According To Freud's Psychosexual Theory Of Personality Quizlet
Breaking News Today
Mar 18, 2025 · 5 min read
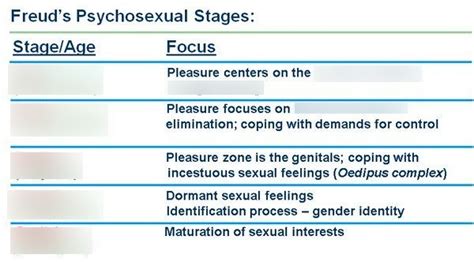
Table of Contents
According to Freud's Psychosexual Theory of Personality: A Comprehensive Guide
Sigmund Freud's psychosexual theory of personality remains one of the most influential, albeit controversial, frameworks in psychology. While modern psychology has moved beyond some of its more specific claims, understanding Freud's ideas is crucial for grasping the historical context of personality theory and appreciating the enduring impact his work has had on our understanding of the human psyche. This in-depth exploration delves into the core tenets of Freud's psychosexual theory, examining each psychosexual stage in detail and addressing common criticisms and contemporary relevance.
The Foundation of Freud's Psychosexual Theory
Freud posited that personality develops through a series of psychosexual stages, each characterized by a specific erogenous zone – a body area that becomes the focus of pleasure-seeking behavior. Successfully navigating each stage is vital for healthy personality development. Failure to resolve the conflict associated with a particular stage can lead to fixation, a lingering focus on that stage's pleasure area, manifesting in specific personality traits in adulthood.
This theory emphasizes the significance of early childhood experiences in shaping adult personality. Freud believed that unconscious drives and conflicts, particularly those related to sexuality and aggression, powerfully influence our thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. These unconscious processes are often manifested through defense mechanisms, strategies employed by the ego to protect itself from anxiety caused by the conflict between the id, ego, and superego.
The Psychosexual Stages: A Detailed Examination
Freud outlined five psychosexual stages:
1. Oral Stage (Birth to 18 months)
The oral stage centers on the mouth as the primary source of pleasure. Infants derive satisfaction from sucking, biting, and chewing. The primary conflict during this stage revolves around weaning, the gradual process of transitioning away from breastfeeding or bottle-feeding.
Oral Fixation: If weaning is too abrupt or traumatic, it can lead to an oral fixation. Adults with oral fixations might exhibit traits such as:
- Oral-receptive personality: Passive, dependent, gullible, and optimistic. They might overeat, smoke, or excessively drink.
- Oral-aggressive personality: Cynical, aggressive, argumentative, and exploitative. They might bite their nails or use sarcasm frequently.
2. Anal Stage (18 months to 3 years)
The anal stage focuses on bowel and bladder control. Toilet training becomes a central issue, representing the child's first encounter with societal demands and expectations.
Anal Fixation: Issues with toilet training can result in anal fixations, manifesting as:
- Anal-retentive personality: Orderly, stingy, stubborn, and perfectionistic. They may hoard possessions and rigidly adhere to routines.
- Anal-expulsive personality: Messy, disorganized, reckless, and defiant. They may be overly generous to a fault and lack self-control.
3. Phallic Stage (3 to 6 years)
The phallic stage is arguably the most controversial aspect of Freud's theory. It centers on the genitals and the Oedipus complex (in boys) and the Electra complex (in girls).
- Oedipus Complex: Boys develop unconscious sexual desires for their mother and feelings of rivalry and jealousy towards their father. Fear of castration by the father (castration anxiety) leads to resolution of the complex through identification with the father.
- Electra Complex: Girls experience penis envy, believing they have been castrated. They develop unconscious sexual desires for their father and rivalry towards their mother. Resolution involves identification with the mother.
Phallic Fixation: Unresolved conflicts in this stage can lead to:
- Excessive masculinity or femininity: Individuals may overcompensate for perceived inadequacies.
- Difficulty forming healthy relationships: Issues with authority figures or intimacy may arise.
4. Latency Stage (6 years to puberty)
During the latency stage, sexual feelings are largely repressed. Children focus on social and intellectual development, engaging in activities with same-sex peers. This stage is relatively calm compared to the preceding stages.
5. Genital Stage (Puberty onwards)
The genital stage marks the resurgence of sexual impulses. Successful navigation of this stage involves establishing healthy intimate relationships and contributing to society. Fixation at earlier stages can hinder the ability to form mature and fulfilling relationships.
Criticisms of Freud's Psychosexual Theory
Despite its influence, Freud's theory has faced significant criticism:
- Lack of empirical evidence: Many aspects of the theory are difficult to test scientifically, relying heavily on case studies and interpretations.
- Overemphasis on sexuality: Critics argue that Freud overemphasized the role of sexual drives in personality development.
- Pessimistic view of human nature: The theory focuses on conflict and repression, neglecting the positive aspects of human development.
- Gender bias: The concepts of penis envy and castration anxiety are considered sexist and outdated.
- Limited generalizability: The theory's development was heavily influenced by Freud's work with a small, specific population, limiting its applicability to diverse populations.
Contemporary Relevance and Legacy
Despite the criticisms, Freud's psychosexual theory holds enduring relevance:
- Influence on subsequent theories: Many subsequent personality theories build upon or react against Freud's ideas.
- Understanding unconscious processes: The concept of the unconscious continues to be a significant area of research in psychology.
- Importance of early childhood experiences: While not the sole determinant, early experiences clearly play a role in personality development.
- Clinical applications: Psychoanalytic therapy, though modified from Freud's original approach, still utilizes some of his core concepts.
Conclusion
Freud's psychosexual theory, while controversial and lacking complete empirical support, has profoundly influenced the field of psychology. Its emphasis on the unconscious, the importance of early childhood experiences, and the concept of psychosexual stages continue to stimulate discussion and research. While contemporary psychology has moved beyond some of its more specific claims, understanding Freud's work provides invaluable insight into the historical context of personality theory and the ongoing quest to understand the complexities of human behavior. By critically evaluating both its strengths and weaknesses, we can appreciate its lasting legacy and its continuing contributions to our understanding of the human psyche. Further research exploring the interaction between biological predispositions, environmental factors, and individual experiences is crucial for developing a more comprehensive and nuanced understanding of personality development. The ongoing dialogue and refinement of personality theories, inspired by Freud's foundational work, ensures that our understanding continues to evolve, creating a richer and more comprehensive view of the human experience.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Kaz Wants To Stop Biting His Nails
Mar 21, 2025
-
Letrs Unit 4 Session 8 Check For Understanding
Mar 21, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is Most Associated With Managerial Accounting
Mar 21, 2025
-
The Planning Steps Of The Planning Control Cycle Are
Mar 21, 2025
-
The Nose Is Located Blank And Blank To The Ears
Mar 21, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about According To Freud's Psychosexual Theory Of Personality Quizlet . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
