What Is The Functional Role Of The T Tubules Quizlet
Breaking News Today
Mar 23, 2025 · 6 min read
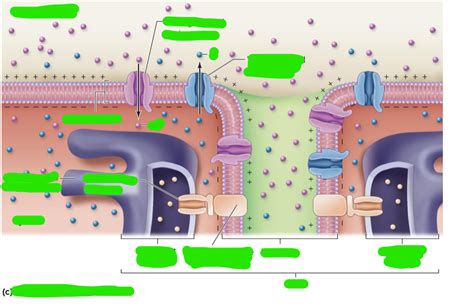
Table of Contents
What is the Functional Role of the T-Tubules? A Deep Dive
The intricate machinery of muscle contraction relies on a complex interplay of proteins and structures. Central to this process are the T-tubules (transverse tubules), invaginations of the sarcolemma (muscle cell membrane) that penetrate deep into the muscle fiber. Understanding their functional role is crucial to grasping the mechanics of muscle excitation-contraction coupling. This article will explore the functional role of T-tubules in detail, examining their structure, their interaction with the sarcoplasmic reticulum, and their significance in various muscle types.
The Structure of T-Tubules: A Network for Efficient Signal Transmission
T-tubules are essentially extensions of the sarcolemma, forming a network of interconnected tubules that run transversely across the muscle fiber, encircling the myofibrils – the contractile units of the muscle cell. This intricate arrangement ensures that the action potential (electrical signal) propagating along the sarcolemma quickly and efficiently reaches all parts of the muscle fiber simultaneously. The precise spacing and organization of T-tubules vary depending on the muscle fiber type, impacting the speed and efficiency of excitation-contraction coupling.
Key Structural Features:
- Invaginations of the Sarcolemma: The T-tubule membrane is continuous with the sarcolemma, sharing its lipid bilayer and associated proteins. This continuity is vital for the rapid transmission of the action potential.
- Triad Formation: In skeletal muscle, T-tubules form specialized junctions called triads with the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR), the intracellular calcium store. These triads are crucial for the rapid release of calcium ions (Ca²⁺), initiating muscle contraction. The precise arrangement of T-tubules and SR in the triad maximizes the efficiency of Ca²⁺ release.
- Protein Composition: The T-tubule membrane contains a variety of ion channels, pumps, and receptors, including voltage-gated sodium channels, dihydropyridine receptors (DHPRs), and ryanodine receptors (RyRs). These proteins play key roles in action potential propagation and calcium release.
T-Tubules and the Sarcoplasmic Reticulum: A Partnership in Contraction
The functional relationship between T-tubules and the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) is pivotal for muscle contraction. The SR is an elaborate network of intracellular calcium storage compartments. The release of Ca²⁺ from the SR is the trigger for muscle contraction, and T-tubules are essential for initiating this release.
Excitation-Contraction Coupling: The Role of T-Tubules
The process of excitation-contraction coupling involves the following steps:
- Action Potential Arrival: An action potential travels along the sarcolemma and enters the T-tubules.
- DHPR Activation: The arrival of the action potential activates dihydropyridine receptors (DHPRs) located in the T-tubule membrane. These voltage-sensitive receptors are directly coupled to ryanodine receptors (RyRs) located in the SR membrane.
- RyR Activation and Calcium Release: The conformational change in the DHPRs triggers the opening of the RyRs, leading to the rapid release of Ca²⁺ from the SR into the cytoplasm.
- Muscle Contraction: The increase in cytosolic Ca²⁺ concentration binds to troponin C on the thin filaments, initiating the cross-bridge cycle and muscle contraction.
- Calcium Reuptake: After the action potential subsides, Ca²⁺ is actively pumped back into the SR by the sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum Ca²⁺-ATPase (SERCA) pump, terminating the contraction.
The Importance of Precise T-Tubule-SR Junctions:
The proximity and precise arrangement of T-tubules and SR are essential for efficient excitation-contraction coupling. The tightly coupled arrangement of DHPRs and RyRs in the triad ensures that the signal from the action potential is rapidly and effectively translated into Ca²⁺ release. Any disruption in this arrangement can impair muscle function.
T-Tubules in Different Muscle Types: Variations and Adaptations
While the fundamental role of T-tubules in excitation-contraction coupling is conserved across muscle types, there are variations in their structure and function depending on the muscle's specific requirements.
Skeletal Muscle: The Triad System
Skeletal muscle fibers exhibit a well-defined triad structure, with one T-tubule positioned between two terminal cisternae of the SR. This arrangement ensures rapid and uniform Ca²⁺ release across the entire myofibril, allowing for forceful and precisely controlled contractions.
Cardiac Muscle: The Diad System
Cardiac muscle fibers typically exhibit a dyad structure, with a T-tubule positioned between a single terminal cisterna of the SR. This arrangement, while less extensive than the triad in skeletal muscle, still allows for effective Ca²⁺ release and contraction. However, the process of excitation-contraction coupling in cardiac muscle is more complex, involving Ca²⁺-induced Ca²⁺ release, where Ca²⁺ entry from the T-tubules triggers further Ca²⁺ release from the SR.
Smooth Muscle: A Less Defined System
Smooth muscle lacks the highly organized T-tubule system seen in skeletal and cardiac muscle. Instead, Ca²⁺ entry into the cell occurs through various pathways, including voltage-gated calcium channels and receptor-operated calcium channels. The SR is less extensive in smooth muscle, and Ca²⁺ release is less tightly coupled to membrane depolarization. This results in slower and less precisely controlled contractions compared to skeletal and cardiac muscle.
T-Tubules and Muscle Diseases: The Consequences of Dysfunction
Disruptions in the structure or function of T-tubules can have significant consequences, leading to various muscle disorders.
Muscular Dystrophies:
In muscular dystrophies, such as Duchenne muscular dystrophy, the integrity of the sarcolemma and T-tubules is compromised. This leads to impaired excitation-contraction coupling, muscle weakness, and progressive muscle degeneration.
Malignant Hyperthermia:
Malignant hyperthermia is a rare genetic disorder that can trigger a life-threatening increase in body temperature during anesthesia. This condition is associated with mutations in RyRs, leading to excessive Ca²⁺ release and sustained muscle contraction.
Heart Failure:
Dysfunction of T-tubules in cardiac muscle can contribute to heart failure. Alterations in T-tubule structure and function can impair Ca²⁺ handling, leading to reduced contractility and impaired cardiac function.
Conclusion: T-Tubules - Essential for Muscle Function
The T-tubules play a crucial functional role in muscle contraction, acting as a conduit for the rapid transmission of action potentials and facilitating the efficient release of Ca²⁺ from the SR. Their intricate structure and precise interaction with the SR are essential for the coordinated and effective contraction of skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle. Disruptions in T-tubule structure or function have significant implications for muscle health, highlighting their vital role in overall physiological function. Further research into the intricate details of T-tubule function and their involvement in muscle diseases is critical for developing effective therapies and treatments. The understanding of T-tubule function continues to evolve, with ongoing research uncovering new aspects of their role in various physiological processes and pathological conditions. The continued study of these fascinating structures promises to provide further insights into the complex mechanisms of muscle contraction and the development of effective treatments for muscle-related diseases.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Graphics Such As Shapes Diagrams Lines Or Circles
Mar 25, 2025
-
Rn Ati Capstone Proctored Comprehensive Assessment A
Mar 25, 2025
-
According To The Text Ethical Behavior Begins With
Mar 25, 2025
-
This Is A Gauge That Indicates High And Low
Mar 25, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Describes The Event Of Ovulation
Mar 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Functional Role Of The T Tubules Quizlet . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
