Which Of The Following Are Components Of High-quality Cpr
Breaking News Today
Mar 25, 2025 · 6 min read
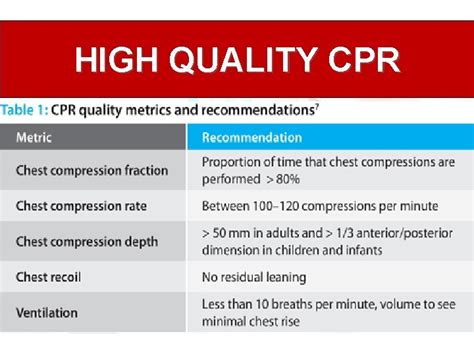
Table of Contents
Which of the Following are Components of High-Quality CPR?
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is a life-saving technique that can help someone who has stopped breathing or has a sudden cardiac arrest. High-quality CPR significantly increases the chances of survival and positive neurological outcomes. But what exactly constitutes "high-quality" CPR? It's not just about doing something; it's about doing the right thing, correctly, and consistently. This article delves into the crucial components of high-quality CPR, breaking them down into manageable segments for clarity and understanding.
I. Chest Compressions: The Foundation of Effective CPR
Chest compressions are the cornerstone of CPR, responsible for circulating blood containing oxygen to the vital organs. High-quality chest compressions are characterized by several key elements:
A. Rate and Depth:
- Rate: Aim for a compression rate of 100-120 compressions per minute. This is crucial for maintaining adequate blood flow. Rushing or slowing down significantly reduces effectiveness. Using a metronome or CPR feedback device can help maintain the correct rate.
- Depth: Compressions should be at least 2 inches (5 cm) deep for adults. For children and infants, depth is adjusted according to age and size, following guidelines provided by organizations like the American Heart Association (AHA) and the European Resuscitation Council (ERC). Insufficient depth will not adequately circulate blood. Excessive depth can cause harm.
B. Complete Chest Recoil:
Allowing the chest to fully recoil after each compression is paramount. This allows the heart to refill with blood, maximizing the effectiveness of each pump. Incomplete recoil significantly reduces cardiac output.
C. Minimizing Interruptions:
Interruptions to chest compressions should be kept to an absolute minimum. Each interruption reduces blood flow to the brain and other vital organs. Minimize pauses for anything other than essential actions like checking for a pulse or switching compressors. Aim for minimal interruption time.
D. Proper Hand Placement and Body Position:
Correct hand placement is vital. For adult CPR, place the heel of one hand on the center of the chest, between the nipples. Place the other hand on top, interlacing fingers. Maintain a straight arm position, using your body weight to perform compressions, rather than just your arms. This helps avoid fatigue and ensures consistent depth.
II. Breathing (Ventilations): Supplementing Oxygen Delivery
While chest compressions are the priority, proper ventilations are equally important in providing oxygen to the victim's blood. High-quality ventilations are characterized by:
A. Adequate Breath Volume:
Deliver breaths that are sufficient to visibly raise the chest. Over-ventilation can be harmful, but under-ventilation is ineffective. Follow guidelines for appropriate breath volume based on the age of the victim.
B. Proper Breath Delivery:
Ensure an airtight seal around the mouth (or nose and mouth for infants) to prevent air leakage. Administer breaths smoothly and gently, avoiding forceful delivery. Avoid hyperventilation.
C. Breath Rate:
The recommended breath rate varies based on the CPR scenario (single rescuer vs. two-rescuer CPR), but generally involves delivering breaths after a certain number of chest compressions. Adhere to the latest AHA or ERC guidelines for specific breath-to-compression ratios.
III. Early Defibrillation (If Applicable): Restoring Heart Rhythm
For victims of sudden cardiac arrest (SCA), early defibrillation is absolutely crucial. Defibrillation uses an electrical shock to restore a normal heart rhythm. High-quality CPR incorporating defibrillation involves:
A. Immediate Access to AED:
Locate an automated external defibrillator (AED) as quickly as possible. Time is of the essence; every minute without defibrillation reduces survival chances.
B. Prompt Defibrillation:
Once the AED is available, follow the device's voice prompts to analyze the heart rhythm and deliver a shock if necessary. This should be done as quickly and efficiently as possible, adhering to the device's instructions.
C. Post-Shock CPR:
After delivering a shock, immediately resume high-quality CPR, continuing chest compressions and ventilations according to guidelines.
IV. Teamwork and Effective Communication (For Multi-Rescuer CPR): Synergy for Success
When multiple rescuers are involved, effective teamwork is crucial for delivering high-quality CPR. This involves:
A. Clear Roles and Responsibilities:
Assign roles clearly, such as compressor, ventilator, and AED operator (if applicable). This ensures a coordinated effort, minimizes confusion, and avoids interruptions.
B. Effective Communication:
Maintain clear and concise communication among rescuers, especially during transitions between compressors or during AED operation. Verbal cues and a well-defined system for switching roles will avoid disruptions and maintain the rhythm.
C. Organized and Efficient Transitions:
Smooth transitions between rescuers are vital to avoid any interruption in chest compressions. Establish a system for efficient changes to prevent pauses in compressions.
V. Post-CPR Care: The Aftermath and Ongoing Support
Even after CPR is complete, high-quality care continues. This involves:
A. Continuous Monitoring:
Monitor the victim's vital signs carefully after CPR, ensuring they receive appropriate medical attention and ongoing care. Observe for any changes in their condition.
B. Early and Effective Advanced Care:
Ensure the victim receives immediate advanced medical care, such as emergency medical services (EMS) transport to a hospital. This ensures continued treatment and stabilization.
C. Post-Resuscitation Care:
Once stabilized, appropriate post-resuscitation care should be provided, focusing on preventing further complications and maximizing the chances of a full recovery.
VI. Continuous Improvement and Training: The Lifelong Pursuit of Excellence
High-quality CPR is not a one-time achievement; it's an ongoing process of learning and improvement.
A. Regular Training and Refresher Courses:
Participating in regular CPR training courses keeps skills sharp and updated with the latest guidelines. Regular practice and refresher courses are crucial to maintain proficiency.
B. Practice and Skill Maintenance:
Regular practice, even in a simulated environment, helps maintain the necessary skills and confidence to deliver effective CPR during a real emergency.
C. Staying Updated with Guidelines:
The guidelines for CPR are regularly updated by organizations like the AHA and ERC to reflect new research and best practices. Staying informed about these updates is crucial for providing the most effective care.
Conclusion: The Sum of its Parts
High-quality CPR is not a single action, but a combination of several key elements working together harmoniously. From the precise execution of chest compressions and ventilations to the timely use of defibrillation and effective teamwork, each component plays a crucial role in maximizing survival rates and improving neurological outcomes. By focusing on all aspects of high-quality CPR – rate, depth, recoil, minimal interruptions, proper hand placement, adequate breath volume, timely defibrillation, teamwork, and post-CPR care – rescuers can significantly increase the chances of saving a life. Remember, every second counts, and the pursuit of excellence in CPR is a continuous journey that demands dedication, training, and a commitment to saving lives.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Insect Symbolizes Both Death And Rebirth
Mar 28, 2025
-
Prevention Of The Spread Of Infections Begins And Ends With
Mar 28, 2025
-
The Entry To Establish A Petty Cash Fund Includes
Mar 28, 2025
-
What Can A Budget Help You Do Everfi
Mar 28, 2025
-
Which Event Marks The Beginning Of A Supernova
Mar 28, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of The Following Are Components Of High-quality Cpr . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
