Which Of The Following Describes The Event Of Ovulation
Breaking News Today
Mar 25, 2025 · 6 min read
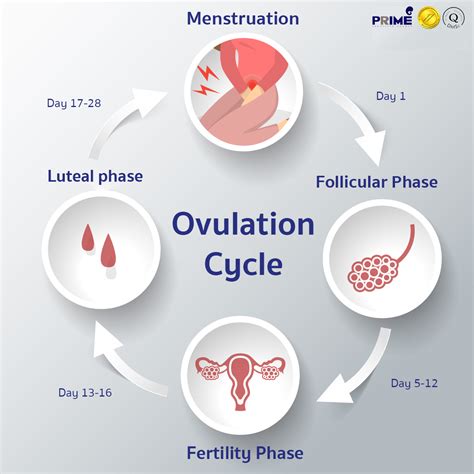
Table of Contents
Which of the Following Describes the Event of Ovulation? A Comprehensive Guide
Ovulation, a pivotal event in the female reproductive cycle, is often misunderstood. While many associate it simply with the release of an egg, the process is far more complex and nuanced. This comprehensive guide will delve deep into the intricacies of ovulation, explaining what it is, the hormonal triggers, the associated symptoms, and how to identify it. We will also address common misconceptions and provide information on how to track ovulation for various purposes, including conception and family planning.
Understanding Ovulation: More Than Just Egg Release
Ovulation is the process where a mature egg (ovum) is released from the ovary, making it available for fertilization by sperm. This isn't a spontaneous event; it's a carefully orchestrated sequence driven by hormonal fluctuations throughout the menstrual cycle. Understanding these hormonal fluctuations is key to grasping the complexity of ovulation.
The Hormonal Orchestra: A Symphony of Reproduction
The primary players in the ovulation drama are several hormones:
-
Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH): Produced by the pituitary gland, FSH stimulates the growth of several follicles in the ovaries. Each follicle contains an immature egg.
-
Luteinizing Hormone (LH): Also from the pituitary gland, LH plays a crucial role in triggering ovulation. A surge in LH levels is the ultimate signal for the mature follicle to rupture and release the egg. This surge is typically the most reliable indicator of impending ovulation.
-
Estrogen: Produced by the ovaries, estrogen levels rise throughout the follicular phase (the first half of the menstrual cycle), contributing to follicle growth and the eventual LH surge. Estrogen also plays a role in preparing the uterine lining for potential implantation of a fertilized egg.
-
Progesterone: Produced by the corpus luteum (the structure that forms from the ruptured follicle after ovulation), progesterone prepares the uterine lining for a possible pregnancy. If fertilization doesn't occur, progesterone levels decline, leading to menstruation.
The interplay between these hormones is crucial. A delicate balance is necessary for successful ovulation. Imbalances can lead to anovulation (absence of ovulation), irregular cycles, and infertility.
The Ovulatory Process: A Step-by-Step Guide
-
Follicular Development: The cycle begins with the recruitment of several follicles in the ovaries. FSH stimulates their growth, and one follicle typically becomes dominant.
-
Follicular Maturation: The dominant follicle continues to mature, containing the egg that will eventually be released. Estrogen levels rise steadily during this phase.
-
The LH Surge: A surge in LH is the trigger for ovulation. This surge occurs approximately 24-36 hours before ovulation. This is the most critical point in the entire ovulatory process.
-
Ovulation: The mature follicle ruptures, releasing the egg into the fallopian tube. The egg is viable for fertilization for approximately 12-24 hours.
-
Corpus Luteum Formation: The ruptured follicle transforms into the corpus luteum, which produces progesterone to prepare the uterine lining for a potential pregnancy.
-
Luteal Phase: The luteal phase follows ovulation and lasts approximately 14 days. If fertilization occurs, the corpus luteum continues to produce progesterone to support the pregnancy. If fertilization doesn't occur, the corpus luteum degenerates, leading to a drop in progesterone and the onset of menstruation.
Signs and Symptoms of Ovulation: Recognizing Your Body's Signals
While the LH surge is the definitive marker of ovulation, many women experience various physical signs and symptoms. However, it's crucial to remember that these signs can vary significantly between individuals, and some women may experience none at all.
Common Signs and Symptoms:
-
Cervical Mucus Changes: Cervical mucus becomes clearer, more stretchy, and more abundant in the days leading up to ovulation. This change in mucus is often described as "egg white" consistency and is a highly reliable indicator.
-
Basal Body Temperature (BBT) Shift: BBT, taken first thing in the morning before getting out of bed, typically rises by 0.4-1.0°F after ovulation due to the increase in progesterone. This shift is a retrospective indicator, meaning it confirms ovulation has already occurred.
-
Mittelschmerz: Some women experience mild to moderate pain in the lower abdomen on one side, often referred to as mittelschmerz. This pain is believed to be caused by the follicle rupturing or the released egg irritating the surrounding tissues.
-
Breast Tenderness: Increased breast tenderness or sensitivity can be a sign of ovulation, although this is a less reliable indicator.
-
Increased Libido: Some women experience an increase in sexual desire around the time of ovulation.
-
Slight Spotting: A small amount of spotting can occur around the time of ovulation.
It's essential to note that the absence of these symptoms does not necessarily mean ovulation hasn't occurred.
Tracking Ovulation: Methods and Techniques
Tracking ovulation is crucial for various reasons, including family planning, conception, and diagnosing fertility issues. Several methods are available:
-
Ovulation Predictor Kits (OPKs): These kits detect the LH surge in urine, providing a relatively accurate prediction of ovulation.
-
Basal Body Temperature (BBT) Charting: This method involves meticulously tracking your BBT daily to identify the post-ovulatory temperature shift. While accurate, it's a retrospective method, meaning it confirms ovulation after it has occurred.
-
Cervical Mucus Monitoring: Observing changes in cervical mucus consistency provides a reliable indicator of ovulation. This requires daily monitoring and understanding of the different mucus types.
-
Ovulation Calendar: While less accurate, tracking your menstrual cycle length can provide a rough estimate of your ovulation window. This method is most reliable for women with regular cycles.
-
Ultrasound: A transvaginal ultrasound can directly visualize the ovaries and follicles, providing a precise determination of ovulation timing. This method is primarily used in fertility clinics.
Combining multiple methods offers the most accurate and reliable ovulation tracking.
Misconceptions about Ovulation: Debunking the Myths
Several misconceptions surround ovulation. Addressing these myths is crucial for accurate understanding and appropriate family planning:
-
Myth: Ovulation always occurs on day 14 of the cycle. Fact: Ovulation typically occurs 12-16 days before the next menstrual period, but this can vary depending on cycle length.
-
Myth: All women experience noticeable signs and symptoms of ovulation. Fact: Many women experience no obvious signs or symptoms.
-
Myth: Intercourse only needs to occur on the day of ovulation for conception. Fact: Sperm can survive in the female reproductive tract for several days, allowing for conception even if intercourse occurs a few days before ovulation.
-
Myth: Once you have ovulated, you are fertile for the entire menstrual cycle. Fact: The released egg is only viable for fertilization for approximately 12-24 hours.
Ovulation and Fertility: Maximizing Your Chances of Conception
For couples trying to conceive, understanding and tracking ovulation is crucial. By accurately identifying the fertile window, couples can significantly increase their chances of conception. Timing intercourse to coincide with the period of highest fertility is a key strategy. However, it's important to remember that even with perfect timing, conception is not guaranteed.
Ovulation and Irregular Cycles: Addressing Anovulation
Irregular cycles can indicate problems with ovulation. Anovulation, the absence of ovulation, is a common cause of infertility. Several factors can contribute to irregular cycles, including hormonal imbalances, stress, weight fluctuations, and underlying medical conditions. If you are experiencing irregular cycles or difficulty conceiving, seeking medical advice is essential.
Conclusion: A Deeper Understanding of Ovulation
Ovulation is a complex yet fascinating process that is central to female reproduction. Understanding the hormonal mechanisms, signs and symptoms, and methods of tracking ovulation can empower women to make informed decisions regarding family planning, conception, and overall reproductive health. While this article provides comprehensive information, it's crucial to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice and guidance. Remember, every woman's body is unique, and what works for one may not work for another. Seeking professional medical advice ensures you receive accurate and tailored information based on your individual needs and circumstances.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Is Not A Period Cost
Mar 27, 2025
-
Hay 13 6 Chicas Y 20 12 Chicos
Mar 27, 2025
-
Se Sugiere Buscar Una Casa En Un Barrio Seguro Safe
Mar 27, 2025
-
What Are The Key Clauses In Ap Government
Mar 27, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Best Describes An Inside Attacker
Mar 27, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of The Following Describes The Event Of Ovulation . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
