Which Identified Clinical Manifestation Is A Sign Of Allergic Rhinitis
Breaking News Today
Mar 22, 2025 · 7 min read
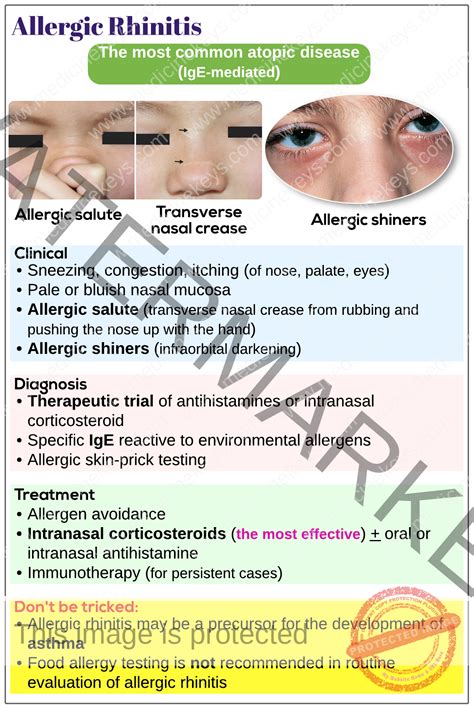
Table of Contents
Which Identified Clinical Manifestation is a Sign of Allergic Rhinitis?
Allergic rhinitis, commonly known as hay fever, is a prevalent inflammatory condition affecting the nasal passages. It's triggered by an allergic reaction to airborne allergens such as pollen, dust mites, pet dander, and mold spores. Understanding its clinical manifestations is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective management. This comprehensive guide delves deep into the key symptoms and signs that characterize allergic rhinitis, equipping you with the knowledge to recognize this condition and seek appropriate medical attention.
Key Clinical Manifestations of Allergic Rhinitis
The hallmark of allergic rhinitis is a constellation of symptoms primarily affecting the nose, eyes, and sometimes the throat and ears. The severity and combination of symptoms can vary greatly among individuals.
Nasal Symptoms: The Cornerstone of Diagnosis
Nasal symptoms are the most prominent and defining features of allergic rhinitis. These include:
-
Rhinorrhea (Runny Nose): This is a hallmark symptom, characterized by a watery nasal discharge. The discharge may become thicker and more mucus-like as the inflammation persists. The watery nature distinguishes allergic rhinitis from other nasal conditions like common colds, where the discharge often progresses from watery to thicker and more opaque.
-
Nasal Congestion: Swelling of the nasal mucous membranes leads to blockage of the nasal passages, making breathing through the nose difficult. This can disrupt sleep, affect sense of smell, and cause snoring.
-
Nasal Itch: An intense itching sensation inside the nose is frequently reported by individuals with allergic rhinitis. This itchiness can be quite bothersome and often prompts nose rubbing, which can exacerbate the symptoms.
-
Sneezing: Frequent and often intense sneezing fits are common, especially upon exposure to the allergen. This forceful expulsion of air from the lungs is the body's attempt to clear the nasal passages of the irritating allergen. The pattern of sneezing can be a helpful diagnostic clue.
Ocular Symptoms: Beyond the Nose
Allergic rhinitis often involves symptoms affecting the eyes, further supporting the diagnosis. These include:
-
Itchy, Watery Eyes: Similar to the nasal itch, intense itching in and around the eyes is a common symptom. This is often accompanied by excessive tearing (watery eyes). The combination of itchy, watery eyes and runny nose strongly suggests allergic rhinitis.
-
Eye Redness: Inflammation of the conjunctiva (the membrane lining the inside of the eyelids and covering the white part of the eye) leads to redness and bloodshot appearance. This redness is a direct result of the allergic reaction.
-
Eye Swelling (Periorbital Edema): In some cases, particularly with severe allergic reactions, swelling around the eyes (periorbital edema) may occur. This is due to fluid accumulation in the tissues surrounding the eyes.
Other Associated Symptoms: Expanding the Clinical Picture
While nasal and ocular symptoms are central, other symptoms can co-occur, contributing to the overall clinical picture of allergic rhinitis:
-
Postnasal Drip: Excessive mucus production drains down the back of the throat, causing a sensation of mucus dripping down the throat. This can lead to a persistent cough, especially at night.
-
Ear Congestion/Pressure: The inflammation associated with allergic rhinitis can extend to the Eustachian tubes, leading to a feeling of fullness or pressure in the ears. This can occasionally result in temporary hearing impairment.
-
Facial Pressure/Pain: Sinus pain or pressure may occur due to inflammation and swelling of the sinuses. This is more common in cases where allergic rhinitis is complicated by sinusitis.
-
Fatigue: The persistent symptoms of allergic rhinitis, along with disrupted sleep, can lead to significant fatigue and reduced energy levels.
-
Headache: Headaches can also be associated with allergic rhinitis, possibly due to sinus congestion or inflammation.
-
Reduced Sense of Smell (Hyposmia): Nasal congestion can impair the sense of smell, making it difficult to appreciate aromas. This is usually temporary and resolves with treatment of the nasal congestion.
-
Cough: As mentioned, postnasal drip often triggers a persistent, often dry, cough. This is particularly prominent at night.
Differentiating Allergic Rhinitis from Other Conditions
It's crucial to differentiate allergic rhinitis from other conditions that share similar symptoms. This requires a careful clinical assessment, including considering the patient's history, symptom pattern, and physical examination findings. Conditions that can mimic allergic rhinitis include:
-
Common Cold (Viral Rhinitis): Unlike allergic rhinitis, which is typically chronic or recurrent, the common cold is usually self-limiting, lasting only a few days to a week. The presence of fever, body aches, and a more significant feeling of illness points more towards a viral infection.
-
Sinusitis: While sinusitis can coexist with allergic rhinitis, it involves inflammation and infection of the sinuses. Sinusitis often presents with more severe facial pain, pressure, and thicker, discolored nasal discharge.
-
Nasal Polyps: These benign growths in the nasal passages can cause nasal congestion and loss of smell. They often require surgical removal.
-
Non-allergic Rhinitis: This encompasses various conditions causing rhinitis without an allergic mechanism, such as vasomotor rhinitis triggered by temperature or humidity changes. These can be distinguished by the absence of specific allergen triggers.
-
Drug-induced rhinitis: Some medications can lead to nasal congestion and other rhinitis-like symptoms as a side effect.
Diagnostic Approach: Unveiling the Allergen
Confirming the diagnosis of allergic rhinitis typically involves a combination of methods:
-
Detailed Medical History: A thorough history taking, focusing on the onset, duration, and pattern of symptoms, as well as potential exposure to allergens, is crucial. A family history of allergies is also relevant.
-
Physical Examination: A physical examination of the nose and eyes assesses for signs of inflammation, swelling, and discharge.
-
Allergy Testing: Skin prick tests or blood tests (RAST) can identify specific allergens responsible for the reaction. These tests reveal sensitivities to various substances like pollen, dust mites, pet dander, and mold.
-
Symptom Diary: Keeping a detailed record of symptoms, their severity, and the potential triggers can provide valuable information for diagnosis and management.
Management Strategies: Alleviating Symptoms and Improving Quality of Life
Managing allergic rhinitis involves a combination of strategies aimed at controlling symptoms and improving the patient's quality of life. These include:
-
Allergen Avoidance: Identifying and avoiding exposure to known allergens is a cornerstone of management. This may involve measures such as using air purifiers, removing carpets, washing bedding regularly, and avoiding pets or certain outdoor activities during peak pollen seasons.
-
Pharmacological Interventions: A variety of medications are effective in relieving symptoms. These include:
- Intranasal corticosteroids: These are considered the first-line treatment for allergic rhinitis. They effectively reduce inflammation and improve nasal symptoms.
- Antihistamines: These medications block the action of histamine, a key mediator of allergic reactions, providing relief from itching, sneezing, and runny nose. They are available in oral and nasal spray formulations.
- Decongestants: These temporarily relieve nasal congestion, but prolonged use should be avoided due to the risk of rebound congestion.
- Leukotriene inhibitors: These medications block the production of leukotrienes, another inflammatory mediator involved in allergic reactions. They are often prescribed for patients who do not respond well to other treatments.
- Immunotherapy (Allergy Shots): This involves gradually exposing the patient to increasing doses of the allergen over time, leading to a reduction in sensitivity and symptom improvement. It's considered a long-term treatment option.
-
Lifestyle Modifications: Certain lifestyle adjustments can help manage symptoms. This includes getting adequate sleep, staying hydrated, and maintaining good overall health. Stress management techniques may also help, as stress can exacerbate allergic reactions.
Conclusion: Recognizing the Signs and Seeking Help
Recognizing the clinical manifestations of allergic rhinitis is crucial for timely diagnosis and effective management. The characteristic combination of nasal symptoms, such as rhinorrhea, congestion, and itch, along with ocular symptoms like itchy, watery eyes, strongly suggests allergic rhinitis. Differentiating it from other conditions requires a thorough clinical assessment. A combination of allergen avoidance, pharmacological interventions, and lifestyle modifications can effectively control symptoms and improve the quality of life for individuals with allergic rhinitis. If you suspect you have allergic rhinitis, consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and personalized management plan. Early intervention and appropriate treatment are essential to minimize the impact of this common condition.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Ap Lang Unit 8 Progress Check Mcq Quizlet
Mar 23, 2025
-
Tell The Energy Transformation In A Television
Mar 23, 2025
-
Left Bundle Branch Block Is Characterized By Quizlet
Mar 23, 2025
-
By Establishing Judicial Review John Marshall Quizlet
Mar 23, 2025
-
Archaea Differ From Bacteria In That Archaea Quizlet
Mar 23, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Identified Clinical Manifestation Is A Sign Of Allergic Rhinitis . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
