Where Is The Pineal Gland Located Quizlet
Breaking News Today
Mar 17, 2025 · 6 min read
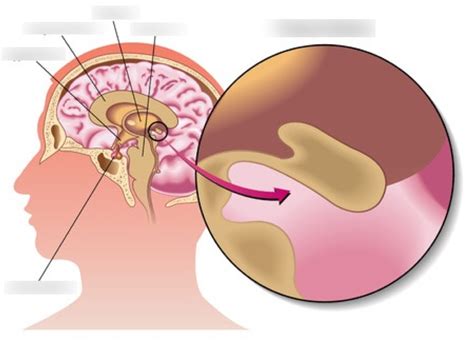
Table of Contents
Decoding the Pineal Gland: Location, Function, and More
The pineal gland, a small, cone-shaped endocrine gland, often sparks curiosity due to its unique location and intriguing functions. While a quick "where is the pineal gland located quizlet" search might provide a concise answer, understanding its intricacies requires a deeper dive. This comprehensive guide explores the pineal gland's location, its vital role in regulating our circadian rhythm, its potential links to spiritual experiences, and common misconceptions surrounding it.
Pinpointing the Pineal Gland: Anatomical Location
The pineal gland, also known as the epiphysis cerebri, is nestled deep within the brain. Its precise location is in the epithalamus, a region of the diencephalon. This area sits superior to the midbrain and posterior to the third ventricle. Think of it as a tiny structure residing near the center of the brain, close to where the two hemispheres meet.
Precise Anatomical Relationships:
-
Superior to the midbrain: The midbrain is a crucial part of the brainstem, responsible for various functions including vision, hearing, motor control, sleep/wake cycles, alertness, and temperature regulation. The pineal gland's proximity suggests potential interaction and influence.
-
Posterior to the third ventricle: The third ventricle is one of the four ventricles of the brain, filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). This strategic placement ensures the pineal gland receives adequate CSF circulation, essential for nutrient delivery and waste removal.
-
Between the two hemispheres: Its central location between the brain's hemispheres highlights its potential role in coordinating functions across the entire brain.
-
Attached to the habenular commissure: The habenular commissure is a small bundle of nerve fibers connecting the two habenular nuclei, playing a role in emotional responses and reward pathways. This anatomical connection further underscores the pineal gland's involvement in complex brain processes.
The Pineal Gland's Primary Function: Regulating Circadian Rhythms
The pineal gland's most well-established function is the production and secretion of melatonin. Melatonin is a hormone crucial for regulating the sleep-wake cycle, otherwise known as the circadian rhythm. The pineal gland's activity is highly sensitive to light levels. When light decreases (e.g., at night), the pineal gland increases melatonin production, signaling the body to prepare for sleep. Conversely, when light increases, melatonin production decreases, facilitating wakefulness.
Melatonin's Role Beyond Sleep:
While sleep regulation is paramount, melatonin's influence extends beyond this primary function. Research suggests it plays a role in:
-
Antioxidant properties: Melatonin is a potent antioxidant, protecting cells from damage caused by free radicals.
-
Immune system modulation: Studies indicate melatonin can influence the immune system's response, although the specifics are still under investigation.
-
Blood pressure regulation: Some evidence suggests melatonin may play a role in regulating blood pressure, though further research is needed.
-
Seasonal affective disorder (SAD): The reduced sunlight exposure during winter months can disrupt melatonin production, potentially contributing to SAD. Light therapy, aiming to regulate melatonin levels, is often used as a treatment.
Dispelling Myths: The Pineal Gland and Spirituality
The pineal gland has long been associated with spiritual and esoteric beliefs. Some believe it acts as the "third eye," a gateway to higher consciousness or psychic abilities. While these claims lack scientific evidence, the pineal gland's unique location and function have fueled such interpretations. It's crucial to differentiate between scientific understanding and speculative interpretations.
Scientific Understanding vs. Speculation:
The scientific community focuses on the pineal gland's established physiological roles, particularly melatonin production and circadian rhythm regulation. While the gland's functions are complex and not fully understood, the claims of paranormal abilities or "third eye" functions are not supported by current scientific research.
The Importance of Critical Thinking:
It is essential to approach information critically, distinguishing between scientifically validated knowledge and speculative claims. While the pineal gland's functions remain a fascinating area of ongoing research, it's crucial to base our understanding on evidence-based findings.
Potential Health Concerns Related to the Pineal Gland
While relatively rare, certain conditions can affect the pineal gland. These include:
-
Pineal tumors: These are relatively uncommon but can cause a range of symptoms, depending on their size and location. Symptoms can include headaches, visual disturbances, hormonal imbalances, and neurological issues.
-
Calcification: Over time, calcium deposits can accumulate in the pineal gland, a process known as calcification. This is often a normal age-related change and doesn't always cause symptoms. However, in some cases, it can be associated with altered melatonin production.
-
Inflammation: Inflammation of the pineal gland is rare but can be caused by infections or autoimmune diseases.
The Pineal Gland and Its Interactions with Other Brain Regions
The pineal gland doesn't operate in isolation. It interacts with various brain regions through complex neural and hormonal pathways. These interactions contribute to its overall function and influence on the body.
Key Interactions:
-
Hypothalamus: The hypothalamus, a crucial region for regulating various bodily functions, receives input from the pineal gland and plays a critical role in the circadian rhythm. This interaction ensures coordinated regulation of sleep-wake cycles and other related processes.
-
Suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN): The SCN, located in the hypothalamus, is the brain's primary circadian clock. The SCN receives light signals from the eyes and regulates melatonin production by the pineal gland. This feedback loop maintains the body's internal timekeeping system.
-
Other endocrine glands: The pineal gland interacts with other endocrine glands, influencing the production and release of various hormones. This complex interplay helps maintain hormonal balance and overall bodily homeostasis.
Ongoing Research and Future Directions
Research on the pineal gland continues to evolve. Scientists are exploring its potential roles in various physiological processes, including:
-
Aging and age-related diseases: The role of melatonin in slowing down aging and protecting against age-related diseases is being extensively investigated.
-
Neurodegenerative diseases: Research is exploring the potential connections between pineal gland dysfunction and neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's.
-
Cancer: Melatonin's antioxidant and immunomodulatory properties are being studied in relation to cancer prevention and treatment.
Conclusion: A Deeper Understanding of the Pineal Gland
The pineal gland, despite its diminutive size, plays a vital role in maintaining bodily homeostasis and regulating crucial physiological processes. Its primary function, melatonin production, is essential for regulating circadian rhythms and maintaining a healthy sleep-wake cycle. While intriguing claims surround the pineal gland's spiritual significance, separating scientific understanding from speculative interpretations is crucial. Ongoing research continues to unravel the complexities of this fascinating endocrine gland, revealing its potential contributions to human health and well-being. The journey to a comprehensive understanding of the pineal gland is ongoing, and future research promises to shed more light on its intricate functions and interactions within the body. Remembering its location within the epithalamus, superior to the midbrain and posterior to the third ventricle, provides a solid anatomical foundation for further exploration.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Direct Carry Is Used To Transfer A Patient
Mar 18, 2025
-
The Emancipation Proclamation Of January 1 1863 Quizlet
Mar 18, 2025
-
These Cards Will Get You Drunk Quizlet
Mar 18, 2025
-
Did Quizlet Get Rid Of Q Chat
Mar 18, 2025
-
Myasthenia Gravis Is An Autoimmune Disease In Which Quizlet
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Where Is The Pineal Gland Located Quizlet . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
