Which Of The Following Is True Of A Qualified Plan
Breaking News Today
Mar 15, 2025 · 6 min read
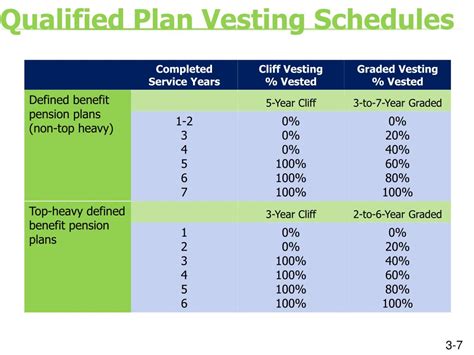
Table of Contents
Which of the Following is True of a Qualified Plan? A Deep Dive into Retirement Savings
Choosing the right retirement plan is a crucial decision impacting your financial future. Understanding the nuances of qualified retirement plans is essential for maximizing your savings and minimizing tax liabilities. This comprehensive guide will explore the characteristics of qualified plans, comparing them to non-qualified plans and clarifying common misconceptions. We'll delve into the intricacies of eligibility, contribution limits, tax advantages, and potential penalties, equipping you with the knowledge to make informed choices.
What is a Qualified Retirement Plan?
A qualified retirement plan is a retirement savings plan that meets specific requirements set by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS). These requirements ensure the plan offers significant tax advantages to both the employer and the employee. The primary advantage lies in the tax-deferred growth of investments within the plan. This means that you don't pay taxes on the earnings until you withdraw them in retirement. This contrasts sharply with non-qualified plans where investment earnings are taxed annually.
Several types of qualified plans exist, each catering to different needs and employer structures. We'll explore some of the most common types below.
Types of Qualified Retirement Plans
Several types of qualified plans cater to diverse needs and organizational structures. Let's examine some of the most prominent:
1. 401(k) Plans
401(k) plans are perhaps the most well-known qualified retirement plan. Offered by many employers, these plans allow employees to contribute a portion of their pre-tax salary. Employers may also match a percentage of employee contributions, effectively boosting savings. The contributions are tax-deductible, reducing your current taxable income. Growth on investments is tax-deferred, meaning you only pay taxes upon withdrawal during retirement. There are often limitations on early withdrawals, designed to encourage long-term savings. Vesting schedules determine when you own the employer's matching contributions – this timeline varies between plans.
2. 403(b) Plans
403(b) plans are similar to 401(k) plans but are specifically designed for employees of public schools, non-profit organizations, and certain tax-exempt organizations. The contribution limits and tax advantages are generally comparable to 401(k) plans. However, the investment options might be more limited, often focusing on annuities and mutual funds.
4. Traditional IRA (Individual Retirement Account)
A Traditional IRA is a qualified retirement plan available to individuals, regardless of employment status. Contributions are tax-deductible, similar to 401(k) and 403(b) plans. Investment earnings grow tax-deferred until retirement. Income limits may affect the deductibility of contributions.
5. Roth IRA
Unlike Traditional IRAs, Roth IRAs involve contributions made with after-tax dollars. The key advantage is that withdrawals in retirement are tax-free. This contrasts with Traditional IRAs where withdrawals are taxed in retirement. Income limits may restrict eligibility for full contributions.
6. SEP IRA (Simplified Employee Pension Plan)
SEP IRAs are designed for self-employed individuals and small business owners. Contributions are made directly into a traditional IRA set up for the business owner. The contribution limit is a percentage of net self-employment income, allowing for significant tax-deductible contributions.
7. SIMPLE IRA (Savings Incentive Match Plan for Employees)
SIMPLE IRAs are straightforward plans for small businesses with fewer than 100 employees. They offer a combination of employee contributions and employer matching contributions, resulting in a potentially substantial retirement nest egg.
Key Characteristics of Qualified Plans
Several defining characteristics distinguish qualified plans from their non-qualified counterparts:
1. Tax Advantages
The most significant advantage is the tax-deferred growth of investments. This means you don't pay income taxes on investment earnings until you withdraw them in retirement. This can significantly boost your retirement savings over time, due to the compounding effect of tax-free growth. Moreover, contributions are often tax-deductible, lowering your current taxable income.
2. Eligibility Requirements
Qualified plans have eligibility requirements, ensuring a fair distribution of benefits within the workforce. These often include factors like age, years of service, and employment status.
3. Contribution Limits
The IRS sets annual contribution limits for most qualified plans. These limits help ensure plan solvency and prevent abuse of tax benefits. Exceeding these limits can lead to penalties. Contribution limits also vary based on the plan type, age, and individual income.
4. Vesting
Vesting refers to the ownership of employer contributions to the plan. Vesting schedules dictate when an employee gains full ownership of employer contributions. This is a crucial aspect to consider, particularly when changing employers.
5. Withdrawal Restrictions
Qualified plans typically impose restrictions on early withdrawals. Withdrawing funds before retirement (generally age 59 1/2) usually incurs penalties, discouraging premature access to retirement funds. Exceptions exist for specific circumstances like financial hardship.
6. IRS Regulations
Qualified plans are meticulously governed by the IRS. They must comply with stringent regulations, ensuring proper administration, record-keeping, and distribution of benefits. Non-compliance can lead to substantial penalties for both the employer and the employee.
Qualified Plans vs. Non-Qualified Plans
Understanding the differences between qualified and non-qualified plans is critical for making informed retirement planning decisions:
| Feature | Qualified Plan | Non-Qualified Plan |
|---|---|---|
| Tax Advantages | Tax-deferred growth, tax-deductible contributions | Taxable annually on earnings |
| Regulations | Stringently regulated by the IRS | Fewer regulatory requirements |
| Contribution Limits | Subject to annual limits set by the IRS | Typically no contribution limits |
| Withdrawal Restrictions | Restrictions on early withdrawals | More flexible withdrawal options |
| Employer Matching | Often includes employer matching contributions | Usually does not include employer matching |
Common Misconceptions about Qualified Plans
Several misconceptions surrounding qualified plans can hinder effective retirement planning:
1. "I don't need a qualified plan if I'm young."
Starting early is crucial, leveraging the power of compounding. Even small contributions made early can snowball into substantial savings over time.
2. "My employer's matching contribution isn't worth it."
Employer matching contributions are essentially free money. Contributing enough to receive the full match significantly boosts your retirement savings potential.
3. "I can easily withdraw from my qualified plan if needed."
Early withdrawals come with significant tax penalties and may impact the long-term growth of your retirement savings.
Conclusion: Making Informed Choices for a Secure Retirement
Choosing the right qualified plan is a crucial aspect of securing your financial future. Understanding the various options – 401(k)s, 403(b)s, IRAs, and others – and their respective characteristics is vital. Consider factors like your employment status, income level, risk tolerance, and long-term financial goals. It's advisable to consult with a qualified financial advisor for personalized guidance, tailoring your retirement plan to your unique circumstances. Remember to diligently monitor your plan's performance and make adjustments as necessary to stay on track toward achieving your retirement objectives. Careful planning now will significantly contribute to a more comfortable and secure retirement later.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
World History Sem A Unit 1 Post Test Ofy
Mar 15, 2025
-
Anything That Interferes With A Message And Is Usually Temporary
Mar 15, 2025
-
If Your Truck Or Bus Has Dual Parking Control Valves
Mar 15, 2025
-
Correctly Label The Anterior Muscles Of The Thigh
Mar 15, 2025
-
The Great Depression And New Deal Unit Test
Mar 15, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of The Following Is True Of A Qualified Plan . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
