Which Property Would Cesium Most Likely Have
Breaking News Today
Mar 15, 2025 · 6 min read
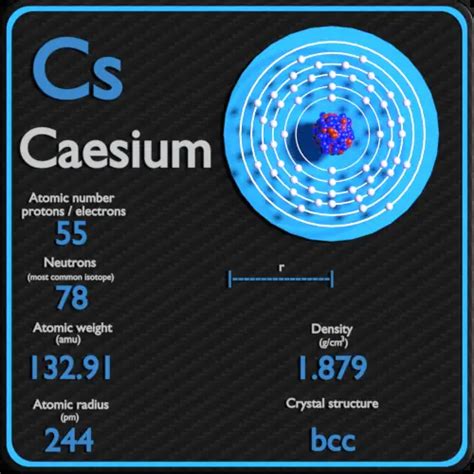
Table of Contents
Which Properties Would Cesium Most Likely Have? Predicting the Behavior of an Alkali Metal
Cesium (Cs), a fascinating element residing in Group 1 of the periodic table, is an alkali metal renowned for its unique properties. Understanding its behavior requires examining its electronic structure and position within the periodic trends. This article delves into the predictable properties of cesium, exploring its physical characteristics, chemical reactivity, and potential applications, all within the context of its position in the periodic table.
Predicting Cesium's Properties Based on Periodic Trends
Cesium's properties are largely predictable based on its position as the heaviest stable alkali metal. The periodic table organizes elements based on their atomic structure, revealing recurring trends in properties. These trends allow us to anticipate the characteristics of cesium based on the behavior of its lighter alkali metal counterparts: lithium (Li), sodium (Na), potassium (K), rubidium (Rb).
1. Atomic Radius and Density:
-
Large Atomic Radius: Moving down Group 1, the atomic radius increases due to the addition of electron shells. Cesium possesses the largest atomic radius among stable alkali metals. This is a direct consequence of its increased number of electron shells and the shielding effect of inner electrons, which reduces the effective nuclear charge experienced by the outermost electron.
-
Low Density: While cesium has a relatively high atomic mass, its large atomic radius results in a surprisingly low density. The loosely packed atoms mean there is more space between atoms, compared to the more tightly packed atoms of heavier metals in other groups. This low density makes cesium one of the least dense metals.
2. Ionization Energy and Electronegativity:
-
Low Ionization Energy: Alkali metals readily lose one electron to achieve a stable noble gas configuration. Cesium, with its outermost electron farthest from the nucleus, exhibits the lowest ionization energy among all the elements, meaning it requires the least amount of energy to remove its valence electron. This makes cesium exceptionally reactive.
-
Low Electronegativity: Cesium has a very low electronegativity, meaning it has a low tendency to attract electrons towards itself in a chemical bond. This is consistent with its tendency to lose an electron rather than gain one.
3. Melting and Boiling Points:
- Low Melting and Boiling Points: Alkali metals generally possess relatively low melting and boiling points compared to other metals. This is due to the weak metallic bonding between the atoms. The weak bonding in cesium leads to it having a relatively low melting point (28.44 °C) and boiling point (671 °C) compared to other metals.
4. Chemical Reactivity:
-
High Reactivity: Cesium's low ionization energy and electronegativity translate to exceptionally high chemical reactivity. It readily reacts with air and water, even more vigorously than other alkali metals. The reaction with water is highly exothermic, producing hydrogen gas and a significant amount of heat. The reaction with air leads to the formation of cesium oxide and other oxides.
-
Reaction with Nonmetals: Cesium readily reacts with halogens, forming ionic compounds such as cesium fluoride (CsF), cesium chloride (CsCl), cesium bromide (CsBr), and cesium iodide (CsI). Similar reactions are observed with other nonmetals like sulfur, phosphorus, and oxygen.
5. Physical Appearance and Properties:
-
Silvery-Gold Appearance: Cesium is a silvery-gold, soft metal. Its softness is a direct consequence of its weak metallic bonding.
-
Conductivity: Like other alkali metals, cesium is a good conductor of heat and electricity, owing to its loosely held valence electron that can move freely within the metallic lattice.
Specific Properties and Applications of Cesium
The unique properties of cesium give rise to its various applications in different fields:
1. Atomic Clocks:
Cesium's precise atomic transitions have revolutionized timekeeping. Cesium atomic clocks utilize the hyperfine transition frequency of the cesium-133 isotope to define the second. The incredibly consistent frequency of this transition makes cesium atomic clocks the most accurate timekeeping devices available, essential for navigation, communication, and scientific research.
2. Oil and Gas Exploration:
Cesium formate is used in drilling fluids for oil and gas exploration. Its properties make it effective in increasing the density of drilling fluids, enhancing well control and maintaining borehole stability.
3. Medical Imaging:
Radioactive cesium isotopes are used in certain medical imaging techniques, providing valuable diagnostic information. However, their use is carefully controlled due to the inherent radioactivity.
4. Scientific Research:
Cesium's unique properties make it a vital element in various scientific research endeavors, including:
-
Spectroscopy: Cesium's readily excitable electrons enable its use in various spectroscopic applications.
-
Ion Propulsion: Cesium is used as a propellant in some ion thrusters, providing efficient propulsion for spacecraft.
-
Photoelectric Cells: Cesium's low work function (the minimum energy required to remove an electron from the surface) makes it suitable for photoelectric cells, which convert light energy into electrical energy.
Safety Considerations When Handling Cesium
Cesium's high reactivity demands careful handling and safety protocols. Direct contact with air or water causes vigorous reactions, posing risks of burns and explosions. Proper safety equipment, including gloves, eye protection, and appropriate containment, is essential when working with cesium. Its radioactive isotopes further necessitate additional safety precautions.
Comparison with other Alkali Metals
To better understand cesium's properties, a comparison with its alkali metal counterparts is crucial:
| Property | Lithium (Li) | Sodium (Na) | Potassium (K) | Rubidium (Rb) | Cesium (Cs) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Atomic Radius | Smallest | Largest | |||
| Density | Lowest | ||||
| Ionization Energy | Highest | Lowest | |||
| Electronegativity | Highest | Lowest | |||
| Melting Point | Lowest | ||||
| Boiling Point | Lowest | ||||
| Reactivity | High | High | High | High | Highest |
As evident from the table, cesium's properties represent the extreme values within the alkali metal group, reflecting the consistent trends observed across the periodic table.
Conclusion: A Powerful Element with Unique Characteristics
Cesium, with its extreme properties, stands as a testament to the predictable yet remarkable behavior of elements within the periodic table. Its low ionization energy, large atomic radius, and high reactivity are all consequences of its electronic structure and position in the periodic system. While its reactivity demands careful handling, its unique properties find valuable applications in various fields, particularly in atomic clocks, oil and gas exploration, and scientific research. Understanding cesium's behavior provides valuable insight into the predictable trends that govern the properties of elements and their potential applications. The continued research and development focusing on cesium will undoubtedly uncover even more of its potential uses in the future. The exploration of its properties not only helps us better understand the fundamentals of chemistry but also provides opportunities for technological advancement across various sectors.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Direct Carry Is Used To Transfer A Patient
Mar 18, 2025
-
The Emancipation Proclamation Of January 1 1863 Quizlet
Mar 18, 2025
-
These Cards Will Get You Drunk Quizlet
Mar 18, 2025
-
Did Quizlet Get Rid Of Q Chat
Mar 18, 2025
-
Myasthenia Gravis Is An Autoimmune Disease In Which Quizlet
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Property Would Cesium Most Likely Have . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
