Which Antibacterials Are Effective Against Pseudomonas Aeruginosa
Breaking News Today
Mar 28, 2025 · 5 min read
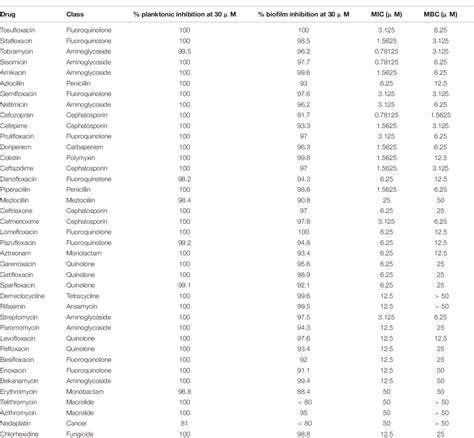
Table of Contents
Which Antibacterials are Effective Against Pseudomonas Aeruginosa?
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a ubiquitous, opportunistic Gram-negative bacterium notorious for its intrinsic resistance to many antibiotics and its ability to develop resistance to others rapidly. This makes treating infections caused by P. aeruginosa a significant challenge for healthcare professionals. This article will explore the various antibacterial agents effective against this pathogen, highlighting their mechanisms of action, spectrum of activity, and limitations. We will also discuss the importance of susceptibility testing and the growing threat of multi-drug resistant P. aeruginosa.
Understanding Pseudomonas aeruginosa and its Resistance Mechanisms
P. aeruginosa thrives in diverse environments, including soil, water, and hospitals. Its ability to form biofilms – complex communities of bacteria encased in a self-produced extracellular matrix – significantly contributes to its persistence and resistance to antibiotics. This bacterium possesses several intrinsic and acquired resistance mechanisms:
Intrinsic Resistance Mechanisms:
-
Outer Membrane Permeability: The outer membrane of P. aeruginosa acts as a formidable barrier, limiting the penetration of many antibiotics. Porins, channels within the outer membrane, regulate the entry of antimicrobial agents. P. aeruginosa often possesses low levels of porins that restrict the passage of certain drugs.
-
Efflux Pumps: P. aeruginosa produces a range of efflux pumps that actively expel antibiotics from the bacterial cell. These pumps can transport a broad spectrum of antimicrobial agents, contributing significantly to multi-drug resistance.
-
Enzyme Production: The bacterium produces various enzymes, including beta-lactamases, which inactivate beta-lactam antibiotics like penicillin and cephalosporins. Other enzymes can modify or degrade aminoglycosides and other drug classes.
Acquired Resistance Mechanisms:
-
Mutation: Mutations in chromosomal genes can alter the target sites of antibiotics or enhance the expression of efflux pumps.
-
Horizontal Gene Transfer: P. aeruginosa can acquire resistance genes from other bacteria through mechanisms like conjugation, transformation, and transduction. This allows for the rapid dissemination of resistance determinants within bacterial populations.
Antibacterial Agents Effective Against Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Despite the inherent and acquired resistance mechanisms of P. aeruginosa, several antibiotic classes remain effective against susceptible strains. However, it's crucial to remember that susceptibility testing is paramount before initiating treatment. Empiric therapy should be guided by local antibiograms and infection site considerations.
1. Beta-Lactams:
While many beta-lactams are rendered ineffective by beta-lactamases produced by P. aeruginosa, some options remain viable:
-
Piperacillin/Tazobactam: This combination antibiotic features piperacillin, a broad-spectrum penicillin, and tazobactam, a beta-lactamase inhibitor. Tazobactam protects piperacillin from inactivation by many beta-lactamases, extending its effectiveness against P. aeruginosa. However, resistance is emerging.
-
Ceftazidime: This cephalosporin exhibits activity against P. aeruginosa, but resistance is increasing. Ceftazidime-avibactam, a combination of ceftazidime and a novel beta-lactamase inhibitor, has broader activity against beta-lactamase-producing strains.
-
Cefepime: This fourth-generation cephalosporin possesses a wider spectrum of activity compared to earlier generations, including some activity against P. aeruginosa. However, similar to other beta-lactams, resistance is a growing concern.
-
Carbapenems (e.g., Imipenem, Meropenem, Doripenem): These broad-spectrum beta-lactams are often considered drugs of choice for severe P. aeruginosa infections. However, carbapenem resistance is a significant and growing threat, necessitating careful monitoring of susceptibility patterns.
2. Aminoglycosides:
Aminoglycosides, such as gentamicin, tobramycin, and amikacin, are often used in combination with other agents to treat P. aeruginosa infections. However, resistance is common, and their use is often limited by nephrotoxicity and ototoxicity. Synergistic effects are often seen when combined with beta-lactams.
3. Fluoroquinolones:
Ciprofloxacin and levofloxacin are fluoroquinolones that exhibit activity against P. aeruginosa. However, widespread use has led to a significant increase in resistance. Their role in treating P. aeruginosa infections is now significantly reduced in many regions.
4. Polymyxins:
Polymyxins, including polymyxin B and colistin (polymyxin E), are last-resort antibiotics for multi-drug-resistant P. aeruginosa. These drugs target the bacterial cell membrane and are effective against a wide range of Gram-negative bacteria, including many resistant strains. However, they are associated with significant toxicity, including nephrotoxicity and neurotoxicity, limiting their use.
5. Newer Antibacterial Agents:
Research continues to explore novel antimicrobial agents to combat P. aeruginosa. Several compounds are under investigation, including:
-
New beta-lactamase inhibitors: These are being developed to overcome the challenges posed by beta-lactamase-producing P. aeruginosa strains.
-
Agents targeting bacterial efflux pumps: Inhibiting efflux pumps can restore the activity of existing antibiotics.
-
Novel mechanisms of action: Researchers are exploring completely new targets within P. aeruginosa to develop antibiotics with unique modes of action.
The Importance of Susceptibility Testing
Given the high prevalence of antibiotic resistance in P. aeruginosa, susceptibility testing is absolutely crucial before initiating treatment. This involves performing laboratory tests to determine the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of various antibiotics against the specific isolate. The MIC represents the lowest concentration of an antibiotic that inhibits bacterial growth. This information guides the selection of the most appropriate antibiotic therapy, maximizing efficacy and minimizing the risk of treatment failure.
Strategies to Combat Antibiotic Resistance
The increasing prevalence of multi-drug-resistant P. aeruginosa necessitates a multi-pronged approach to combat antibiotic resistance:
-
Antibiotic Stewardship Programs: Implementing strict protocols for antibiotic prescribing and use, promoting appropriate antibiotic selection and duration of therapy, is critical.
-
Infection Control Measures: Implementing rigorous infection control practices in hospitals and other healthcare settings can prevent the spread of resistant bacteria. This includes hand hygiene, environmental cleaning, and contact precautions.
-
Development of Novel Antibacterial Agents: Continued investment in research and development is essential to discover and develop new antibiotics with novel mechanisms of action.
-
Alternative Therapeutic Strategies: Exploring alternative therapeutic strategies, such as phage therapy (using bacteriophages to target bacteria), could provide new options for treating resistant infections.
Conclusion
Treating infections caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa presents a significant challenge due to its inherent and acquired resistance mechanisms. While several antibacterial agents remain effective against susceptible strains, the emergence and spread of resistance necessitates a cautious and targeted approach. Careful consideration of local antibiograms, susceptibility testing, and implementation of robust infection control measures are crucial for effective treatment and prevention of P. aeruginosa infections. The development and implementation of novel therapeutic strategies are also paramount in combating the growing threat of multi-drug resistant P. aeruginosa. The future of managing these infections relies heavily on a combination of improved diagnostics, judicious antibiotic use, and the discovery of new antimicrobial agents.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How To Cheat In Quizlet Match 2023
Mar 31, 2025
-
Which Type Of Thermometer Checks The Surface Temperature Of Food
Mar 31, 2025
-
Ati Medical Surgical Proctored Exam 2023 Quizlet
Mar 31, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is A Function Of Proteins
Mar 31, 2025
-
Where Did Ranching And Mining Take Place
Mar 31, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Antibacterials Are Effective Against Pseudomonas Aeruginosa . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
