Which Of These Is An Ergonomic Guideline To Technology Use
Breaking News Today
Mar 16, 2025 · 6 min read
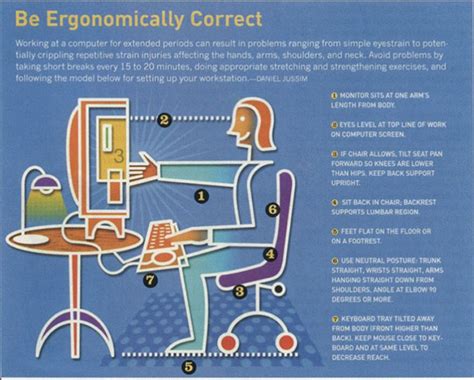
Table of Contents
Which of These is an Ergonomic Guideline to Technology Use? A Comprehensive Guide
The modern workplace, and indeed modern life, is inextricably linked to technology. From smartphones and laptops to large monitors and ergonomic keyboards, technology pervades our daily routines. However, prolonged and improper use can lead to a range of musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs), including carpal tunnel syndrome, eye strain, neck pain, and back problems. Understanding and implementing ergonomic guidelines is crucial for preventing these issues and maintaining both productivity and well-being. This comprehensive guide explores various ergonomic principles related to technology use and helps you identify which practices promote healthy technology habits.
Understanding Ergonomics and Its Importance in Technology Use
Ergonomics, also known as human factors, is the scientific study of designing workplaces, products, and systems to fit the people who use them. The goal is to create an environment that minimizes physical strain, promotes comfort, and enhances productivity. In the context of technology use, this means arranging your workspace, selecting appropriate equipment, and adapting your work habits to prevent discomfort and injury.
The Cost of Poor Ergonomics
Ignoring ergonomic principles can have significant consequences:
- Physical discomfort and pain: This can range from mild aches and pains to chronic conditions like carpal tunnel syndrome and tendonitis.
- Reduced productivity: Discomfort and pain can significantly impact concentration and efficiency.
- Increased absenteeism: MSDs often require time off work for recovery and treatment.
- Higher healthcare costs: Treating MSDs can be expensive, both for individuals and employers.
- Lower employee morale: Chronic pain and discomfort contribute to stress and reduced job satisfaction.
Key Ergonomic Guidelines for Technology Use
Adopting an ergonomic approach to technology use involves a multifaceted strategy encompassing posture, equipment selection, workspace arrangement, and work habits.
1. Posture: The Foundation of Ergonomic Technology Use
Maintaining proper posture is paramount. Poor posture puts undue stress on your muscles and joints, leading to pain and discomfort.
- Sitting Posture: Aim for a neutral spine posture with your back straight, shoulders relaxed, and hips slightly higher than your knees. Use a chair with lumbar support to maintain the natural curve of your lower back. Avoid slumping or hunching.
- Standing Posture: If you use a standing desk, ensure your feet are flat on the floor, your knees are slightly bent, and your weight is evenly distributed. Consider using an anti-fatigue mat to provide cushioning and support.
- Head and Neck Position: Keep your head aligned with your torso, avoiding tilting or craning your neck to look at the screen. The top of your monitor should be roughly at eye level.
2. Equipment Selection: Choosing the Right Tools
The equipment you use significantly impacts your comfort and well-being. Consider the following:
- Chair: Invest in an ergonomic chair with adjustable height, lumbar support, and armrests. The chair should provide adequate support and allow for proper posture.
- Monitor: Position your monitor at arm's length and slightly below eye level to prevent neck strain. Use a larger monitor to reduce the need for excessive scrolling and zooming. Consider a monitor arm for optimal positioning.
- Keyboard and Mouse: Choose a keyboard and mouse that fit your hand size and allow for a neutral wrist position. Consider ergonomic keyboards that promote a more natural wrist angle. Use a trackball or vertical mouse to reduce wrist strain.
- Laptop Stands: If using a laptop, elevate it to bring the screen to eye level using a laptop stand. This prevents hunching and neck strain. Use an external keyboard and mouse for better ergonomics.
3. Workspace Arrangement: Optimizing Your Environment
A well-organized workspace minimizes strain and promotes efficiency.
- Monitor Placement: Position your monitor directly in front of you, at arm's length, and slightly below eye level. Avoid placing it too close or too far away.
- Keyboard and Mouse Placement: Keep your keyboard and mouse within easy reach, allowing your elbows to be bent at a 90-degree angle.
- Document Placement: Place documents at the same height as your monitor to minimize neck strain when switching between the screen and documents.
- Lighting: Ensure adequate lighting to minimize eye strain. Avoid glare from windows or overhead lights by adjusting blinds or using a monitor hood.
- Cable Management: Keep cables organized to prevent tripping hazards and clutter.
4. Work Habits: Developing Healthy Practices
Good work habits are essential for maintaining comfort and preventing injury.
- Regular Breaks: Take short breaks every 30-60 minutes to stretch and move around. This helps to prevent stiffness and fatigue. The 20-20-20 rule (every 20 minutes, look at something 20 feet away for 20 seconds) is helpful for eye strain.
- Proper Lifting Techniques: If you need to lift heavy objects, use proper lifting techniques to avoid back strain. Bend your knees, keep your back straight, and lift with your legs.
- Microbreaks: Incorporate microbreaks throughout the day. Even a few seconds of stretching can make a significant difference.
- Exercise: Regular exercise helps to strengthen your muscles and improve your posture.
- Hydration and Nutrition: Staying hydrated and maintaining a healthy diet also contributes to overall health and well-being.
5. Addressing Specific Technology-Related Issues
Certain technology-related activities require specific ergonomic considerations:
- Smartphone Use: Avoid hunching over your smartphone. Hold it at eye level or use a stand. Take frequent breaks.
- Tablet Use: Similar to smartphones, use a stand or case to avoid awkward postures.
- Gaming: Ensure proper posture and take frequent breaks during extended gaming sessions.
Identifying Ergonomic Guidelines: A Checklist
Let’s revisit the question: Which of these is an ergonomic guideline to technology use? The answer isn't a single item but rather a collection of best practices. Consider the following checklist:
Good Ergonomic Practices (Check if you do these):
- [ ] Proper posture: Maintaining a neutral spine, avoiding slouching or hunching.
- [ ] Adjustable chair: Using a chair with adjustable height, lumbar support, and armrests.
- [ ] Monitor at eye level: Positioning the top of the monitor at or slightly below eye level.
- [ ] Keyboard and mouse within reach: Keeping elbows bent at approximately 90 degrees.
- [ ] Regular breaks: Taking short breaks every 30-60 minutes to stretch and move around.
- [ ] Adequate lighting: Ensuring sufficient lighting to prevent eye strain.
- [ ] Organized workspace: Maintaining a clutter-free and organized workspace.
- [ ] Use of ergonomic equipment: Utilizing ergonomic keyboards, mice, and other peripherals.
- [ ] Document placement at monitor level: Avoiding neck strain by keeping documents at the same height as your monitor.
Poor Ergonomic Practices (Uncheck if you do these):
- [ ] Slouching or hunching: Maintaining poor posture while using technology.
- [ ] Using an unsuitable chair: Using a chair without adequate support.
- [ ] Monitor positioned too high or too low: Causing neck strain.
- [ ] Reaching for the keyboard or mouse: Leading to strain on your shoulders and arms.
- [ ] Ignoring breaks: Working continuously without breaks.
- [ ] Poor lighting: Working in poorly lit conditions.
- [ ] Cluttered workspace: Having a disorganized and cluttered workspace.
- [ ] Using non-ergonomic equipment: Using standard keyboards and mice without considering ergonomics.
By checking the good practices and unchecking the poor ones, you can quickly assess your current ergonomic setup and identify areas for improvement.
Conclusion: Investing in Your Well-being
Implementing ergonomic guidelines for technology use isn't just about comfort; it's an investment in your long-term health and well-being. By adopting these principles, you can significantly reduce your risk of developing MSDs, increase your productivity, and maintain a higher quality of life. Remember that ergonomic solutions are personalized; what works for one person might not work for another. Experiment and find what best suits your needs and preferences. Don't hesitate to consult with an occupational therapist or ergonomist for personalized recommendations if you experience persistent discomfort or pain. Prioritizing ergonomics is a crucial step in creating a healthy and sustainable relationship with technology.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Unit 5 Progress Check Mcq Ap Lit
Mar 16, 2025
-
Hoses And Hose Connections Should Be Able To Withstand
Mar 16, 2025
-
Assigning Manufacturing Overhead To Product Is Complicated Because
Mar 16, 2025
-
What Is The Coordinating Mechanism In A Market System
Mar 16, 2025
-
The Philosophy Of Community Policing Is Based On Two Perspectives
Mar 16, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of These Is An Ergonomic Guideline To Technology Use . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
