Which Material Is A Common Indoor Air Pollutant
Breaking News Today
Mar 28, 2025 · 6 min read
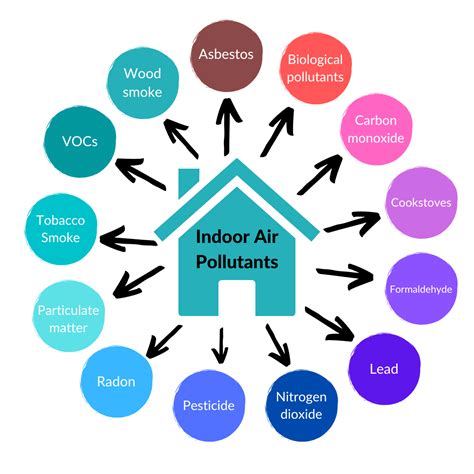
Table of Contents
Which Material is a Common Indoor Air Pollutant? A Comprehensive Guide
Indoor air quality is a critical concern for our health and well-being. While we often focus on outdoor pollution, the air within our homes and workplaces can be significantly more polluted, potentially exposing us to harmful pollutants at much higher concentrations for extended periods. Understanding which materials contribute to this indoor air pollution is crucial for mitigating risks and creating healthier living and working environments. This article delves into the common culprits, explaining their sources, effects, and mitigation strategies.
Common Indoor Air Pollutants and Their Sources
Many materials commonly found in our homes and offices release volatile organic compounds (VOCs), particulate matter (PM), and other harmful substances into the air we breathe. Let's explore some of the most prevalent:
1. Paints and Coatings: A Major Source of VOCs
Paints, varnishes, stains, and other coatings often contain high concentrations of VOCs. These chemicals evaporate into the air during and after application, contributing significantly to poor indoor air quality. Formaldehyde, toluene, and xylene are common VOCs found in these products.
-
Health Effects: Exposure to high levels of VOCs from paints can lead to headaches, eye, nose, and throat irritation, nausea, and dizziness. Long-term exposure may be associated with more serious health problems.
-
Mitigation: Choose low-VOC or zero-VOC paints and coatings whenever possible. Ensure adequate ventilation during and after application. Use respirators when painting to avoid direct inhalation.
2. Carpets and Upholstery: Hidden Reservoirs of Pollutants
Carpets and upholstery, especially those made with synthetic fibers, can trap dust, pollen, pet dander, and other allergens. They can also release VOCs, particularly if treated with flame retardants or other chemicals. Formaldehyde is frequently found in some carpet adhesives and backing materials.
-
Health Effects: Exposure to allergens trapped in carpets can trigger allergic reactions such as sneezing, coughing, runny nose, and itchy eyes. VOCs released from carpets can contribute to the same symptoms as those from paints.
-
Mitigation: Regular vacuuming, especially using a vacuum cleaner with a HEPA filter, is crucial. Consider using natural fiber rugs or carpets. Proper ventilation can help reduce VOC build-up. Regular professional cleaning can help remove deeply embedded allergens.
3. Furniture and Furnishings: A Mix of Potential Hazards
Many pieces of furniture, particularly those made from particleboard, plywood, or medium-density fiberboard (MDF), release formaldehyde. Some fabrics used in upholstery and curtains may also release VOCs. Additionally, certain types of wood finishes can also contribute to indoor air pollution.
-
Health Effects: Formaldehyde exposure can lead to eye, nose, and throat irritation, breathing difficulties, and allergic reactions. Long-term exposure has been linked to more serious health issues.
-
Mitigation: Opt for furniture made from solid wood whenever possible. Choose furniture with low-formaldehyde emissions or formaldehyde-free materials. Ensure proper ventilation in rooms with new furniture.
4. Cleaning Products: Unexpected Indoor Air Pollutants
Household cleaning products often contain harsh chemicals, many of which are VOCs, that evaporate into the air during use. These products can contribute to poor indoor air quality, especially in poorly ventilated areas.
-
Health Effects: Exposure to cleaning product chemicals can lead to eye, nose, and throat irritation, headaches, and respiratory problems. Some chemicals may have more serious long-term health effects.
-
Mitigation: Choose cleaning products that are low-VOC or plant-based. Always follow product instructions carefully and ensure adequate ventilation during use. Consider using natural cleaning solutions like vinegar and baking soda.
5. Building Materials: The Foundation of Indoor Air Pollution
Building materials themselves can contribute to indoor air pollution. Materials like plywood, particleboard, and insulation can release formaldehyde, as well as other VOCs. Asbestos, though largely banned, can still be found in older buildings and poses a significant health risk.
-
Health Effects: Asbestos fibers can cause serious lung diseases, including asbestosis and lung cancer. Formaldehyde and other VOCs released from building materials can lead to the same health problems as discussed above.
-
Mitigation: For new construction, choose building materials with low VOC emissions. If dealing with older buildings that may contain asbestos, professional asbestos abatement is essential.
6. Combustion Appliances: Producing a Range of Pollutants
Gas stoves, fireplaces, and other combustion appliances release pollutants such as carbon monoxide, nitrogen dioxide, and particulate matter into the air. Incomplete combustion can exacerbate this problem.
-
Health Effects: Carbon monoxide is a colorless, odorless gas that can be fatal. Nitrogen dioxide can irritate the lungs and worsen respiratory conditions. Particulate matter can aggravate respiratory problems and contribute to cardiovascular disease.
-
Mitigation: Ensure proper ventilation when using combustion appliances. Regular maintenance of appliances is crucial to ensure efficient combustion. Consider using alternative heating methods if feasible.
7. Personal Care Products: Unexpected Contributors
Hair sprays, perfumes, air fresheners, and other personal care products can release VOCs and other harmful chemicals into the air. These products often contain phthalates and other potentially harmful substances.
-
Health Effects: Phthalates have been linked to hormonal disruption and reproductive problems. Other chemicals in these products can contribute to respiratory issues and allergic reactions.
-
Mitigation: Choose personal care products with natural ingredients and avoid products with strong fragrances. Use these products in well-ventilated areas.
8. Pesticides and Insecticides: Potential Indoor Threats
Pesticides and insecticides, even those designed for indoor use, can release harmful chemicals into the air. These products are often more potent than many other household items, resulting in significant air pollution if not applied and managed correctly.
-
Health Effects: Exposure to pesticides can lead to neurological problems, respiratory issues, and other health problems. Some pesticides are known carcinogens.
-
Mitigation: Use pesticides sparingly and follow the manufacturer's instructions carefully. Ensure proper ventilation after application. Consider using natural pest control methods whenever possible.
Identifying and Addressing Indoor Air Pollution: Practical Strategies
Tackling indoor air pollution requires a multi-pronged approach:
1. Source Control: The most effective way to reduce indoor air pollution is to eliminate or minimize the sources of pollution. This involves choosing low-VOC materials, using natural cleaning products, and properly maintaining combustion appliances.
2. Ventilation: Adequate ventilation is crucial for removing pollutants from the indoor air. This can be achieved through opening windows and doors, using exhaust fans in kitchens and bathrooms, and installing mechanical ventilation systems.
3. Air Purification: Air purifiers with HEPA filters can effectively remove particulate matter and some VOCs from the air. Choose a purifier appropriate for the size of the room.
4. Regular Cleaning: Regular cleaning, including vacuuming with a HEPA filter vacuum, dusting, and wiping surfaces, can help remove allergens and pollutants.
5. Monitoring: Consider using indoor air quality monitors to track levels of pollutants and identify areas that need improvement.
Conclusion: Creating Healthier Indoor Environments
Indoor air pollution is a significant public health concern. Understanding the common sources of pollutants and implementing appropriate mitigation strategies is essential for creating healthier living and working environments. By making informed choices about materials, employing effective cleaning and ventilation techniques, and utilizing air purification technology, we can significantly reduce our exposure to harmful pollutants and improve our overall health and well-being. Remember, proactive measures are crucial to ensuring clean and safe indoor air. The effort invested in improving indoor air quality is an investment in health and longevity.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Defining Research With Human Subjects Sbe Quizlet
Mar 31, 2025
-
Hesi A2 Anatomy And Physiology Quizlet 2023
Mar 31, 2025
-
A Disorder Caused By Hyperthyroidism Is Quizlet
Mar 31, 2025
-
An Example Of An Automatic Stabilizer Is Quizlet
Mar 31, 2025
-
Budgeting For Life After High School Worksheet Answers Quizlet
Mar 31, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Material Is A Common Indoor Air Pollutant . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
