Which Of The Following Options Indicates A Non-random Pattern
Breaking News Today
Mar 22, 2025 · 6 min read
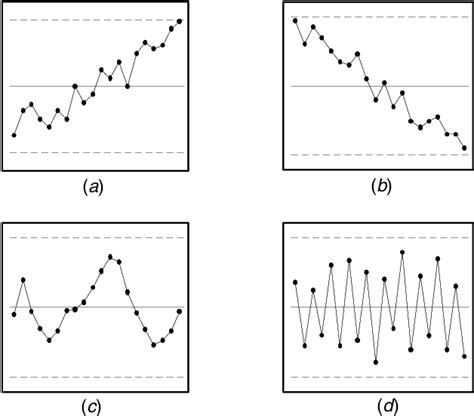
Table of Contents
Which of the Following Options Indicates a Non-Random Pattern?
Identifying non-random patterns within data is crucial across numerous fields, from scientific research and financial markets to cryptography and epidemiology. Understanding how to distinguish random noise from meaningful structure is key to drawing accurate conclusions and making informed decisions. This article delves into the characteristics of non-random patterns, exploring various methods and examples to help you determine which option displays a non-random sequence.
What Constitutes a Random Pattern?
Before we dissect non-randomness, let's define its opposite: randomness. A truly random pattern exhibits no discernible order or predictability. Key characteristics include:
-
Uniform Distribution: In a random sequence of numbers, each number (or range of numbers) has an equal probability of appearing. For example, in a fair coin toss, heads and tails should each appear approximately 50% of the time over many trials.
-
Independence: Each event in the sequence is independent of the others. The outcome of one event doesn't influence the outcome of subsequent events. Consider a roulette wheel; the result of one spin has no bearing on the next.
-
Lack of Predictability: It's impossible to accurately predict the next element in a truly random sequence based on preceding elements.
Identifying Non-Random Patterns: Key Indicators
Several indicators strongly suggest a non-random pattern in a sequence of data. These indicators often work in conjunction, reinforcing the likelihood of non-randomness.
1. Recurring Sequences or Motifs:
The presence of recurring sequences or motifs within a dataset is a significant sign of non-randomness. This could involve:
- Simple Repeats: Obvious repetition of the same element or short sequence (e.g., ABABABAB).
- Periodic Patterns: Sequences that repeat at regular intervals (e.g., ABCABCABC).
- Near Repeats: Sequences that are almost identical but with slight variations. These might require more sophisticated analysis to detect.
Example: The sequence "1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 1, 3, 5, 7, 9..." clearly exhibits a non-random pattern due to the repeating sequence "1, 3, 5, 7, 9".
2. Autocorrelation and Serial Correlation:
Autocorrelation measures the correlation between a variable and its lagged values. High autocorrelation indicates that values closer together in time (or space) are more similar than values further apart, signifying a non-random pattern. This is often visualized using correlograms.
Example: Stock prices often exhibit autocorrelation. A high price today might suggest a slightly higher price tomorrow, breaking the random walk hypothesis.
3. Trends and Cycles:
Trends represent a consistent upward or downward movement in the data over time. Cycles involve periodic fluctuations around a mean value. Both trends and cycles deviate significantly from randomness, indicating underlying systematic factors at play.
Example: Global temperature data shows a clear upward trend over the past century, indicating a non-random warming pattern.
4. Clustering and Outliers:
Clustering refers to the concentration of data points in specific regions of the dataset. Outliers, on the other hand, are data points that fall significantly outside the expected range. Both can suggest a non-random distribution.
Example: In a scatter plot of income versus education level, we might observe clustering of high earners with high education levels and outliers representing individuals who achieved high income despite limited formal education.
5. Statistical Tests for Randomness:
Various statistical tests can quantitatively assess the randomness of a data sequence. These tests often focus on aspects like:
-
Runs Test: This test checks for the number of runs (sequences of identical outcomes) in a binary sequence. Too few or too many runs suggest non-randomness.
-
Chi-Square Test: This test compares the observed frequencies of different outcomes to the expected frequencies under a random distribution. Significant deviations indicate non-randomness.
-
Autocorrelation Tests: These tests measure the correlation between a variable and its lagged values, as mentioned earlier.
-
Spectral Analysis: This technique is used to identify periodicities or cyclical patterns in a time series, which would indicate non-random behavior.
Using these tests provides a more rigorous and objective way to confirm suspected non-randomness. The choice of test depends on the nature and type of data being analyzed.
Practical Applications: Identifying Non-Randomness in Different Contexts
Identifying non-random patterns is crucial across diverse fields:
1. Financial Markets:
Analyzing stock prices, trading volumes, and other financial data for non-random patterns is vital for investors and traders. Identifying trends, cycles, or recurring patterns can help inform investment strategies. However, the efficiency of financial markets means that truly predictable patterns are rare and short-lived.
2. Cryptography:
Random number generators are crucial for cryptography. Non-random patterns in cryptographic keys severely compromise security, making them vulnerable to attacks. Rigorous testing for randomness is therefore essential.
3. Scientific Research:
Identifying non-random patterns in experimental data allows researchers to draw meaningful conclusions about cause-and-effect relationships and to develop scientific models that accurately reflect the underlying processes.
4. Epidemiology:
Analyzing the spatial and temporal distribution of disease outbreaks allows epidemiologists to identify clusters of cases, potentially pinpoint sources of infection, and predict future outbreaks. Non-random spatial clustering may reveal environmental factors contributing to disease transmission.
5. Bioinformatics:
In bioinformatics, non-random patterns in DNA sequences and protein structures can help scientists understand biological functions and evolution. Identifying motifs and repetitive sequences helps in understanding gene regulation and protein folding.
Differentiating Between Random Fluctuation and True Non-Randomness: The Importance of Sample Size and Context
It's crucial to remember that random data can still exhibit apparent patterns, especially with small sample sizes. What appears to be a non-random pattern might simply be random fluctuation. Therefore, it’s critical to:
-
Consider the sample size: With larger datasets, random fluctuations tend to average out, making it easier to discern true non-random patterns.
-
Understand the context: The meaning of a pattern depends heavily on the context. A seemingly non-random pattern in one situation might be entirely random in another.
-
Employ multiple methods: Combining visual inspection, statistical tests, and domain expertise helps avoid misinterpreting random fluctuations as significant patterns.
Conclusion: The Ongoing Quest for Pattern Recognition
The ability to distinguish between random and non-random patterns remains a critical skill across many disciplines. While intuitive observation can sometimes suffice, rigorous statistical analysis and a deep understanding of the underlying processes are often necessary for accurate conclusions. By combining visual inspection, statistical tests, and domain expertise, we can effectively identify and interpret non-random patterns, leading to informed decisions and significant breakthroughs in various fields. Remember that the interpretation of patterns should always be supported by robust evidence and a thoughtful consideration of the context. The quest for pattern recognition is an ongoing and evolving process, constantly refined by advancements in computational power and statistical methods.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
1967 Supreme Court Case Loving V Virginia Quizlet
Mar 24, 2025
-
What Is The Difference Between Race And Ethnicity Quizlet
Mar 24, 2025
-
What Is A Bonds Current Yield Quizlet
Mar 24, 2025
-
Orthostatic Hypotension May Be A Manifestation Of Quizlet
Mar 24, 2025
-
Ati Med Surg Proctored Exam 2023 Retake Quizlet
Mar 24, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of The Following Options Indicates A Non-random Pattern . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
