Which Best Explains How The Law Of Demand Affects Consumers
Breaking News Today
Mar 17, 2025 · 6 min read
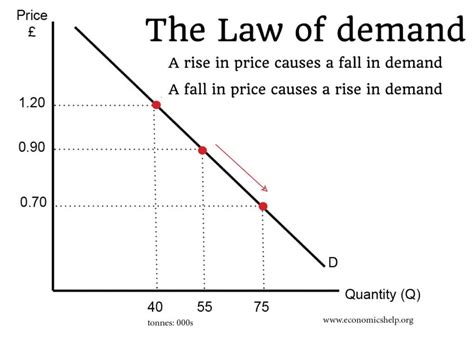
Table of Contents
How the Law of Demand Affects Consumers: A Deep Dive
The law of demand is a fundamental principle in economics that describes the relationship between the price of a good or service and the quantity demanded by consumers. It states that, all other factors being equal (ceteris paribus), as the price of a good increases, the quantity demanded will decrease, and vice versa. This seemingly simple concept has profound implications for consumers, shaping their purchasing decisions, influencing market dynamics, and impacting overall economic activity. This article will delve into the intricacies of the law of demand, exploring its various facets and how it directly affects consumers in the real world.
Understanding the Law of Demand: Beyond the Basics
The law of demand isn't just a theoretical construct; it's a powerful force driving consumer behavior. It rests on two key assumptions:
-
Diminishing Marginal Utility: As a consumer consumes more units of a good, the additional satisfaction (utility) derived from each extra unit decreases. Think about eating pizza: the first slice is heavenly, the second is enjoyable, but by the fifth, you might be feeling quite full, and the satisfaction gained is significantly less. This diminishing marginal utility means consumers are less willing to pay a high price for additional units.
-
Substitution Effect: When the price of a good rises, consumers often look for substitutes – alternative goods or services that satisfy the same need. If the price of coffee increases, some consumers might switch to tea or another beverage. This substitution effect reduces the quantity demanded of the more expensive good.
-
Income Effect: A price increase reduces the purchasing power of a consumer's income. Even if the consumer's income remains the same, a higher price for a good effectively makes them "poorer" as they can buy less of that good with their existing budget. This leads to a reduction in the quantity demanded.
The Demand Curve: A Visual Representation
The law of demand is often illustrated graphically using a demand curve. This curve slopes downward from left to right, showing the inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded. The higher the price, the lower the quantity demanded, and vice versa.
(Insert a simple, clear graph showing a downward-sloping demand curve here. Label the axes clearly: Price (Vertical) and Quantity Demanded (Horizontal))
How the Law of Demand Impacts Consumer Choices
The law of demand profoundly influences how consumers make purchasing decisions:
1. Budget Allocation and Prioritization:
Consumers have limited budgets. The law of demand forces them to prioritize their spending. If the price of a luxury item, like a new car, increases significantly, consumers may postpone the purchase or opt for a cheaper alternative, reallocating their budget to essential goods and services.
2. Search for Value and Bargain Hunting:
Consumers are always searching for the best value for their money. The law of demand encourages them to actively seek out bargains, discounts, and sales. An increase in price incentivizes consumers to explore cheaper options or wait for a price drop.
3. Brand Switching and Substitution:
When the price of a preferred brand or product rises, consumers are more likely to switch to a competing brand or a substitute product. This competitive pressure keeps companies on their toes, forcing them to innovate, improve quality, and potentially lower prices to retain customers.
4. Demand Elasticity and Consumer Responsiveness:
The law of demand operates differently depending on the elasticity of demand for a particular good or service. Elastic demand refers to situations where a small price change significantly impacts the quantity demanded (e.g., luxury goods). Inelastic demand means that even large price changes have a relatively small effect on quantity demanded (e.g., essential goods like medicine). Understanding elasticity helps businesses predict how price changes will affect their sales and consumers understand how price sensitive their purchases are.
5. Influence on Market Equilibrium:
The interaction of supply and demand determines market equilibrium – the point where the quantity demanded equals the quantity supplied. The law of demand plays a crucial role in reaching this equilibrium. If prices are too high, the quantity demanded falls, creating a surplus. Conversely, if prices are too low, the quantity demanded rises, leading to a shortage. The market adjusts until equilibrium is reached.
Beyond the Simple Model: Factors Influencing Demand
While the law of demand provides a fundamental framework, other factors can also influence consumer demand:
-
Consumer Income: An increase in consumer income generally leads to an increase in demand for most goods, particularly normal goods. However, demand for inferior goods (those for which demand decreases as income increases) will decrease with rising income.
-
Consumer Preferences and Tastes: Changing tastes and trends significantly affect demand. The popularity of a product can fluctuate dramatically based on fashion, technological advancements, and social influences.
-
Prices of Related Goods: The demand for a good can be affected by the prices of complementary goods (goods used together, like cars and gasoline) and substitute goods (goods that can be used in place of each other, like Coke and Pepsi).
-
Consumer Expectations: Expectations about future prices, income, or availability of goods can influence current demand. For example, if consumers expect a price increase in the future, they may buy more now.
-
Number of Buyers: The size of the market (number of consumers) directly influences the overall demand for a product or service. A larger market means higher overall demand.
Real-World Examples of the Law of Demand in Action
Numerous real-world examples illustrate the law of demand's impact on consumers:
-
The Gasoline Market: When gasoline prices rise sharply, consumers often reduce their driving, carpool, or switch to more fuel-efficient vehicles, demonstrating a decrease in the quantity demanded.
-
The Smartphone Market: The introduction of cheaper smartphones often leads to a surge in demand, as more consumers can afford access to this technology.
-
The Housing Market: In periods of high housing prices, fewer people can afford to buy homes, leading to a decrease in the quantity demanded.
-
The Fast Food Industry: During economic downturns, demand for fast food, an inexpensive option, often increases as consumers seek more affordable alternatives.
-
The Luxury Goods Market: Luxury goods are highly sensitive to price changes; an increase in price often results in a substantial decrease in demand, highlighting the concept of elasticity.
Conclusion: The Enduring Relevance of the Law of Demand
The law of demand remains a cornerstone of economic understanding. It provides a powerful framework for analyzing consumer behavior and predicting market responses to price changes. While other factors influence demand, the inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded remains a consistent and significant driver of consumer choices. Understanding this law is critical for both consumers, to make informed purchasing decisions, and businesses, to effectively price their goods and services and understand market dynamics. By grasping the nuances of the law of demand, individuals and businesses can navigate the complexities of the marketplace with greater clarity and success. The ongoing relevance of this fundamental principle underscores its enduring importance in understanding the intricate dance between price, quantity, and consumer behavior.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Describe The Continuous Nature Of The Physical Fitness Concept
Mar 18, 2025
-
High Levels Of Cholesterol Can First Lead Directly To
Mar 18, 2025
-
True Or False Professional And Technical Communication Is Research Oriented
Mar 18, 2025
-
Which Best Describes The Terrorist Planning Cycle
Mar 18, 2025
-
Cdl Combination Test Questions And Answers Pdf
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Best Explains How The Law Of Demand Affects Consumers . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
