs occurring throughout the day. The most prominent surge usually occurs during sleep, particularly in the first few hours of deep sleep. This pulsatile release pattern reflects the complex regulation of GH secretion.
Nutritional Factors:
Nutritional status significantly impacts GH secretion. Protein deficiency can suppress GH levels, while adequate protein intake promotes its release. Similarly, calorie restriction and starvation can decrease GH secretion, while a balanced diet promotes normal GH levels.
Exercise:
Physical exercise, particularly intense and prolonged exertion, stimulates GH release. The exact mechanisms are not fully understood, but it may involve stress-related hormonal changes and altered metabolic demands.
Stress:
Stressful events, including physical trauma, infections, and emotional distress, can influence GH secretion. The impact can be either stimulatory or inhibitory, depending on the nature and duration of the stressor.
Age:
GH secretion declines with age, contributing to the age-related loss of muscle mass, bone density, and other physiological changes. This decline is gradual and begins in early adulthood.
Sleep:
The sleep-wake cycle profoundly affects GH secretion. Sleep deprivation significantly reduces GH levels, underscoring the importance of adequate sleep for maintaining normal GH secretion and overall health.
Gender:
While both males and females have similar GH levels during childhood, minor differences emerge during puberty and adulthood. Sex hormones exert some influence on GH secretion and metabolism.
Clinical Significance of Growth Hormone: Deficiency and Excess
Dysregulation of GH secretion can lead to various clinical conditions, each with unique manifestations and treatment approaches.
Growth Hormone Deficiency (GHD):
GHD, characterized by insufficient GH production, can present with various symptoms depending on the age of onset. In children, it leads to short stature, delayed puberty, and impaired linear growth. In adults, GHD can manifest as reduced muscle mass, increased body fat, decreased bone density, fatigue, and diminished quality of life. Treatment involves GH replacement therapy.
Growth Hormone Excess (Acromegaly):
Acromegaly, caused by excessive GH production, often results from a benign pituitary tumor (adenomas). It leads to the overgrowth of bones, soft tissues, and organs. Symptoms include enlarged hands and feet, facial features changes, joint pain, sleep apnea, and increased risk of cardiovascular complications. Treatment may involve surgery, radiation therapy, or medication to suppress GH secretion.
Conclusion: A Holistic Understanding of Growth Hormone's Action
Growth hormone is a pivotal hormone with far-reaching effects on human physiology. Its actions extend far beyond linear growth, impacting various metabolic pathways, tissue development, and overall health. Understanding its complex mechanisms, regulatory factors, and clinical implications is crucial for effective diagnosis and treatment of conditions related to GH dysregulation. The intricate interplay between GH, IGF-1, and various feedback loops highlights the body's sophisticated ability to maintain hormonal balance and promote optimal health. Further research into GH's actions continues to unveil its multifaceted roles and potential therapeutic applications. While this article provides a comprehensive overview, it is essential to consult with healthcare professionals for any health concerns or questions relating to growth hormone. They can provide personalized advice and guidance based on individual needs and circumstances. This information should not be considered as medical advice and does not replace the need for a consultation with a qualified medical professional.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Do The Kidneys Regulate Blood Volume And Blood Quizlet
Mar 18, 2025
-
After Weeks Of Protest In Zuccotti Park Quizlet
Mar 18, 2025
-
Information May Be Cui In Accordance With Quizlet
Mar 18, 2025
-
Schizophrenia Spectrum Disorders And Psychosis Ati Quizlet
Mar 18, 2025
-
Motor Nerve Neuropathy Is Characterized By Quizlet
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is An Action Of Growth Hormone Quizlet . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
