What Is The Definition Of A Risk Decision
Breaking News Today
Mar 19, 2025 · 7 min read
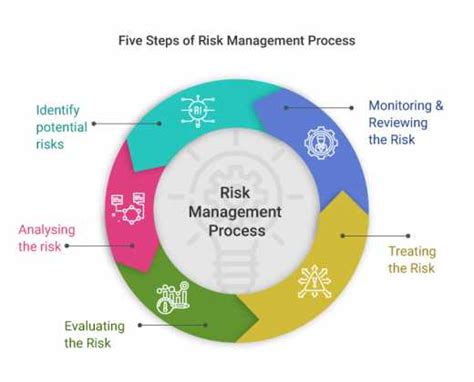
Table of Contents
What is the Definition of a Risk Decision? A Deep Dive into Risk Assessment and Management
Making decisions is an inherent part of life, both personally and professionally. However, not all decisions are created equal. Some decisions are straightforward, with clear-cut consequences. Others are shrouded in uncertainty, demanding a careful consideration of potential risks and rewards. This article delves into the definition of a risk decision, exploring its components, the process involved in making one, and the critical role of risk assessment and management in ensuring sound judgment.
Defining a Risk Decision
A risk decision is a choice made in the face of uncertainty, where the potential outcomes involve a range of positive and negative consequences. It's a conscious act of selecting a course of action despite the presence of known or unknown risks. The key differentiator between a standard decision and a risk decision lies in the acknowledgment and assessment of potential adverse outcomes. A simple decision might involve choosing between two known options with predictable results. A risk decision, on the other hand, involves weighing the probabilities and potential impacts of several possible outcomes, some of which could be significantly negative.
Key characteristics of a risk decision:
- Uncertainty: The future outcomes are not perfectly predictable.
- Multiple potential outcomes: Several possible scenarios exist, each with its own likelihood and impact.
- Consequences: The chosen course of action will have consequences, both positive and negative.
- Risk assessment: A process of identifying, analyzing, and evaluating potential risks is undertaken before making the decision.
- Decision-making under pressure: Often, time constraints or pressure from stakeholders add complexity to the process.
The Components of a Risk Decision
Understanding the components of a risk decision is crucial for making informed choices. These components typically include:
- Objectives: What are you trying to achieve? Clearly defined objectives provide a framework for evaluating the potential risks and rewards associated with different options.
- Options: What are the available courses of action? Identifying all feasible alternatives is crucial for making a well-informed decision.
- Risks: What are the potential negative consequences of each option? This includes identifying the likelihood and impact of each risk.
- Rewards: What are the potential benefits of each option? These are the positive outcomes that could result from the chosen course of action.
- Risk tolerance: What level of risk are you willing to accept? This is a crucial factor in determining the best course of action.
The Risk Decision-Making Process
The process of making a risk decision isn't arbitrary. It's a structured approach that involves several key steps:
1. Risk Identification
This initial stage involves systematically identifying all potential hazards and threats that could affect the outcome of a decision. Brainstorming sessions, checklists, historical data analysis, and expert opinions are valuable tools for comprehensive risk identification. Neglecting this step can lead to unforeseen problems and significantly impact the success of the chosen course of action.
2. Risk Analysis
Once potential risks are identified, the next step is to analyze them. This involves determining the likelihood and potential impact of each risk. Techniques like qualitative risk analysis (using descriptions like low, medium, and high) and quantitative risk analysis (using numerical data and statistical methods) are often employed. This analysis provides a clearer picture of the potential consequences of different choices.
3. Risk Evaluation
Risk evaluation combines the likelihood and impact of each risk to determine its overall significance. This often involves creating a risk matrix, which visually represents the risks based on their probability and severity. This step allows prioritization of risks, focusing efforts on the most critical ones.
4. Risk Response Planning
This stage involves developing strategies to address the identified risks. Common risk response strategies include:
- Risk avoidance: Eliminating the activity that causes the risk.
- Risk mitigation: Reducing the likelihood or impact of the risk.
- Risk transfer: Shifting the risk to a third party (e.g., through insurance).
- Risk acceptance: Accepting the risk and its potential consequences.
The choice of strategy depends on various factors including risk tolerance, available resources, and the potential impact of the risk.
5. Decision Making and Implementation
After analyzing and evaluating risks and developing response plans, the decision-maker chooses the best course of action. This involves weighing the potential rewards and risks of each option and selecting the one that best aligns with the objectives and risk tolerance. Implementation involves putting the chosen plan into action and monitoring its progress.
6. Monitoring and Review
Even after implementing a decision, ongoing monitoring and review are crucial. This ensures that the chosen course of action is effective and that new risks are identified and addressed promptly. Regular review allows for adjustments to the plan as needed, improving its effectiveness and minimizing potential negative impacts.
The Role of Risk Assessment and Management
Risk assessment and management are integral parts of the risk decision-making process. Risk assessment involves identifying, analyzing, and evaluating potential risks. Risk management encompasses the entire process, from identifying risks to developing and implementing response plans and monitoring outcomes. Effective risk management minimizes the likelihood of negative outcomes and maximizes the chances of success. It involves not only identifying potential problems but also proactively developing strategies to address them.
Key elements of effective risk management:
- Communication: Open communication among stakeholders is crucial for effective risk management. This ensures that everyone is aware of potential risks and their roles in addressing them.
- Collaboration: A collaborative approach involving relevant stakeholders leads to better risk identification and more effective response strategies.
- Flexibility: Being adaptable to changing circumstances is essential. Risk management plans should be flexible enough to accommodate unforeseen events.
- Continuous improvement: Regularly reviewing and improving the risk management process is key to its effectiveness.
Types of Risk Decisions
Risk decisions can be categorized in several ways depending on various factors:
Based on the level of uncertainty:
- Decisions under certainty: The outcomes of each decision alternative are known with certainty.
- Decisions under risk: The probabilities of different outcomes are known.
- Decisions under uncertainty: The probabilities of different outcomes are unknown.
Based on the decision-making approach:
- Strategic decisions: Long-term, high-level decisions that affect the entire organization.
- Tactical decisions: Shorter-term decisions that support the implementation of strategic decisions.
- Operational decisions: Day-to-day decisions related to specific tasks and activities.
Based on the level of risk tolerance:
- Risk-averse decisions: Decisions that prioritize avoiding risk, even if it means sacrificing potential rewards.
- Risk-neutral decisions: Decisions where the level of risk is not a primary concern.
- Risk-seeking decisions: Decisions that are willing to accept higher levels of risk in pursuit of greater rewards.
Examples of Risk Decisions
Risk decisions are ubiquitous in various aspects of life. Consider these examples:
- Investing in the stock market: This involves weighing the potential for high returns against the risk of losing money.
- Starting a new business: This entails assessing the risks associated with market competition, financial constraints, and operational challenges.
- Choosing a career path: This requires considering the potential risks and rewards associated with different career options.
- Medical decisions: Patients and doctors often face difficult decisions involving weighing the risks and benefits of different treatments.
- Launching a new product: Businesses assess market demand, competition, and potential production challenges before launching a new product.
Conclusion
Making sound risk decisions is essential for personal and professional success. It's a process that requires careful consideration of potential outcomes, a structured approach to risk assessment and management, and the willingness to adapt and learn from experience. By understanding the definition of a risk decision and the steps involved in the decision-making process, individuals and organizations can make more informed choices and navigate uncertainty effectively. The ability to effectively identify, analyze, and manage risks is a vital skill in today's complex and dynamic environment. Mastering this skill empowers individuals and organizations to achieve their objectives while minimizing the potential negative consequences of their actions. Continuously refining your approach to risk assessment and decision-making is crucial for sustained success in any endeavor.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Balance In The Accumulated Depreciation Account Represents The
Mar 19, 2025
-
You Should Always Check Behind Your Vehicle Before Getting In
Mar 19, 2025
-
Why Is The Human Body Compared To A Fine Tuned Machine
Mar 19, 2025
-
According To The Results Of The Pillbug Experiment
Mar 19, 2025
-
Ratings That Require A Person To Be A Us Citizen
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Definition Of A Risk Decision . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
