What Is The Defining Characteristic Of Formal Operational Thought
Breaking News Today
Mar 21, 2025 · 6 min read
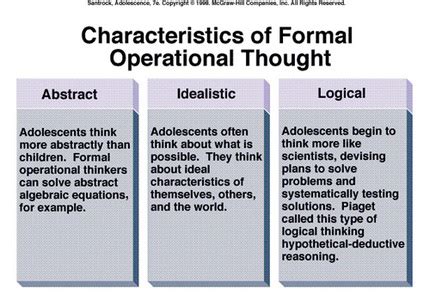
Table of Contents
What is the Defining Characteristic of Formal Operational Thought?
Jean Piaget's theory of cognitive development posits four distinct stages: sensorimotor, preoperational, concrete operational, and formal operational. While the earlier stages focus on developing fundamental understanding of the physical world, the formal operational stage marks a significant leap forward, characterized by the ability to think abstractly, hypothetically, and systematically. This article delves deep into the defining characteristic of formal operational thought, exploring its key features, implications, and limitations.
The Hallmark of Formal Operational Thought: Abstract Reasoning
The most defining characteristic of formal operational thought is the emergence of abstract reasoning. Unlike concrete operational thinkers who rely heavily on concrete objects and experiences, individuals in the formal operational stage can grapple with concepts that are not directly tied to the physical world. This allows them to:
Understanding Abstract Concepts
This ability to grasp abstract concepts opens up a world of possibilities. They can now understand concepts like justice, freedom, and love – ideas that lack tangible representation. They can ponder philosophical questions, engage in theoretical discussions, and critically evaluate abstract systems of thought. This marks a significant shift from the concrete, tangible focus of earlier stages.
Hypothetical Reasoning
Closely intertwined with abstract reasoning is the ability to engage in hypothetical reasoning. Formal operational thinkers can systematically consider possibilities and generate hypotheses, even if those possibilities are not grounded in immediate reality. This allows them to:
- Conduct scientific experiments: They can formulate hypotheses, design experiments to test them, and analyze the results to draw conclusions.
- Engage in "what if" scenarios: They can contemplate different outcomes based on hypothetical situations and plan accordingly.
- Solve complex problems: By considering multiple variables and possibilities, they can develop more effective strategies for problem-solving.
This ability to engage in hypothetical reasoning is crucial for scientific thinking, problem-solving, and strategic planning, all hallmarks of advanced cognitive functioning.
Beyond Abstract Reasoning: Other Key Features of Formal Operational Thought
While abstract reasoning forms the cornerstone of formal operational thought, several other key features contribute to its unique character:
Deductive Reasoning
Formal operational thinkers demonstrate a strong capacity for deductive reasoning. This involves drawing logical conclusions from a set of premises. They can identify the underlying logic in arguments, assess the validity of conclusions, and differentiate between valid and invalid inferences. This ability is essential for critical thinking and evaluating information objectively.
Propositional Thought
Another defining aspect is propositional thought. This involves the ability to evaluate the logic of verbal statements without needing to refer to concrete situations. They can understand and manipulate statements like "If A, then B," even if they have no direct experience with A and B. This is a key element in understanding complex relationships and drawing inferences from symbolic representations.
Metacognition
Formal operational thinking is also marked by enhanced metacognition, or "thinking about thinking." Individuals at this stage become more aware of their own cognitive processes, understanding their strengths and weaknesses, and employing strategies to improve their thinking skills. This reflective awareness allows them to monitor their understanding, identify biases, and adapt their thinking accordingly.
Systematic Problem Solving
Formal operational thinkers approach problem-solving in a much more systematic and organized manner. They can identify variables, develop systematic plans to test hypotheses, and analyze results efficiently. They can also consider multiple perspectives and approaches when addressing a problem, leading to more comprehensive solutions. This systematic approach is vital in academic settings, scientific research, and complex professional tasks.
Implications of Formal Operational Thought
The development of formal operational thought has profound implications for various aspects of life:
Education and Learning
Formal operational skills are essential for success in higher education. The ability to understand abstract concepts, engage in critical thinking, and solve complex problems is crucial for mastering advanced academic subjects. Furthermore, the development of metacognitive skills empowers individuals to learn more effectively and efficiently.
Career Choices and Success
Many professions demand the ability to engage in abstract reasoning, problem-solving, and critical thinking. Scientists, engineers, lawyers, doctors, and researchers all rely heavily on formal operational skills to excel in their careers. The capacity for systematic planning and strategic decision-making also contributes significantly to professional success.
Social and Personal Development
Formal operational thinking plays a vital role in social and personal development. The ability to understand abstract concepts like justice, fairness, and morality allows individuals to engage in meaningful social interactions and participate actively in democratic processes. The capacity for self-reflection and metacognition enhances self-awareness and contributes to personal growth.
Limitations of Piaget's Formal Operational Stage
While Piaget's theory offers valuable insights into cognitive development, it is crucial to acknowledge its limitations:
Cultural Influences
The development of formal operational thinking is not universally achieved. Cultural factors, educational opportunities, and individual experiences significantly influence the attainment of this stage. Individuals in some cultures might not encounter the types of abstract problems necessary to stimulate the development of formal operational thought.
Individual Differences
Even within a culture, there are significant individual differences in the development of formal operational thinking. Some individuals may reach this stage earlier than others, while some might never fully develop the capacity for abstract and hypothetical reasoning. Individual differences in cognitive abilities, motivation, and learning experiences contribute to this variation.
Post-Formal Operational Thought
Some researchers have proposed the existence of a post-formal operational stage of cognitive development. This stage is characterized by even more sophisticated thinking skills, including dialectical thinking (considering multiple perspectives and integrating contradictory ideas) and relativistic thinking (acknowledging the context-dependent nature of truth). This suggests that cognitive development may extend beyond Piaget's formal operational stage.
Conclusion: The Enduring Significance of Formal Operational Thought
Despite its limitations, the concept of formal operational thought remains a cornerstone of developmental psychology. The ability to think abstractly, hypothetically, and systematically is a significant milestone in cognitive development, paving the way for advanced learning, successful careers, and meaningful participation in society. While the specifics of its attainment may vary across cultures and individuals, the core characteristics – abstract reasoning, deductive reasoning, propositional thought, metacognition, and systematic problem-solving – remain crucial markers of advanced cognitive maturity. Understanding these characteristics provides valuable insights into human cognition and its development throughout the lifespan. Further research into the nuances of formal operational thought, considering cultural and individual variations, will continue to refine our understanding of this critical stage in cognitive development and its implications for human potential. This deeper understanding will, in turn, allow for more effective educational strategies and interventions aimed at fostering optimal cognitive development across diverse populations. The enduring significance of formal operational thought lies in its ability to illuminate the path towards higher-order thinking and its crucial role in shaping individuals’ intellectual and personal growth.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Is Not A Period Cost
Mar 27, 2025
-
Hay 13 6 Chicas Y 20 12 Chicos
Mar 27, 2025
-
Se Sugiere Buscar Una Casa En Un Barrio Seguro Safe
Mar 27, 2025
-
What Are The Key Clauses In Ap Government
Mar 27, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Best Describes An Inside Attacker
Mar 27, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Defining Characteristic Of Formal Operational Thought . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
