Which Of The Following Is Most Associated With Managerial Accounting
Breaking News Today
Mar 21, 2025 · 6 min read
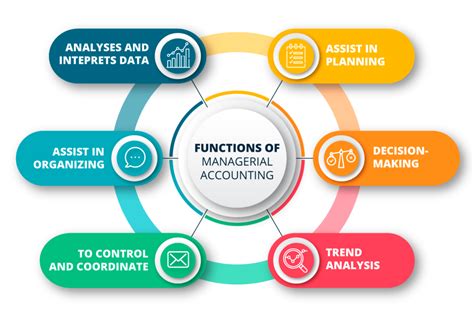
Table of Contents
Which of the Following is Most Associated with Managerial Accounting?
Managerial accounting, unlike financial accounting, focuses on providing information for internal use within an organization. While financial accounting adheres to strict Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) for external reporting, managerial accounting is flexible and adapts to the specific needs of the organization. This flexibility allows for a wide range of applications and analyses, making it crucial for effective decision-making. Let's explore which aspects are most strongly associated with this critical field.
The Core Functions of Managerial Accounting
Several key functions are inextricably linked to managerial accounting. These functions are not mutually exclusive; they often overlap and support one another to provide a holistic view of an organization's performance and future prospects.
1. Planning: Setting the Stage for Success
Managerial accounting plays a crucial role in the planning process. This involves:
-
Budgeting: Developing detailed budgets for various departments and functions, forecasting revenues, and allocating resources effectively. Managerial accountants create budgets that are both realistic and challenging, striving for optimal performance within the constraints of available resources. They also use different budgeting techniques (zero-based budgeting, incremental budgeting, activity-based budgeting) to suit the company's needs.
-
Forecasting: Predicting future trends and outcomes based on historical data, market analysis, and other relevant factors. This involves analyzing sales projections, cost estimates, and potential risks to develop realistic financial forecasts. Accurate forecasting is critical for making informed strategic decisions.
-
Strategic Planning: Collaborating with management to establish long-term goals and objectives. Managerial accountants provide data-driven insights to help guide strategic decisions, ensuring that the organization aligns its resources and capabilities with its strategic vision. They analyze potential investment opportunities, market expansion plans, and competitive advantages.
2. Controlling: Monitoring Performance and Making Adjustments
Once plans are in place, managerial accounting helps monitor performance and make necessary adjustments. This involves:
-
Performance Evaluation: Tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) to assess the effectiveness of various operations and departments. KPIs are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) metrics that provide a clear picture of progress towards goals. Managerial accountants identify variances between planned and actual results, analyze the causes of these variances, and recommend corrective actions.
-
Variance Analysis: Investigating differences between budgeted and actual results. This involves identifying the factors that contributed to the variances and determining their impact on overall profitability. By understanding the reasons behind variances, managers can take proactive steps to improve efficiency and profitability.
-
Cost Control: Implementing strategies to minimize costs without compromising quality or efficiency. This includes optimizing production processes, negotiating favorable supplier contracts, and identifying areas where costs can be reduced. Managerial accountants play a critical role in ensuring that cost control measures are effective and aligned with the organization's overall goals.
3. Decision Making: Providing Data-Driven Insights
Managerial accounting provides crucial information for making informed business decisions. This involves:
-
Cost-Volume-Profit (CVP) Analysis: Analyzing the relationship between costs, volume, and profit to determine the break-even point and the impact of changes in sales volume on profitability. This is a fundamental tool for making pricing decisions and assessing the financial viability of new products or services.
-
Capital Budgeting: Evaluating potential investments in long-term assets, such as new equipment or facilities. Managerial accountants use various techniques (Net Present Value, Internal Rate of Return) to assess the financial feasibility of capital projects.
-
Pricing Decisions: Determining appropriate prices for products or services, considering factors such as costs, competition, and market demand. This involves analyzing various pricing strategies (cost-plus pricing, value-based pricing, competitive pricing) to optimize profitability.
-
Make-or-Buy Decisions: Evaluating whether it's more cost-effective to manufacture a product internally or outsource its production. Managerial accountants analyze the relevant costs and benefits of each option to make informed decisions.
Key Differences from Financial Accounting
While both managerial and financial accounting deal with numbers, their purposes and methods differ significantly. Financial accounting's primary focus is on external reporting, while managerial accounting serves internal stakeholders. Here are some key distinctions:
-
Purpose: Financial accounting aims to provide information to external users (investors, creditors, government agencies) for decision-making. Managerial accounting focuses on providing information to internal users (managers, employees) for planning, controlling, and decision-making.
-
Rules and Regulations: Financial accounting strictly adheres to GAAP and other regulatory frameworks. Managerial accounting is not bound by these rules and can utilize various methods and techniques to meet the specific needs of the organization.
-
Time Horizon: Financial accounting focuses on historical data and past performance. Managerial accounting uses both historical data and future projections to inform current and future decisions.
-
Scope: Financial accounting provides a broad overview of the organization's financial position. Managerial accounting can delve into specific departments, products, or processes to provide detailed information.
-
Reporting Frequency: Financial accounting reports are typically prepared annually or quarterly. Managerial accounting reports can be generated as frequently as needed, depending on the organization's requirements.
The Most Associated Aspects: A Deeper Dive
Given the multifaceted nature of managerial accounting, pinpointing the single most associated aspect is challenging. However, several consistently stand out as central to its function:
1. Cost Accounting: This is arguably the most fundamental aspect. Understanding costs—both fixed and variable—is essential for virtually all aspects of managerial accounting. Cost accounting involves:
-
Cost Classification: Categorizing costs by behavior (fixed, variable, mixed), function (manufacturing, selling, administrative), and traceability (direct, indirect).
-
Cost Allocation: Distributing indirect costs (e.g., overhead) to various products or departments based on a chosen allocation base.
-
Cost Estimation and Prediction: Using various techniques (e.g., regression analysis) to estimate and predict future costs.
2. Performance Measurement: Measuring and evaluating performance is crucial for improving efficiency and profitability. This goes beyond simply tracking financial metrics; it encompasses:
-
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Establishing and monitoring KPIs that are aligned with the organization's strategic goals.
-
Balanced Scorecard: A comprehensive performance measurement system that considers financial, customer, internal processes, and learning & growth perspectives.
-
Benchmarking: Comparing performance against industry best practices to identify areas for improvement.
3. Decision Support: Managerial accounting provides data-driven insights to support a wide range of decisions, including:
-
Pricing Strategies: Determining optimal pricing strategies that maximize profitability while considering competition and market demand.
-
Capital Investment Decisions: Evaluating the financial viability of long-term investments in assets.
-
Product Mix Decisions: Determining the optimal mix of products to produce to maximize profits, considering resource constraints.
Conclusion: A Holistic Approach
While cost accounting, performance measurement, and decision support are strongly associated with managerial accounting, it's important to view these aspects holistically. They are interconnected and work together to provide a complete picture of the organization's financial health and operational effectiveness. The ultimate goal of managerial accounting is to empower managers with the information they need to make informed decisions that drive profitability and achieve organizational success. The flexibility and adaptability of managerial accounting techniques allow for tailored solutions to fit the unique circumstances of each organization, making it an indispensable tool for modern business operations. Its ability to provide actionable insights, predict future trends, and optimize resource allocation places it at the heart of effective management and strategic planning in any industry.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Area Underneath The Nail Tip Is Called The
Mar 22, 2025
-
John Received An Email About A Potential Shutdown
Mar 22, 2025
-
When Lifting Pallets Of Ae Using A Forklift
Mar 22, 2025
-
In Broad Terms What Is The Definition Of Social Deviance
Mar 22, 2025
-
If A Food Contact Surface Is In Constant Use
Mar 22, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of The Following Is Most Associated With Managerial Accounting . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
