Which Of The Following Are Included In The Opsec Cycle
Breaking News Today
Mar 14, 2025 · 7 min read
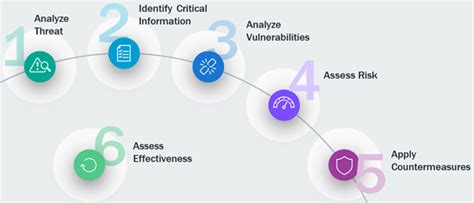
Table of Contents
Decoding the OPSEC Cycle: A Comprehensive Guide to Protecting Your Information
Operational Security (OPSEC) isn't just a buzzword; it's a critical process for safeguarding sensitive information and maintaining a competitive edge, whether you're a multinational corporation, a government agency, or even an individual with valuable data. Understanding the OPSEC cycle is crucial for implementing effective security measures. But what exactly is included in this cycle? Let's break it down. This in-depth guide will explore each phase, providing practical examples and highlighting best practices for robust OPSEC implementation.
The Five Core Steps of the OPSEC Cycle
The OPSEC cycle is a continuous, iterative process, not a one-time fix. It involves five key steps:
- Identification of Critical Information: This is the foundational step. Without identifying what needs protection, all subsequent efforts are futile.
- Analysis of Threats: Understanding who might target your information and their capabilities is vital for prioritizing your defenses.
- Analysis of Vulnerabilities: Identifying weaknesses in your systems, processes, and personnel that could expose your critical information.
- Risk Assessment: Weighing the likelihood of a threat exploiting a vulnerability and the potential impact of a successful attack.
- Implementation of OPSEC Measures: Developing and implementing countermeasures to mitigate identified risks.
Let's delve deeper into each phase:
1. Identification of Critical Information (CI): The Foundation of OPSEC
This stage is paramount. It involves systematically identifying all information that, if compromised, could significantly harm your organization. This isn't just about classified data; it encompasses anything that could provide a competitive advantage to adversaries, cause reputational damage, or expose you to legal liability. This includes:
-
Business Plans and Strategies: Detailed outlines of future projects, market analysis, and expansion plans. Leaking these could allow competitors to steal your innovative ideas or undercut your market position.
-
Financial Information: Sensitive financial data, including budgets, sales figures, profit margins, and intellectual property valuation, is highly sought after by competitors and malicious actors. Compromise can lead to financial losses and legal repercussions.
-
Research and Development Data: Patents, trade secrets, experimental data, and innovative technologies are prime targets for industrial espionage. Loss of R&D data can cripple innovation and cost significant time and resources to rebuild.
-
Customer Data: Personal information of customers, including names, addresses, credit card numbers, and medical records, is protected by various regulations (like GDPR and CCPA). A breach can result in massive fines and irreparable damage to reputation.
-
Employee Data: Sensitive employee information such as salaries, performance reviews, social security numbers, and health records. Compromise can lead to identity theft, legal action, and loss of employee trust.
-
Supply Chain Information: Details about suppliers, contracts, logistics, and manufacturing processes. Compromise can disrupt operations and expose vulnerabilities within the supply chain.
Best Practices for CI Identification:
-
Involve Multiple Stakeholders: Gather input from across different departments to get a holistic view of the organization's critical information.
-
Regular Reviews: Conduct periodic reviews of CI to account for changes in the business environment and technological advancements.
-
Documentation: Maintain a comprehensive and up-to-date inventory of all identified critical information.
-
Classification System: Implement a clear classification system to categorize information based on its sensitivity level.
2. Analysis of Threats: Identifying Potential Adversaries
Once you've identified your critical information, the next step is to analyze the threats that could potentially target it. Threats can range from sophisticated state-sponsored actors to opportunistic hackers and disgruntled employees. Consider:
-
Competitors: Analyze their capabilities, motivations, and past actions to assess their potential for industrial espionage.
-
Cybercriminals: Evaluate the sophistication and tactics of different cybercriminal groups, focusing on their targets and methods.
-
Hacktivists: Understand the motivations and targets of hacktivist groups, and assess the potential for attacks based on your organization's public profile.
-
Nation-States: Consider the potential for state-sponsored espionage or cyber warfare, especially if your organization handles sensitive national security information.
-
Insider Threats: Identify employees or contractors who might have access to critical information and the potential for malicious intent.
Best Practices for Threat Analysis:
-
Threat Intelligence: Leverage open-source and commercial threat intelligence to stay informed about emerging threats and vulnerabilities.
-
Vulnerability Scanning: Regularly scan your systems for known vulnerabilities that could be exploited by attackers.
-
Penetration Testing: Simulate real-world attacks to identify weaknesses in your security defenses.
-
Social Engineering Awareness Training: Educate employees about social engineering techniques used by attackers to gain access to sensitive information.
3. Analysis of Vulnerabilities: Finding Weak Points in Your Defenses
This phase focuses on identifying weaknesses in your organization's systems, processes, and personnel that could expose your critical information. Vulnerabilities can be technical, physical, or human. Examples include:
-
Technical Vulnerabilities: Outdated software, unpatched systems, weak passwords, insecure network configurations, and lack of encryption.
-
Physical Vulnerabilities: Lack of physical security measures, such as inadequate access control, surveillance, or perimeter security.
-
Human Vulnerabilities: Lack of security awareness training, phishing susceptibility, social engineering vulnerabilities, and insider threats.
-
Procedural Vulnerabilities: Inefficient or insecure processes for handling sensitive information, such as inadequate data handling policies or lack of access control procedures.
Best Practices for Vulnerability Analysis:
-
Regular Security Audits: Conduct regular audits of your systems and processes to identify and address vulnerabilities.
-
Vulnerability Management System: Implement a vulnerability management system to track and manage identified vulnerabilities.
-
Security Awareness Training: Provide regular security awareness training to employees to educate them about potential threats and vulnerabilities.
-
Access Control Management: Implement strong access control measures to limit access to sensitive information only to authorized personnel.
4. Risk Assessment: Evaluating the Likelihood and Impact of Attacks
This stage involves evaluating the likelihood of a threat exploiting a vulnerability and the potential impact of a successful attack. This requires a careful assessment of the following factors:
-
Likelihood: The probability of a specific threat exploiting a specific vulnerability. This is influenced by factors such as the sophistication of the threat actor and the effectiveness of your security controls.
-
Impact: The potential consequences of a successful attack. This could include financial losses, reputational damage, legal penalties, and operational disruption.
-
Risk Level: The overall risk level is determined by combining the likelihood and impact of an attack. This helps prioritize which vulnerabilities to address first.
Best Practices for Risk Assessment:
-
Quantitative Risk Assessment: Use quantitative methods to assign numerical values to likelihood and impact, providing a more objective assessment.
-
Qualitative Risk Assessment: Use qualitative methods to assess likelihood and impact based on expert judgment and experience.
-
Risk Register: Maintain a risk register to track identified risks, their associated vulnerabilities, and mitigation strategies.
-
Regular Risk Reviews: Conduct regular reviews of your risk assessment to account for changes in the threat landscape and your organization's security posture.
5. Implementation of OPSEC Measures: Protecting Your Critical Information
The final stage involves developing and implementing countermeasures to mitigate the identified risks. This includes a range of measures, such as:
-
Technical Controls: Implementing strong passwords, multi-factor authentication, encryption, intrusion detection systems, firewalls, and regular software updates.
-
Physical Controls: Implementing access control measures, surveillance systems, perimeter security, and secure storage for sensitive information.
-
Administrative Controls: Developing and enforcing security policies, providing security awareness training, and establishing incident response plans.
-
Personnel Controls: Conducting thorough background checks on employees, implementing strong access control measures, and monitoring employee activity.
-
Data Loss Prevention (DLP): Employ DLP tools to monitor and prevent the unauthorized transfer of sensitive information.
-
Security Awareness Training: Regular and engaging training to educate employees about phishing scams, social engineering tactics, and safe data handling practices.
-
Incident Response Plan: A documented and tested plan for handling security incidents, including procedures for containment, eradication, and recovery.
Best Practices for Implementing OPSEC Measures:
-
Layered Security: Implement multiple layers of security to provide redundancy and resilience.
-
Continuous Monitoring: Continuously monitor your systems and processes for security threats and vulnerabilities.
-
Regular Updates: Keep your software and systems up to date with the latest security patches.
-
Documentation: Maintain comprehensive documentation of your OPSEC measures, including policies, procedures, and training materials.
-
Regular Testing: Regularly test your security controls to ensure they are effective.
Conclusion: OPSEC – An Ongoing Commitment
The OPSEC cycle isn't a static process; it's a continuous journey. Regular review and adaptation are vital to staying ahead of evolving threats and ensuring the ongoing protection of your critical information. By diligently following these steps, organizations can significantly reduce their risk of data breaches, maintain a competitive advantage, and protect their reputation and bottom line. Remember, effective OPSEC requires a holistic approach, integrating technical, physical, and administrative controls, and most importantly, a strong security culture within the organization. The commitment to continuous improvement is the key to successful and lasting OPSEC implementation.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Amoeba Sisters Video Recap Photosynthesis And Cellular Respiration Answers Pdf
May 09, 2025
-
Human Anatomy And Physiology Lab Manual Answer Key Pdf
May 09, 2025
-
Free 360 Training Food Manager Final Exam Answers Pdf Texas
May 09, 2025
-
Which Type Of Tissue Conducts Electrochemical Impulses
May 09, 2025
-
Which Invention Allowed The Greatest Personal Freedom Of Travel
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of The Following Are Included In The Opsec Cycle . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.