What Would Be The Physiologic Basis For A Placenta Previa
Breaking News Today
Mar 25, 2025 · 5 min read
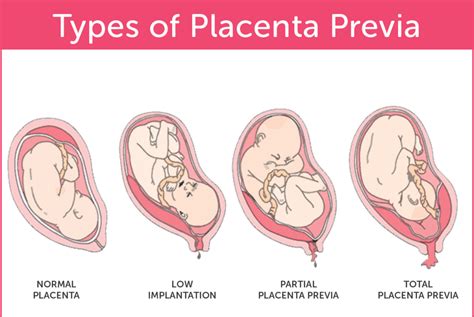
Table of Contents
The Physiologic Basis of Placenta Previa: A Comprehensive Overview
Placenta previa, a condition where the placenta implants in the lower uterine segment, obscuring the internal cervical os, poses significant risks to both mother and fetus. While the exact etiology remains incompletely understood, a confluence of factors contributes to its development. This article delves into the complex physiological mechanisms underlying placenta previa, exploring the interplay of uterine anatomy, implantation processes, and potential contributing factors.
I. Uterine Anatomy and Decidualization: Setting the Stage for Implantation
The location of placental implantation is fundamentally linked to the uterine anatomy and the decidualization process. Normal placental implantation occurs in the upper uterine segment, which possesses several characteristics crucial for successful pregnancy:
-
Thick Myometrium: The upper uterine segment boasts a thicker myometrium compared to the lower segment. This robust muscular layer provides structural support and facilitates efficient blood flow to the developing placenta. A thinner myometrium in the lower segment could predispose to abnormal implantation.
-
Abundant Spiral Arteries: The upper uterine segment is richly supplied with spiral arteries, modified maternal vessels that undergo crucial remodeling during pregnancy. This remodeling, driven by trophoblast invasion, is essential for ensuring adequate uteroplacental blood flow. Insufficient remodeling or abnormal spiral artery distribution in the lower segment may impair placental perfusion and contribute to previa.
-
Decidualization: The transformation of the endometrium into the decidua is crucial for successful implantation. Decidualization involves complex hormonal and cellular changes that prepare the uterine lining to receive the blastocyst. Inadequate decidualization, particularly in the lower uterine segment, might impair proper anchoring of the placenta. Factors influencing decidualization, such as maternal age and underlying medical conditions, may play a role.
II. Impaired Trophoblast Invasion and Spiral Artery Remodeling
Successful implantation relies on the appropriate invasion of the uterine wall by trophoblast cells. These cells, originating from the developing embryo, play a vital role in:
-
Anchoring the Placenta: Trophoblasts firmly attach the placenta to the uterine wall, ensuring its stability. Compromised trophoblast invasion could lead to unstable placental attachment, potentially resulting in previa.
-
Spiral Artery Remodeling: Trophoblasts invade and remodel the maternal spiral arteries, converting them from high-resistance vessels to low-resistance vessels. This transformation is critical for optimizing uteroplacental blood flow. Insufficient or incomplete remodeling can compromise blood supply to the placenta, potentially leading to placental malperfusion and previa. Genetic factors affecting trophoblast function could influence this process.
-
Immunological Tolerance: Trophoblasts also play a significant role in establishing immunological tolerance between the mother and the semi-allogeneic fetus. Dysregulation in this process might contribute to inflammatory responses affecting implantation and potentially leading to previa.
III. Factors Influencing Placental Implantation and the Risk of Previa
Several factors are associated with an increased risk of placenta previa, impacting various aspects of implantation and uterine physiology:
-
Previous Cesarean Section (C-Section): The most significant risk factor for placenta previa is a history of cesarean section. The scar tissue resulting from previous surgeries can disrupt the normal uterine anatomy and affect decidualization, potentially leading to ectopic placental implantation in the lower segment. The extent and location of the scar, along with the healing process, can all influence the risk.
-
Previous Placenta Previa: Women with a history of placenta previa have a considerably higher risk of recurrence in subsequent pregnancies. This suggests a potential underlying predisposition, possibly involving inherent uterine factors or persistent abnormalities in implantation mechanisms.
-
Uterine Abnormalities: Congenital uterine anomalies, such as uterine septums or bicornuate uterus, can alter uterine anatomy and create conditions favoring abnormal placental implantation. These anomalies may disrupt the normal distribution of spiral arteries and the thickness of the myometrium in the lower segment.
-
Multiple Gestations: In pregnancies with multiple fetuses, the increased uterine volume and expansion might lead to overcrowding and potentially alter the placental implantation site. The competitive implantation of multiple placentas can result in abnormal placement, increasing the risk of previa.
-
Advanced Maternal Age: Older mothers may experience changes in endometrial receptivity and decidualization, potentially increasing the risk of implantation anomalies. Age-related changes in hormonal profiles could also influence the trophoblast invasion process.
-
Smoking: Smoking during pregnancy is linked to an increased risk of placenta previa. Nicotine and other components of cigarette smoke might negatively affect uterine blood flow, decidualization, and trophoblast function, impacting placental implantation.
-
Previous uterine surgery: Any type of uterine surgery other than C-section, including myomectomy or endometrial ablation, can also increase the risk of abnormal placental implantation. The impact of these surgeries varies depending on the surgical technique and extent of the intervention.
IV. Other Contributing Factors: Genetic and Epigenetic Influences
While anatomical and environmental factors play a crucial role, emerging research suggests a potential contribution from genetic and epigenetic mechanisms:
-
Genetic Polymorphisms: Variations in genes involved in uterine vascular development, trophoblast invasion, and immune regulation may influence the risk of placenta previa. Research is ongoing to identify specific genes and their roles in this complex process.
-
Epigenetic Modifications: Epigenetic changes, such as DNA methylation and histone modification, can alter gene expression without changing the DNA sequence. These modifications might affect trophoblast function and decidualization, potentially increasing the susceptibility to previa. Environmental factors like smoking could contribute to these epigenetic changes.
V. Diagnostic Approaches and Management Strategies
Accurate diagnosis of placenta previa is crucial for appropriate management. Ultrasound imaging is the primary diagnostic tool. Depending on the severity and location of the previa, management strategies range from expectant observation to emergent cesarean section. The specific approach depends on gestational age, the degree of bleeding, and maternal and fetal well-being.
VI. Conclusion: A Complex Interplay of Factors
Placenta previa arises from a complex interplay of anatomical, physiological, and potentially genetic factors. Understanding the underlying mechanisms is crucial for improving diagnostic accuracy and developing preventative measures. Further research focusing on the intricate interplay between uterine anatomy, trophoblast function, immune regulation, and the impact of environmental factors is essential for fully elucidating the pathogenesis of placenta previa and optimizing pregnancy outcomes. The ultimate goal is to identify women at high risk and implement timely interventions to minimize maternal and fetal complications. This necessitates a multidisciplinary approach, encompassing obstetric care, genetic counseling, and basic scientific research. The journey toward a deeper comprehension of placenta previa is ongoing, promising advances in diagnosis, prevention, and management of this challenging obstetric complication.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Allocates Expenses To Revenues In The Proper Period
Mar 28, 2025
-
Stores Raw Data In A Relational Database
Mar 28, 2025
-
A Mi 1 Of 1 Los Platos
Mar 28, 2025
-
Flor Quiere Ir Al Almacen Don Guapo
Mar 28, 2025
-
What Is The Fundamental Unit Of Life
Mar 28, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Would Be The Physiologic Basis For A Placenta Previa . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
