What Is The Function Of The Auditory Tube Quizlet
Breaking News Today
Mar 23, 2025 · 5 min read
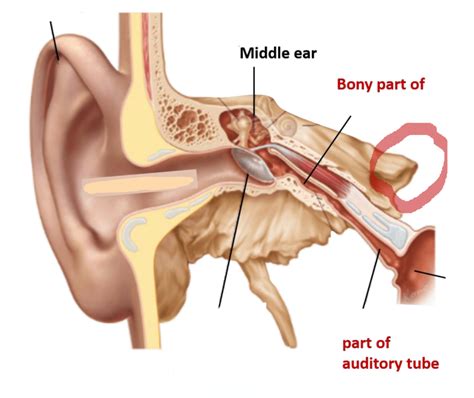
Table of Contents
What is the Function of the Auditory Tube? A Comprehensive Guide
The auditory tube, also known as the Eustachian tube, is a vital part of the middle ear. Its primary function is to equalize the pressure between the middle ear and the atmosphere. This seemingly simple function is crucial for proper hearing and overall ear health. Understanding the intricacies of the auditory tube's function is essential for appreciating its role in preventing ear infections and maintaining healthy hearing. This in-depth guide will explore the auditory tube's function, its anatomy, associated conditions, and its importance in maintaining auditory health.
Anatomy and Structure of the Auditory Tube
Before delving into the function, it's crucial to understand the auditory tube's structure. This narrow, roughly 35-40mm long tube connects the middle ear cavity to the nasopharynx (the upper part of the throat behind the nose). Its unique anatomy plays a critical role in its function.
The Three Sections:
The auditory tube is comprised of three distinct sections:
- Bony Portion: This is the inner, shorter section, formed from the temporal bone of the skull. It's rigid and relatively inflexible.
- Cartilaginous Portion: This outer, longer section is made of cartilage. It's more flexible and capable of opening and closing. This flexibility is essential for its pressure-equalizing function.
- Isthmus: This is the narrowest part of the tube, located where the bony and cartilaginous portions meet. Its narrowness is significant in preventing the passage of pathogens.
Muscles Involved in Auditory Tube Function:
Several muscles contribute to the opening and closing of the auditory tube:
- Tensor Veli Palatini: This muscle is the primary muscle responsible for opening the auditory tube. Its contraction widens the tube, allowing for pressure equalization.
- Levator Veli Palatini: While not the primary opener, this muscle plays a supporting role in auditory tube function.
The Primary Function: Pressure Equalization
The most critical function of the auditory tube is pressure equalization between the middle ear and the atmosphere. This is achieved through the opening and closing of the tube. Why is this crucial?
The middle ear contains the delicate ossicles (malleus, incus, and stapes), which transmit sound vibrations from the eardrum to the inner ear. If the pressure in the middle ear differs significantly from atmospheric pressure, this can impact the movement of the eardrum and the ossicles, leading to impaired hearing.
How Pressure Equalization Works:
When there's a pressure difference, the eardrum can become retracted (pulled inward) or bulging (pushed outward), causing discomfort or even pain. Yawning, swallowing, or chewing can stimulate the tensor veli palatini muscle, opening the tube and allowing air to flow, equalizing the pressure. This restores the eardrum's optimal position for efficient sound transmission.
Secondary Functions of the Auditory Tube
While pressure equalization is paramount, the auditory tube also plays a secondary role in:
- Drainage: The auditory tube helps drain mucus and other fluids from the middle ear into the nasopharynx. This drainage is vital in preventing fluid buildup, which can lead to middle ear infections (otitis media).
- Protection: The narrow isthmus and the inherent mucus-producing properties of the tube's lining help prevent the entry of pathogens from the nasopharynx into the middle ear.
Conditions Affecting the Auditory Tube
Several conditions can affect the auditory tube's function, leading to various ear-related problems:
- Eustachian Tube Dysfunction (ETD): This is a common condition where the auditory tube fails to equalize pressure effectively. Symptoms include ear pain, fullness, popping sensations, and hearing impairment. ETD can be caused by inflammation, allergies, or structural abnormalities.
- Otitis Media: This is a middle ear infection, often caused by a blockage of the auditory tube, preventing proper drainage and leading to fluid buildup. Children are particularly susceptible to otitis media due to the shorter and more horizontally oriented auditory tubes compared to adults.
- Barotrauma: This is an injury to the ear caused by a rapid change in atmospheric pressure, such as during air travel or scuba diving. The inability of the auditory tube to equalize pressure quickly enough can lead to discomfort, pain, and even rupture of the eardrum.
Importance of Auditory Tube Function in Hearing Health
The proper functioning of the auditory tube is absolutely vital for healthy hearing. Its ability to equalize pressure ensures optimal movement of the eardrum and ossicles, leading to clear and efficient sound transmission. Its role in drainage and protection helps prevent infections and maintains a healthy middle ear environment.
Treatment and Management of Auditory Tube Dysfunction
Treatment for auditory tube dysfunction varies depending on the underlying cause and severity. Options may include:
- Decongestants: For ETD caused by inflammation or allergies, decongestants can help reduce swelling and improve tube function.
- Nasal Corticosteroids: These can help reduce inflammation in the nasopharynx and improve auditory tube patency.
- Antibiotics: For otitis media caused by bacterial infection, antibiotics may be necessary.
- Myringotomy: In cases of severe otitis media with fluid buildup, a myringotomy (surgical incision in the eardrum) may be performed to drain the fluid.
- Pressure Equalization Tubes (PE Tubes): These small tubes are inserted into the eardrum to provide ventilation and drainage of the middle ear. They are often used in children with recurrent otitis media.
Conclusion
The auditory tube's function extends far beyond simple pressure equalization. It acts as a crucial gatekeeper, protecting the middle ear from infection while ensuring efficient sound transmission. Understanding its anatomy, function, and associated conditions is paramount for maintaining optimal hearing health. Early detection and appropriate management of auditory tube dysfunction are crucial for preventing complications and ensuring clear, healthy hearing throughout life. This comprehensive understanding enables individuals and healthcare providers to take proactive measures to maintain the health of this vital anatomical structure. From preventing infections to ensuring optimal hearing clarity, the auditory tube plays an indispensable role in overall well-being. Its continuous, often unnoticed, work maintains the delicate balance within the middle ear, enabling us to experience the world of sound in all its richness and fullness.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
After Applying The Primer During A Sculptured Nail Service
Mar 25, 2025
-
How Can You Successfully Multitask While Driving A Vehicle
Mar 25, 2025
-
What Process Repairs Damage To A Preexisting Double Helix
Mar 25, 2025
-
Credit Cards That Offer Flashy Rewards Like Airline Miles Often
Mar 25, 2025
-
First Thirty Elements Of The Periodic Table
Mar 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Function Of The Auditory Tube Quizlet . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
