What Is Another Name For A Condensation Reaction
Breaking News Today
Mar 14, 2025 · 5 min read
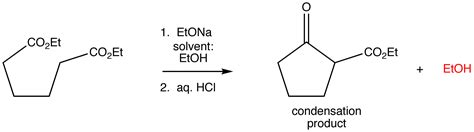
Table of Contents
What is Another Name for a Condensation Reaction?
Condensation reactions are fundamental processes in chemistry, playing a crucial role in the synthesis of a vast array of molecules, from simple polymers to complex biomolecules. Understanding these reactions is key to grasping many aspects of organic chemistry, biochemistry, and materials science. While the term "condensation reaction" is widely used, it's not the only name for this important class of chemical transformations. This comprehensive article will delve into the various synonyms for condensation reactions, explore their mechanisms, and highlight their significance across diverse fields.
Understanding Condensation Reactions: The Basics
Before exploring alternative names, let's establish a solid understanding of what constitutes a condensation reaction. At its core, a condensation reaction is a type of chemical reaction where two molecules combine to form a larger molecule, simultaneously releasing a smaller molecule as a byproduct, often water (H₂O), but sometimes methanol (CH₃OH), hydrogen chloride (HCl), or acetic acid (CH₃COOH). This "smaller molecule" is crucial in differentiating a condensation reaction from other types of reactions like addition reactions.
Key Characteristics of Condensation Reactions:
- Two molecules combine: This is the defining characteristic. Two reactants, often with functional groups capable of reacting with each other, are involved.
- Larger molecule formed: The product molecule has a higher molecular weight than either of the reactants.
- Smaller molecule released: A smaller molecule, like water, is eliminated during the reaction. This is what distinguishes a condensation reaction from an addition reaction.
- Formation of a new bond: A new covalent bond is formed between the two reacting molecules.
Alternative Names for Condensation Reactions: A Comprehensive List
While "condensation reaction" is the most common and widely accepted term, several other names are used interchangeably, depending on the context and the specific type of reaction. These alternative names often provide more specific information about the reaction mechanism or the type of molecules involved.
Here's a list of common alternative names for condensation reactions:
-
Dehydration reaction: This term is particularly apt when water is the byproduct. It emphasizes the removal of water molecules during the reaction. Many examples of condensation reactions, especially those involving alcohols and carboxylic acids to form esters, fall under this category.
-
Esterification: This is a specific type of condensation reaction involving the reaction between a carboxylic acid and an alcohol to produce an ester and water. It's a highly important reaction in organic chemistry, with wide applications in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals, polymers, and fragrances.
-
Amide formation (or peptide bond formation): This term refers to the condensation reaction between a carboxylic acid and an amine to form an amide bond (also known as a peptide bond in the context of protein synthesis). This is fundamental in biochemistry, responsible for the formation of peptide chains and proteins.
-
Glycosidic bond formation: This specific condensation reaction involves the formation of a glycosidic bond between two monosaccharides to form a disaccharide or larger oligosaccharide. This is crucial in carbohydrate chemistry and biochemistry.
-
Polymerization (Condensation Polymerization): Many polymers are formed through repetitive condensation reactions. This process is called condensation polymerization, where monomers combine to form long chains with the release of small molecules. Examples include the formation of polyesters (like polyethylene terephthalate, PET) and polyamides (like nylon).
Mechanisms of Condensation Reactions
The mechanisms of condensation reactions vary depending on the specific reactants and reaction conditions. However, several common steps are often involved:
-
Nucleophilic attack: One of the reactants acts as a nucleophile (an electron-rich species) and attacks an electrophilic center (an electron-deficient center) on the other reactant.
-
Proton transfer: Protons are often transferred between the reactants, leading to the formation of new bonds and the elimination of the smaller molecule.
-
Elimination of the smaller molecule: The smaller molecule (e.g., water) is expelled, often facilitated by the presence of a catalyst or specific reaction conditions.
-
Formation of the new bond: A new covalent bond is formed between the two reactant molecules, resulting in the formation of the larger product molecule.
Examples of Condensation Reactions Across Different Fields
Condensation reactions are ubiquitous in chemistry and related fields. Let's look at specific examples in various areas:
Organic Chemistry:
-
Esterification: The reaction between acetic acid (CH₃COOH) and ethanol (CH₃CH₂OH) to produce ethyl acetate (CH₃COOCH₂CH₃) and water.
-
Formation of acetals and ketals: Reactions between aldehydes or ketones with alcohols.
-
Aldol condensation: A reaction between two aldehydes or ketones to form a β-hydroxy aldehyde or β-hydroxy ketone.
Biochemistry:
-
Peptide bond formation: The formation of peptide bonds between amino acids during protein synthesis.
-
Glycosidic bond formation: The linkage of monosaccharides to form disaccharides, oligosaccharides, and polysaccharides.
-
Formation of phosphodiester bonds in DNA and RNA: The backbone of nucleic acids is formed by condensation reactions.
Materials Science:
- Polymerization reactions: The formation of polyesters, polyamides, and other polymers through repeated condensation reactions. These polymers are used extensively in various applications, from clothing to packaging.
Importance and Applications of Condensation Reactions
Condensation reactions are of immense importance due to their role in the synthesis of a vast array of molecules. Their significance spans various fields:
-
Pharmaceutical Industry: Many drugs and pharmaceuticals are synthesized through condensation reactions. This includes numerous drugs with diverse therapeutic applications.
-
Polymer Industry: Condensation polymerization is crucial for the production of various polymers used in diverse applications. This is fundamental to the production of plastics, fibers, and elastomers.
-
Food Industry: Condensation reactions play a role in food processing, such as the formation of certain food components and preservation techniques.
-
Biotechnology: Condensation reactions are central to the understanding and manipulation of biological macromolecules like proteins and nucleic acids.
-
Materials Science: The synthesis of advanced materials often involves condensation reactions, allowing for tailoring of material properties for specific applications.
Conclusion: Understanding the Nuances of Condensation Reactions
While "condensation reaction" serves as the umbrella term, understanding the various synonyms provides deeper insights into the specific mechanisms and applications of these crucial chemical transformations. The use of terms like "dehydration reaction," "esterification," and "polymerization," highlights the diverse contexts in which condensation reactions occur and the unique products they yield. By appreciating the nuances of these reactions, we can better comprehend their widespread importance in various scientific fields and their impact on our daily lives. The ability to synthesize complex molecules, create advanced materials, and understand biological processes all hinge on the fundamental principles of condensation reactions and their varied manifestations.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Color Constancy Refers To The Fact That
Mar 15, 2025
-
A Recent Delivery Of Eggs Has Been Recalled
Mar 15, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Statements Is True Regarding Learning Difficulties
Mar 15, 2025
-
A Job Cost Sheet Contains Blank The Job
Mar 15, 2025
-
Why Are Fuel Leaks A Problem Aceable
Mar 15, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is Another Name For A Condensation Reaction . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
