Which Of The Following Is A Capital Resource
Breaking News Today
Mar 16, 2025 · 5 min read
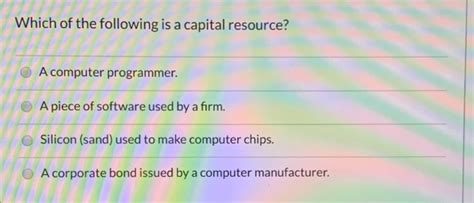
Table of Contents
- Which Of The Following Is A Capital Resource
- Table of Contents
- Which of the Following is a Capital Resource? A Deep Dive into Capital Resources and Their Importance
- What are Capital Resources?
- Key Characteristics of Capital Resources:
- Examples of Capital Resources:
- Manufacturing:
- Agriculture:
- Transportation:
- Services:
- Differentiating Capital Resources from Other Resource Types:
- The Importance of Capital Resources in Economic Growth:
- Which of the Following is a Capital Resource? A Practical Application:
- Conclusion:
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
Which of the Following is a Capital Resource? A Deep Dive into Capital Resources and Their Importance
Understanding capital resources is crucial for grasping fundamental economic principles. While the term might seem straightforward, its nuances often lead to confusion. This comprehensive guide will delve deep into the definition of capital resources, explore various examples, differentiate them from other resource types, and discuss their significance in economic growth and development. We'll address the question, "Which of the following is a capital resource?" in a practical and insightful manner.
What are Capital Resources?
Capital resources, also known as capital goods, are manufactured goods used to produce other goods and services. Unlike natural resources (like land and minerals) or human resources (labor), capital resources are created by humans specifically to aid in production. They are the tools, machinery, equipment, factories, and infrastructure that facilitate the creation of other goods and services. Think of them as the engines of production.
Key Characteristics of Capital Resources:
- Produced: Capital resources are not naturally occurring; they are manufactured or constructed.
- Durable: They are designed to last for a period of time, providing repeated use in the production process. This doesn't mean they're indestructible, but they're expected to have a relatively long lifespan compared to raw materials.
- Used in Production: Their primary purpose is to aid in the production of other goods or services, increasing efficiency and productivity.
- Indirectly Satisfy Wants and Needs: Unlike consumer goods, which directly satisfy individual needs, capital goods contribute indirectly by enabling the production of goods and services that fulfill those needs.
Examples of Capital Resources:
The range of capital resources is incredibly vast, spanning various industries and technological advancements. Here are some examples across different sectors:
Manufacturing:
- Machinery: Lathes, milling machines, assembly lines, robotic arms – these are fundamental to mass production in manufacturing.
- Tools: Hand tools, power tools, and specialized equipment utilized in various manufacturing processes.
- Factories and Plants: The buildings and infrastructure housing the production processes.
- Computers and Software: Crucial for design, production management, and automation.
Agriculture:
- Tractors and Harvesters: Mechanized equipment that dramatically increases agricultural output.
- Irrigation Systems: Infrastructure for efficient water management in farming.
- Storage Facilities: Silos, barns, and cold storage units for preserving agricultural products.
Transportation:
- Trucks, Trains, Ships, and Airplanes: Essential for moving goods and people.
- Roads, Railways, and Airports: The infrastructure supporting transportation systems.
- Warehouses and Distribution Centers: Facilities for storing and distributing goods.
Services:
- Computers and Software: Used in service industries like banking, healthcare, and education.
- Office Equipment: Printers, copiers, and other office supplies.
- Communication Networks: Telecommunications infrastructure and technology.
- Hospital Equipment: Medical imaging devices, surgical tools, and patient monitoring equipment.
Differentiating Capital Resources from Other Resource Types:
It's crucial to distinguish capital resources from other factors of production:
1. Capital Resources vs. Natural Resources:
Natural resources are gifts of nature, such as land, water, minerals, and forests. Capital resources are manufactured from natural resources or other goods. A lumber mill (capital resource) uses trees (natural resource) to produce lumber.
2. Capital Resources vs. Human Resources:
Human resources encompass the labor, skills, and knowledge of individuals. While humans operate and maintain capital resources, they are distinct categories. A skilled welder (human resource) uses a welding machine (capital resource).
3. Capital Resources vs. Consumer Goods:
Consumer goods are items directly purchased and consumed by individuals to satisfy their wants and needs. Capital goods are used to produce consumer goods. A car (consumer good) is manufactured using assembly lines and machinery (capital resources).
The Importance of Capital Resources in Economic Growth:
Capital resources play a vital role in driving economic growth and development. Their impact is multifaceted:
- Increased Productivity: Capital goods significantly enhance productivity by automating tasks, improving efficiency, and enabling larger-scale production. This translates to more goods and services being produced with the same or fewer inputs.
- Technological Advancement: Investment in capital resources often leads to technological advancements, further boosting productivity and efficiency. New machinery and equipment often incorporate innovative technologies that improve the production process.
- Economic Specialization and Division of Labor: Capital resources facilitate specialization and the division of labor. This allows individuals and firms to focus on specific tasks, leading to greater expertise and efficiency.
- Higher Standards of Living: Increased production due to capital investment translates into a higher supply of goods and services, leading to a higher standard of living for the population.
- Job Creation: The production, maintenance, and operation of capital resources create numerous jobs, stimulating economic activity and reducing unemployment.
Which of the Following is a Capital Resource? A Practical Application:
Let's apply our understanding to a practical scenario. Consider the following list:
- A. An oil well
- B. A computer used in a business
- C. A farmer
- D. A loaf of bread
- E. Iron ore
- F. A factory building
- G. A fishing boat
- H. A pair of shoes
Based on our definition, the following are capital resources:
- B. A computer used in a business: This is a manufactured good used to produce goods or services.
- F. A factory building: This is a structure built specifically to house production activities.
- G. A fishing boat: A manufactured good used to catch fish (a good).
The other options are:
- A. An oil well: This is a natural resource.
- C. A farmer: This is a human resource.
- D. A loaf of bread: This is a consumer good.
- E. Iron ore: This is a natural resource.
- H. A pair of shoes: This is a consumer good.
Conclusion:
Understanding the concept of capital resources is essential for analyzing economic systems and promoting sustainable growth. They are the cornerstone of productive economies, driving technological advancements, boosting productivity, and improving standards of living. By distinguishing capital resources from other resource types, we can better appreciate their critical role in creating wealth and improving societal well-being. Remembering their manufactured nature, durability, and contribution to production will help you easily identify capital resources in various scenarios. This knowledge empowers you to make informed decisions regarding investment, resource allocation, and economic planning.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Why Do Antibiotics Not Work Against Viruses Quizlet
Mar 18, 2025
-
The Zoot Suit Riots Of 1943 Quizlet
Mar 18, 2025
-
Circles In The Coordinate Plane Quiz Quizlet
Mar 18, 2025
-
What Are The Types Of Essential Records Quizlet
Mar 18, 2025
-
What Is The Function Of Meiosis Quizlet
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of The Following Is A Capital Resource . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
