What Is The Difference Between Stereotypes Prejudice And Discrimination Quizlet
Breaking News Today
Mar 17, 2025 · 6 min read
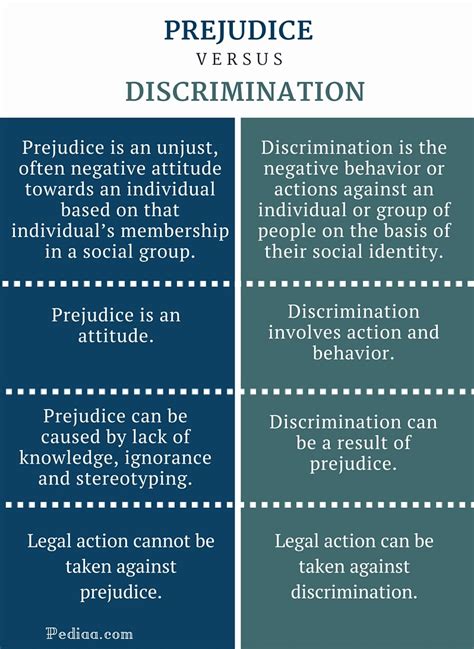
Table of Contents
What's the Difference Between Stereotypes, Prejudice, and Discrimination? A Deep Dive
Understanding the differences between stereotypes, prejudice, and discrimination is crucial for fostering a more equitable and just society. While these three concepts are interconnected and often overlap, they represent distinct stages in a potentially harmful process. This in-depth exploration will clarify their individual meanings, highlight their relationships, and offer practical examples to solidify your understanding. We'll go beyond simple definitions to examine the nuances and complexities of each concept.
What is a Stereotype?
A stereotype is a generalized belief about a particular group of people. These beliefs are often oversimplified and based on limited or inaccurate information. They assign certain characteristics to all members of a group, regardless of individual differences. Stereotypes can be positive, negative, or neutral, but they are inherently problematic because they ignore the individuality of people within a group.
Examples of Stereotypes:
- All Asians are good at math: This positive stereotype, while seemingly harmless, still ignores the diverse mathematical abilities within the Asian community.
- All women are emotional: This negative stereotype unfairly generalizes the emotional range of women, ignoring the wide spectrum of emotional experiences across genders.
- All elderly people are slow: This negative stereotype ignores the wide range of physical and cognitive abilities among older adults.
Why are Stereotypes Harmful?
Stereotypes, even positive ones, can lead to inaccurate and unfair judgments about individuals. They create a framework through which we perceive others, potentially overlooking their unique qualities and experiences. The insidious nature of stereotypes lies in their ability to influence our behavior and interactions, even unconsciously.
The Cognitive Roots of Stereotypes:
Stereotypes are fundamentally cognitive shortcuts. Our brains naturally seek to simplify complex information, and categorization is a fundamental aspect of cognitive processing. However, this cognitive efficiency can lead to harmful generalizations when applied to people. The process often involves:
- Categorization: Grouping individuals based on readily observable characteristics (race, gender, age).
- Schema formation: Developing mental frameworks about the characteristics of each group.
- In-group/out-group bias: Favoring members of one's own group and viewing out-group members as less favorable.
- Confirmation bias: Seeking out and interpreting information that confirms pre-existing beliefs.
Overcoming Stereotypes:
Challenging stereotypes requires conscious effort and a willingness to examine our own biases. Strategies include:
- Increased exposure to diverse groups: Interacting with people from different backgrounds can help break down ingrained stereotypes.
- Critical thinking: Questioning generalizations and considering individual differences.
- Empathy and perspective-taking: Trying to understand the experiences of others.
- Education and awareness: Learning about different cultures and perspectives.
- Mindful communication: Avoiding language that reinforces stereotypes.
What is Prejudice?
Prejudice goes beyond stereotypes; it involves having negative attitudes, feelings, and opinions about a particular group of people. These attitudes are often based on stereotypes and can range from mild dislike to intense hatred. Prejudice is an emotional response, whereas stereotypes are cognitive generalizations.
Examples of Prejudice:
- Racial prejudice: Negative feelings towards individuals based on their race.
- Gender prejudice: Negative feelings towards individuals based on their gender.
- Religious prejudice: Negative feelings towards individuals based on their religious beliefs.
- Ageism: Negative feelings towards individuals based on their age.
Types of Prejudice:
Prejudice can manifest in various ways:
- Explicit prejudice: Conscious and openly expressed negative attitudes.
- Implicit prejudice: Unconscious and subtle biases that may not be readily apparent to the individual holding them. These biases can significantly influence behavior despite a lack of conscious awareness.
The Psychological Roots of Prejudice:
Several psychological factors contribute to the development of prejudice:
- Social learning: Learning prejudiced attitudes from family, peers, and media.
- Realistic conflict theory: Competition for limited resources leading to intergroup hostility.
- Social identity theory: Deriving self-esteem from group membership and viewing out-groups negatively.
- Cognitive dissonance: Maintaining prejudiced beliefs despite contradictory evidence.
Overcoming Prejudice:
Combating prejudice requires addressing its underlying causes:
- Education and awareness: Promoting understanding and challenging negative stereotypes.
- Intergroup contact: Facilitating positive interactions between different groups under favorable conditions.
- Cognitive restructuring: Identifying and challenging one's own prejudiced beliefs.
- Promoting empathy and perspective-taking: Encouraging understanding of others' experiences.
What is Discrimination?
Discrimination is the behavioral manifestation of prejudice. It involves acting on prejudiced beliefs by treating individuals unfairly based on their group membership. Discrimination can be subtle or overt, and it encompasses a wide range of actions.
Examples of Discrimination:
- Racial discrimination: Being denied a job or housing opportunity because of one's race.
- Gender discrimination: Being paid less than a male colleague for the same work.
- Religious discrimination: Being subjected to harassment or bullying because of one's religious beliefs.
- Age discrimination: Being passed over for a promotion because of one's age.
Forms of Discrimination:
- Individual discrimination: Discriminatory actions by an individual against another individual.
- Institutional discrimination: Discriminatory practices embedded within institutions (e.g., discriminatory hiring practices).
- Systemic discrimination: Broader societal patterns and practices that perpetuate inequality.
The Social Roots of Discrimination:
Discrimination is rooted in broader social structures and power dynamics. Dominant groups may use discrimination to maintain their privileged positions. Factors include:
- Power imbalances: Groups with greater power and resources may discriminate against less powerful groups.
- Historical injustices: The legacy of past discrimination can continue to impact present-day inequalities.
- Social norms and values: Societal beliefs and attitudes that justify discriminatory practices.
Combating Discrimination:
Addressing discrimination requires tackling its systemic roots:
- Legislation and policy: Implementing anti-discrimination laws and policies.
- Institutional change: Promoting diversity and inclusion within organizations.
- Social movements and activism: Challenging discriminatory practices and advocating for equality.
- Education and awareness: Raising awareness about the impact of discrimination and promoting tolerance.
The Interconnectedness of Stereotypes, Prejudice, and Discrimination:
These three concepts are interconnected but distinct. Stereotypes provide the cognitive foundation for prejudice, which in turn can lead to discriminatory behavior. It's a chain reaction:
- Stereotypes (beliefs): Generalized beliefs about a group.
- Prejudice (attitudes): Negative feelings and attitudes towards a group based on stereotypes.
- Discrimination (actions): Unfair treatment of individuals based on their group membership, fueled by prejudice.
It's important to note that not all stereotypes lead to prejudice, and not all prejudice leads to discrimination. However, understanding the potential pathways between these concepts is critical for interrupting the cycle of inequality.
Quizlet-Style Questions and Answers:
Here are some example questions in a Quizlet-style format to test your understanding:
1. Question: What is the difference between a stereotype and prejudice? Answer: A stereotype is a generalized belief about a group, while prejudice involves negative attitudes and feelings toward a group often based on stereotypes.
2. Question: Is discrimination always overt and intentional? Answer: No, discrimination can be subtle, unintentional, or systemic, embedded within institutions and practices.
3. Question: Provide an example of a positive stereotype. What is problematic about even positive stereotypes? Answer: "Asians are good at math." Even positive stereotypes create unrealistic expectations and ignore individual differences within a group.
4. Question: How are stereotypes, prejudice, and discrimination interconnected? Answer: Stereotypes can lead to prejudice, which can lead to discrimination. They form a chain reaction where beliefs influence attitudes, and attitudes influence actions.
5. Question: What is implicit prejudice? Give an example. Answer: Implicit prejudice is an unconscious bias. An example could be a hiring manager unconsciously favoring candidates with names that sound more "typically Western."
Conclusion:
Understanding the nuances of stereotypes, prejudice, and discrimination is essential for creating a more inclusive and just world. By recognizing the cognitive, emotional, and behavioral components of these concepts, we can begin to dismantle the systems that perpetuate inequality and build a society that values diversity and respects individual differences. It's a continuous process of education, self-reflection, and active engagement in promoting equality for all.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Treatment That Includes A Focus On Personal Strengths And Development
Mar 18, 2025
-
Which Is Not A Form Of Maltreatment
Mar 18, 2025
-
If An Individual Is Heterozygous For A Particular Trait
Mar 18, 2025
-
If You Add More Enzyme The Reaction Will
Mar 18, 2025
-
The Purpose Of A Hazcom Program Is To Ensure That
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Difference Between Stereotypes Prejudice And Discrimination Quizlet . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
