What Step Should Be Taken Next To Securely Telework
Breaking News Today
Apr 01, 2025 · 7 min read
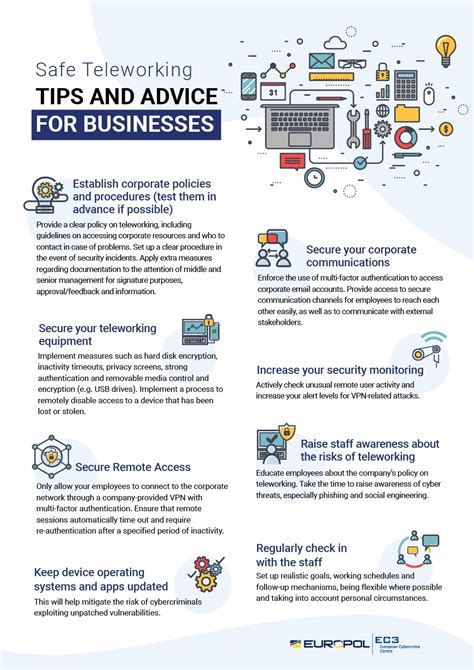
Table of Contents
What Steps Should Be Taken Next to Securely Telework?
The rise of remote work has been nothing short of revolutionary, transforming how we approach our professional lives. However, with this shift comes a heightened need for robust security measures. Simply setting up a laptop at home isn't enough; securing a telework environment requires a multi-faceted approach encompassing technology, policy, and employee training. This comprehensive guide details the crucial steps to take to ensure your remote workforce is secure and productive.
I. Strengthening Your Technological Defenses: The Foundation of Secure Telework
The technological infrastructure underpinning your telework strategy is paramount. A weak link here can compromise the entire operation, leaving your sensitive data vulnerable.
A. Secure Network Access: The First Line of Defense
-
VPN is Non-Negotiable: A Virtual Private Network (VPN) should be mandatory for all remote employees. A VPN encrypts all data transmitted between the employee's device and the company network, protecting sensitive information from interception. Choose a reputable VPN provider with robust security features. Ensure your VPN solution supports strong encryption protocols like OpenVPN or WireGuard. Avoid free VPNs, as they often lack the security features necessary for business use.
-
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): The Extra Layer of Security: MFA adds an extra layer of security beyond just a password. It requires multiple forms of authentication, such as a password, a one-time code from an authenticator app, or a biometric scan. Implementing MFA on all company systems and accounts significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access. This includes email accounts, VPN access, and any cloud-based applications.
-
Strong, Unique Passwords: The Bedrock of Cybersecurity: Educate employees on the importance of creating strong, unique passwords for every account. Password managers can greatly assist in this process, generating and securely storing complex passwords. Regular password changes should also be enforced, according to a defined policy.
-
Regular Software Updates: Patching Vulnerabilities: Outdated software is a prime target for hackers. Implement a system for automatically updating operating systems, applications, and firmware on all company devices. This proactive approach minimizes vulnerabilities and reduces the risk of successful attacks.
-
Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR): Proactive Threat Hunting: EDR solutions constantly monitor endpoints (computers, laptops, mobile devices) for malicious activity. They can detect and respond to threats in real-time, preventing breaches before they escalate. EDR provides an extra layer of protection against advanced threats that traditional antivirus software might miss.
B. Securing Data and Devices: Protecting Your Assets
-
Data Encryption: Keeping Information Confidential: Encrypt sensitive data both in transit (using VPNs and HTTPS) and at rest (using full-disk encryption or file-level encryption). Encryption ensures that even if a device is lost or stolen, the data remains inaccessible to unauthorized individuals.
-
Device Management: Maintaining Control: Implement a Mobile Device Management (MDM) or Unified Endpoint Management (UEM) solution to manage and secure company-owned devices. These tools allow for remote wiping of data, application control, and security policy enforcement. This is crucial for maintaining control over devices used for telework.
-
BYOD Policies: Balancing Flexibility and Security: If you allow employees to use their own devices (Bring Your Own Device – BYOD), establish clear policies outlining acceptable use, security requirements, and data separation. Ensure company data is kept separate from personal data on employee devices.
-
Regular Security Audits: Identifying Weaknesses: Conduct regular security audits to identify vulnerabilities in your telework infrastructure. This can involve penetration testing, vulnerability scanning, and security assessments. Addressing vulnerabilities proactively is far more cost-effective than reacting to a breach.
II. Developing Robust Policies and Procedures: The Governance Framework
Technology alone is insufficient. Strong policies and procedures are essential to guide employee behavior and maintain a secure telework environment.
A. Acceptable Use Policy (AUP): Setting Clear Expectations
-
Clearly Define Acceptable Use: A comprehensive AUP should clearly outline acceptable uses of company technology and resources. This includes guidelines on internet usage, social media access, and data handling. The AUP should be easily accessible and readily understood by all employees.
-
Address Data Security: The AUP must clearly define responsibilities concerning data security, including password management, data encryption, and incident reporting. Emphasize the importance of protecting sensitive information.
-
Outline Consequences of Violations: Clearly state the consequences of violating the AUP, including disciplinary actions. This serves as a deterrent and reinforces the importance of security protocols.
B. Remote Work Policy: Providing Clear Guidelines for Teleworkers
-
Security Protocols for Remote Work: The policy should outline specific security protocols for remote workers, including VPN usage, MFA requirements, and data encryption practices. This ensures consistency and adherence to security standards.
-
Hardware and Software Requirements: Specify the required hardware and software configurations for secure telework. This might include minimum operating system versions, antivirus software, and other security tools. Standardization simplifies management and enhances security.
-
Incident Response Procedures: Clearly define procedures for reporting security incidents, such as data breaches or suspicious activity. A well-defined incident response plan is crucial for minimizing the impact of a security incident.
C. Employee Training: Empowering Your Workforce
-
Regular Security Awareness Training: Provide employees with regular security awareness training to educate them about the risks of phishing, malware, and social engineering attacks. Training should be engaging and tailored to the specific threats faced by remote workers.
-
Hands-on Security Training: Include practical exercises and simulations to reinforce learning and enhance employee understanding of security protocols. This active learning approach improves knowledge retention and practical skills.
-
Ongoing Updates and Reminders: Regularly update employees on emerging threats and security best practices. Keeping employees informed is vital for maintaining a strong security posture.
III. Human Factors: The Often-Overlooked Element
While technology and policies are crucial, the human element remains a significant factor in telework security.
A. Phishing and Social Engineering Awareness: Educating Employees on Deception
Phishing and social engineering attacks remain highly effective. Employees must be trained to identify and avoid these threats. Regular simulated phishing campaigns can significantly improve employee awareness and response.
-
Suspicious Email Recognition: Teach employees to identify the hallmarks of suspicious emails, such as incorrect grammar, urgent requests, and unexpected attachments.
-
Website Verification: Emphasize the importance of verifying websites before entering sensitive information, checking for secure connections (HTTPS).
-
Social Engineering Tactics: Educate employees on common social engineering techniques, such as pretexting, baiting, and quid pro quo.
B. Secure Communication Practices: Protecting Sensitive Information
-
Avoid Sensitive Information in Unsecured Channels: Employees should avoid sharing sensitive information via unsecured channels, such as personal email or instant messaging applications.
-
Use Encrypted Communication Tools: Encourage the use of encrypted communication tools for sensitive discussions, such as video conferencing with end-to-end encryption.
-
Data Disposal Procedures: Establish clear procedures for securely disposing of sensitive data, including shredding physical documents and securely deleting electronic files.
C. Physical Security at Home: Protecting Equipment and Data
-
Secure Workspace: Encourage employees to establish a secure workspace at home, away from prying eyes and unauthorized access.
-
Device Security: Employees should keep their devices secure, using strong passwords and physical security measures such as locks or alarms.
-
Home Network Security: Employees should use strong passwords for their home Wi-Fi networks and keep their routers updated with the latest firmware.
IV. Continuous Monitoring and Improvement: The Ongoing Process
Securing telework is not a one-time event; it's an ongoing process. Regular monitoring and improvement are essential to maintain a strong security posture.
A. Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): Centralized Monitoring
SIEM systems centralize security logs from various sources, allowing for real-time monitoring and threat detection. SIEM provides a comprehensive view of security events across the entire telework environment.
B. Regular Security Assessments: Identifying Vulnerabilities
Conduct regular security assessments to identify potential vulnerabilities and weaknesses in your telework infrastructure. This proactive approach allows for timely remediation and prevents potential breaches.
C. Incident Response Plan: Preparation for the Inevitable
Develop a comprehensive incident response plan to address security incidents effectively. This plan should outline clear procedures for detection, containment, eradication, recovery, and post-incident activity.
Conclusion: A Holistic Approach to Secure Telework
Securing a telework environment demands a holistic approach encompassing strong technology, robust policies, comprehensive employee training, and continuous monitoring. By implementing the strategies outlined in this guide, organizations can significantly reduce the risks associated with remote work and maintain a secure and productive workforce. Remember, security is an ongoing process, not a destination. Continuous adaptation and improvement are crucial in the face of ever-evolving threats.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
According To Texass Attorney Why Should The Flag Be Protected
Apr 02, 2025
-
When Assessing A Patient With A Medical Complaint
Apr 02, 2025
-
Schizoid Personality Disorder Differs From Paranoid Personality Disorder In That
Apr 02, 2025
-
Amoeba Sisters Video Recap Answer Key Cell Transport
Apr 02, 2025
-
What Does Extension Of A Point Refer To
Apr 02, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Step Should Be Taken Next To Securely Telework . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
