Which Of The Following Is An Example Of Green Computing
Breaking News Today
Mar 19, 2025 · 6 min read
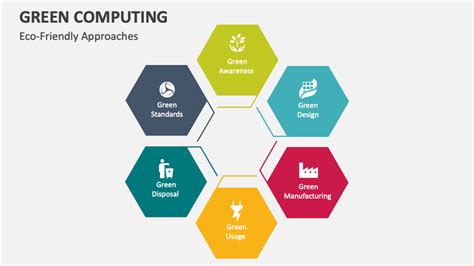
Table of Contents
Which of the following is an example of green computing? A Deep Dive into Sustainable IT Practices
Green computing, also known as sustainable computing or green IT, is more than just a trend; it's a crucial shift in how we approach technology and its environmental impact. In today's digitally driven world, the energy consumption and electronic waste generated by our reliance on computers, servers, and other digital devices are significant concerns. Understanding what constitutes green computing is vital for individuals, businesses, and governments alike. This article will delve into the various aspects of green computing, providing clear examples and demonstrating how seemingly small actions can contribute to a larger, more sustainable technological landscape.
Defining Green Computing: Beyond the Buzzwords
Green computing encompasses a broad range of practices aimed at minimizing the environmental impact of IT. This isn't simply about recycling old hardware (though that's part of it); it involves a holistic approach that considers the entire lifecycle of a computer system, from manufacturing to disposal. Key aspects include:
Reducing Energy Consumption: The Core Principle
The most significant environmental impact of computing stems from its energy consumption. Data centers, in particular, consume vast amounts of electricity. Green computing focuses on minimizing this energy footprint through various strategies:
-
Energy-efficient hardware: Choosing computers, servers, and peripherals with high energy-efficiency ratings (like Energy Star certified products) is a crucial first step. These devices consume less power while maintaining performance.
-
Virtualization: Consolidating multiple physical servers into virtual servers running on fewer physical machines significantly reduces energy consumption and cooling needs.
-
Cloud computing: While the environmental impact of cloud computing is complex and depends on the provider's practices, it can potentially reduce energy consumption for individual users by centralizing resources and optimizing energy usage at large-scale data centers.
-
Power management: Implementing power saving features like sleep mode, hibernation, and automatic shutdowns can drastically reduce energy waste, especially for desktop and laptop computers.
Minimizing Electronic Waste (E-waste): Responsible Disposal
E-waste is a growing global problem. Millions of tons of electronic devices are discarded annually, containing hazardous materials that can leach into the environment. Green computing emphasizes responsible e-waste management:
-
Recycling and reuse: Properly recycling old computers, monitors, and other electronic devices prevents hazardous materials from entering landfills and recovers valuable resources. Reusing components where possible extends the lifespan of hardware and reduces the demand for new manufacturing.
-
Extended producer responsibility (EPR): This policy framework holds manufacturers accountable for the end-of-life management of their products, encouraging them to design for recyclability and to participate in take-back programs.
-
Refurbishing and donating: Instead of discarding functional equipment, consider refurbishing it for reuse or donating it to schools, charities, or individuals in need.
Sustainable Manufacturing Practices: From Creation to Consumption
The environmental impact of computing begins even before a device is used. Green computing considers the manufacturing process itself:
-
Sustainable materials: Using recycled materials in the manufacturing of electronic devices reduces the demand for new resources and minimizes environmental impact.
-
Reduced packaging: Minimizing packaging materials and utilizing recycled and biodegradable packaging reduces waste and transportation costs.
-
Energy-efficient manufacturing processes: Employing energy-efficient manufacturing techniques throughout the production cycle reduces the overall carbon footprint of electronic devices.
Examples of Green Computing in Action
Now, let's look at specific examples that illustrate the principles of green computing:
1. Using Energy Star Certified Equipment: Choosing a laptop or desktop computer certified by the Energy Star program ensures that the device meets specific energy-efficiency standards, consuming less electricity and reducing your carbon footprint.
2. Implementing a Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI): VDI allows users to access their desktops and applications remotely through a centralized server, reducing the number of physical desktops and the associated energy consumption. This is particularly beneficial for large organizations.
3. Utilizing Cloud Services for Data Storage and Processing: Moving data storage and processing tasks to the cloud can leverage the economies of scale of large data centers, potentially leading to more efficient energy usage compared to individual on-premise servers. However, it’s crucial to choose a provider with strong sustainability commitments.
4. Implementing a Power Management Policy: Enforcing power management policies across an organization's computers, setting them to sleep or hibernate after periods of inactivity, can significantly reduce energy consumption and costs.
5. Participating in Electronic Waste Recycling Programs: Properly disposing of old electronics through certified recycling programs ensures that hazardous materials are handled safely and valuable components are recovered.
6. Choosing Products with Eco-Friendly Packaging: Selecting products with minimal packaging or packaging made from recycled or biodegradable materials reduces waste and contributes to a circular economy.
7. Adopting a Telecommuting Policy: Allowing employees to work remotely reduces the need for commuting, which lowers greenhouse gas emissions associated with transportation.
8. Using Dual-Monitor Setups Strategically: While seemingly counterintuitive, using two smaller monitors instead of one large monitor can sometimes consume less energy.
9. Implementing Green Software Practices: Developing and using software that is optimized for energy efficiency and minimizes resource usage contributes to a greener computing environment. This includes optimizing code for performance, utilizing efficient algorithms, and minimizing network traffic.
10. Educating Users About Green Computing Practices: Promoting awareness among users about energy-saving techniques, responsible e-waste disposal, and other green computing best practices is crucial for achieving widespread adoption.
The Role of Individuals and Organizations in Green Computing
The responsibility for green computing rests on multiple stakeholders:
Individuals: We can make a tangible impact through conscious choices regarding our computing habits. This includes choosing energy-efficient devices, implementing power management settings, properly disposing of e-waste, and reducing our overall digital footprint.
Organizations: Businesses have a larger responsibility due to their greater consumption of IT resources. Implementing green computing strategies can lead to cost savings, improve their corporate social responsibility image, and attract environmentally conscious employees and customers. This includes investing in energy-efficient infrastructure, implementing virtualization, adopting cloud services responsibly, and establishing robust e-waste management programs.
Governments: Governments play a vital role in shaping policies and regulations that promote green computing. This includes setting energy-efficiency standards, supporting research and development of sustainable technologies, and implementing extended producer responsibility programs for electronic waste.
The Future of Green Computing: Innovation and Collaboration
Green computing is an evolving field. Ongoing research and development focus on creating more energy-efficient hardware, developing sustainable manufacturing processes, and improving e-waste management systems. The future of green computing requires continued collaboration between individuals, organizations, and governments to create a truly sustainable digital ecosystem. Innovation in areas like low-power processors, efficient cooling systems for data centers, and biodegradable electronics will be crucial in minimizing the environmental impact of our ever-increasing reliance on technology.
Conclusion: Embracing Sustainability in the Digital Age
Green computing is not just about being environmentally responsible; it's about creating a more sustainable and cost-effective future for the technology industry. By understanding the principles of green computing and actively implementing the strategies outlined in this article, we can collectively minimize the environmental footprint of our digital world. The transition to a greener IT landscape is not a single action but a continuous journey of conscious choices, collaborative efforts, and innovative solutions. Embracing these principles will not only benefit the planet but also lead to long-term economic and social advantages.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Wrasse Fish Black Sea Bass Info On Relationship
Mar 19, 2025
-
Chriss Views On Money And Governmental Authority
Mar 19, 2025
-
Removing An Organism From An Ecosystem
Mar 19, 2025
-
First Ten Elements On The Period Table
Mar 19, 2025
-
The Most Critical Part Of Boating Is
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of The Following Is An Example Of Green Computing . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
