A Disease Influenced By Weather Is Referred To As
Breaking News Today
Mar 16, 2025 · 6 min read
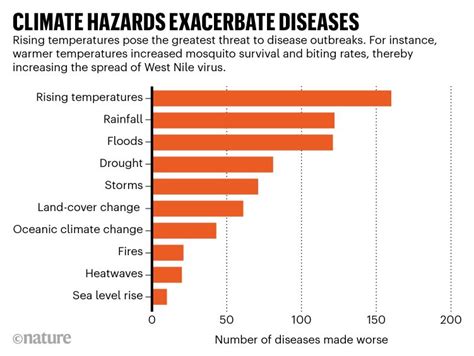
Table of Contents
A Disease Influenced by Weather is Referred to as Weather-Sensitive Disease
Weather plays a significant role in human health, influencing the spread, severity, and even the very existence of numerous diseases. A disease influenced by weather is broadly referred to as a weather-sensitive disease, although more specific terminology might be used depending on the nature of the relationship. Understanding this complex interplay between climate and illness is crucial for public health preparedness, effective disease management, and the development of proactive strategies to mitigate the impact of changing weather patterns.
Understanding the Relationship Between Weather and Disease
The connection between weather and disease is multifaceted and can manifest in several ways:
1. Direct Effects:
-
Temperature: Extreme temperatures, both high and low, can directly impact human health. Heatwaves can lead to heatstroke, dehydration, and cardiovascular complications. Conversely, cold weather can exacerbate respiratory illnesses like asthma and pneumonia, increasing mortality rates, especially among vulnerable populations. The impact of temperature is particularly noticeable in diseases affecting the elderly and those with pre-existing conditions.
-
Humidity: High humidity levels can contribute to the spread of infectious diseases by creating favorable conditions for pathogens to thrive. Mosquito-borne diseases like malaria, dengue fever, and Zika virus are highly sensitive to humidity, with transmission rates increasing in humid environments. Similarly, fungal infections of the skin and respiratory system are more prevalent in humid conditions.
-
Rainfall and Flooding: Heavy rainfall and flooding can create breeding grounds for disease vectors such as mosquitoes and rodents, leading to outbreaks of waterborne illnesses like cholera, typhoid, and leptospirosis. Flooding also disrupts sanitation systems and can contaminate water supplies, increasing the risk of infection. The aftermath of floods often sees a surge in respiratory infections due to mold growth in water-damaged buildings.
-
Wind: Strong winds can spread airborne pathogens over larger distances, increasing the geographical reach of infectious diseases. Wind also plays a role in the dispersal of pollen, exacerbating allergic reactions and respiratory problems in susceptible individuals. Dust storms, often exacerbated by drought, can also contribute to respiratory illnesses.
2. Indirect Effects:
Weather conditions can indirectly influence disease by affecting the environment and human behavior:
-
Air Quality: Weather patterns significantly impact air quality. Heatwaves can trap pollutants near the ground, leading to poor air quality and increased respiratory problems. Wildfires, often triggered by drought and heat, release large amounts of smoke and particulate matter, causing significant respiratory distress and exacerbating existing conditions like asthma and COPD.
-
Vector Abundance and Behavior: Temperature, humidity, and rainfall affect the life cycle, reproduction rate, and distribution of disease vectors such as mosquitoes, ticks, and fleas. Warmer temperatures and increased rainfall can lead to a surge in vector populations, increasing the risk of vector-borne diseases.
-
Changes in Food and Water Supply: Extreme weather events such as droughts and floods can disrupt food and water supplies, leading to malnutrition and increased susceptibility to infectious diseases. This is especially problematic in regions with limited access to healthcare and sanitation.
-
Human Behavior: People's behavior also changes in response to weather. During heatwaves, people might spend more time indoors, potentially increasing the risk of respiratory infections due to poor ventilation. Conversely, during cold spells, people may engage in activities that increase the risk of injuries.
Specific Examples of Weather-Sensitive Diseases
Numerous diseases exhibit a strong relationship with weather patterns. Some notable examples include:
1. Respiratory Diseases:
-
Asthma: Temperature fluctuations, air pollution levels exacerbated by weather conditions, and pollen counts heavily influence asthma attacks. Cold air can constrict airways, while pollutants trapped by atmospheric inversions worsen symptoms.
-
Influenza: Influenza outbreaks often peak during the colder months, partly due to people spending more time indoors in close proximity and the increased survival rate of the influenza virus in cold and dry conditions.
-
Pneumonia: Similar to influenza, pneumonia cases frequently surge during winter due to the decreased immunity and increased susceptibility to infection in cold weather.
2. Vector-Borne Diseases:
-
Malaria: Malaria transmission is highly sensitive to temperature and rainfall. Warmer temperatures accelerate the development of the parasite within mosquitoes, while rainfall creates breeding grounds for mosquito larvae.
-
Dengue Fever: Like malaria, dengue fever transmission is heavily influenced by temperature and rainfall, with outbreaks often following periods of heavy rainfall and warm weather.
-
Lyme Disease: The incidence of Lyme disease is linked to weather conditions that impact the life cycle of blacklegged ticks, the primary vector. Warmer and more humid conditions extend the tick season and increase their activity.
3. Waterborne Diseases:
-
Cholera: Cholera outbreaks are often associated with periods of heavy rainfall and flooding, which contaminate water sources and facilitate the spread of the Vibrio cholerae bacterium.
-
Typhoid Fever: Similar to cholera, typhoid fever transmission is increased after flooding events that contaminate water supplies and sanitation systems.
-
Leptospirosis: Leptospirosis is caused by bacteria found in the urine of infected animals. Flooding often spreads contaminated water, increasing the risk of human infection.
4. Heat-Related Illnesses:
-
Heatstroke: Heatstroke is a serious condition caused by prolonged exposure to high temperatures. It can lead to organ damage and death, particularly among vulnerable populations.
-
Heat exhaustion: A milder form of heat-related illness, heat exhaustion is characterized by symptoms such as headache, dizziness, and weakness.
Predictive Modeling and Public Health Strategies
The growing understanding of the relationship between weather and disease has led to the development of predictive modeling tools. These models use meteorological data and disease surveillance information to forecast potential outbreaks and assess the risk of weather-sensitive diseases. This information allows public health officials to implement proactive measures such as:
-
Early warning systems: These systems provide timely alerts to healthcare providers and the public about potential outbreaks, allowing for early intervention and prevention strategies.
-
Targeted interventions: Based on predictive models, resources can be allocated to areas at high risk, ensuring effective and timely responses.
-
Public health education: Educating the public about the risks associated with weather-sensitive diseases and preventive measures can help individuals protect themselves and their families.
-
Disease surveillance systems: Enhanced surveillance systems can track the spread of diseases in real-time, providing valuable data for predictive models and improving the effectiveness of public health interventions.
-
Infrastructure improvements: Improving sanitation systems and water infrastructure is crucial in reducing the risk of waterborne diseases, especially in areas prone to flooding.
-
Vector control programs: Implementing effective vector control measures, such as mosquito control programs, can significantly reduce the incidence of vector-borne diseases.
Conclusion: The Future of Weather-Sensitive Disease Research
Climate change is expected to exacerbate the impact of weather on human health, increasing the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events and altering the distribution of disease vectors. This necessitates a continuous effort in research, monitoring, and collaboration to:
-
Refine predictive models: Improving the accuracy and sophistication of predictive models is crucial for effective public health planning and resource allocation.
-
Enhance disease surveillance: Strengthening disease surveillance systems is essential for detecting and responding to outbreaks quickly and effectively.
-
Develop innovative interventions: Research into new and innovative interventions, such as vaccines and novel vector control methods, is crucial to combat the challenges posed by weather-sensitive diseases.
-
Promote international collaboration: Climate change and its impact on human health are global challenges requiring international collaboration to address these complex issues effectively.
By understanding the intricate relationship between weather and disease and leveraging advanced technologies, we can build more resilient healthcare systems and reduce the burden of weather-sensitive illnesses on global populations. This requires continued investment in research, strengthening public health infrastructure, and engaging communities to adapt to the challenges of a changing climate. The future of public health depends on our ability to effectively address the dynamic interplay between weather and the health of our populations.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Countless Sparrows Were Twittering In The Eaves Figurative Language
Mar 16, 2025
-
Sister Taxa Are Defined As Those That
Mar 16, 2025
-
Which Of These Is An Ergonomic Guideline To Technology Use
Mar 16, 2025
-
Actions To Take When Capture Is Imminent
Mar 16, 2025
-
The Unit For Sample Standard Deviation Would Be
Mar 16, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about A Disease Influenced By Weather Is Referred To As . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
