What Is The Definition Of Liability Quizlet
Breaking News Today
Mar 18, 2025 · 6 min read
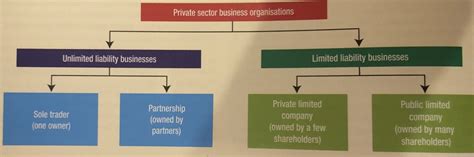
Table of Contents
What is the Definition of Liability? A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding liability is crucial in various aspects of life, from personal interactions to complex business transactions. This comprehensive guide will delve into the multifaceted definition of liability, exploring its different types and implications. We'll go beyond a simple Quizlet-style definition, offering a nuanced understanding that's essential for navigating the legal and financial landscapes.
What is Liability? A Foundation Definition
At its core, liability refers to the state of being legally responsible for something. This responsibility can encompass a wide range of obligations, including financial compensation for damages, fulfilling contractual agreements, or adhering to legal regulations. Essentially, if you are liable for something, you are legally obligated to address it. This obligation could stem from various sources, including negligence, breach of contract, or intentional wrongdoing.
Think of it this way: liability is the flip side of an asset. While an asset is something you own, liability is something you owe.
Types of Liability
Liability isn't a monolithic concept. It manifests in several forms, each with its own unique characteristics and implications:
1. Contractual Liability: This arises from a breach of contract. A contract is a legally binding agreement between two or more parties. If one party fails to uphold their end of the bargain, they become liable for the resulting damages. This could involve financial compensation, specific performance (doing what was promised), or other remedies stipulated in the contract. Examples include failing to deliver goods as agreed, breaching a lease agreement, or not fulfilling the terms of an employment contract.
2. Tort Liability: This type of liability stems from civil wrongs that cause harm to another person or their property. Unlike criminal offenses, torts focus on compensating the victim for their losses. Negligence is a common form of tort liability, where someone fails to exercise the reasonable care that a prudent person would in similar circumstances, resulting in harm to another. Other examples include defamation (false statements that harm someone's reputation), trespass (unauthorized entry onto someone's property), and intentional infliction of emotional distress.
3. Strict Liability: This is a unique form of liability where fault or intent is not required. The person or entity is held liable simply because they were involved in the harmful activity. This is often applied in cases involving defective products or inherently dangerous activities. For instance, a manufacturer can be held strictly liable for injuries caused by a defective product, regardless of whether they were negligent in its production.
4. Vicarious Liability: This occurs when one person or entity is held liable for the actions of another. A common example is the liability of an employer for the negligent actions of their employees while they are acting within the scope of their employment. Parents can also be held vicariously liable for the actions of their minor children under certain circumstances.
5. Criminal Liability: While often conflated with civil liability, criminal liability involves actions that violate criminal law and result in prosecution by the state. The penalties can range from fines to imprisonment, and the focus is on punishing the offender rather than compensating the victim. However, criminal actions can also lead to civil liability, such as when someone is found guilty of assault and is also sued for damages by the victim.
Understanding the Scope of Liability
The extent of liability isn't always straightforward. Several factors influence the scope of liability, including:
- The nature of the event: Was it an accident, a deliberate act, or a result of negligence?
- The degree of fault: How much responsibility does the liable party bear? This is often determined by comparative negligence rules, which apportion liability based on the percentage of fault each party bears.
- The extent of damages: What losses resulted from the event? This includes both economic damages (e.g., medical bills, lost wages) and non-economic damages (e.g., pain and suffering, emotional distress).
- Applicable laws and regulations: Legal jurisdictions have different laws and regulations that govern liability. The specific laws applicable will significantly impact the outcome.
- Existence and terms of insurance: Insurance policies can significantly limit or eliminate personal liability for certain events.
Liability in Different Contexts
The concept of liability extends across various domains:
1. Business Liability: Businesses face a wide array of liability risks, including product liability, employment liability, and environmental liability. Proper risk management, including insurance and safety protocols, is crucial for mitigating these risks. Limited liability companies (LLCs) and corporations offer some protection to their owners from business-related liabilities, but this protection isn't absolute.
2. Personal Liability: Individuals can be held liable for their actions, including negligence, intentional torts, and breaches of contract. This can have significant financial implications, potentially leading to substantial debt or the loss of assets. Personal liability insurance can help mitigate these risks.
3. Environmental Liability: Businesses and individuals can be held liable for environmental damage caused by their actions or omissions. This can involve cleaning up pollution, paying fines, and compensating those affected by the damage.
4. Product Liability: Manufacturers, distributors, and sellers can be held liable for injuries or damages caused by defective products. This can lead to substantial legal costs and financial penalties.
Mitigating Liability Risks
Understanding liability is only half the battle. Proactive steps can significantly reduce liability risks:
- Thorough Contract Review: Carefully review all contracts before signing to ensure you understand your obligations and liabilities.
- Risk Assessment: Regularly assess potential liability risks associated with your activities and implement strategies to mitigate them.
- Insurance Coverage: Secure appropriate insurance coverage to protect yourself from potential financial losses arising from liability claims.
- Compliance with Regulations: Ensure compliance with all relevant laws and regulations to avoid legal penalties.
- Safety Procedures: Implement robust safety procedures to prevent accidents and injuries.
- Record Keeping: Maintain accurate and detailed records of transactions, communications, and other relevant information.
- Professional Advice: Seek professional advice from lawyers, accountants, and other experts to navigate complex liability issues.
Beyond the Quizlet Definition: A Deeper Dive
While a simple Quizlet definition might define liability as "the state of being legally responsible," this article has demonstrated the complexities involved. Understanding liability goes beyond memorizing a definition; it requires a grasp of the various types of liability, the factors influencing its scope, and strategies for mitigating associated risks. It's a multifaceted concept with significant implications in both personal and professional life. A thorough understanding empowers individuals and businesses to navigate legal and financial responsibilities effectively, minimizing risks and protecting their interests. The key is proactive planning and a commitment to understanding the nuances of liability in diverse contexts. Failure to do so can lead to significant legal and financial repercussions. This comprehensive analysis moves beyond a simplistic definition and encourages a deeper understanding of this crucial concept. Remember, seeking professional legal advice is always recommended when dealing with complex liability issues.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Direct Carry Is Used To Transfer A Patient
Mar 18, 2025
-
The Emancipation Proclamation Of January 1 1863 Quizlet
Mar 18, 2025
-
These Cards Will Get You Drunk Quizlet
Mar 18, 2025
-
Did Quizlet Get Rid Of Q Chat
Mar 18, 2025
-
Myasthenia Gravis Is An Autoimmune Disease In Which Quizlet
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Definition Of Liability Quizlet . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
