Air Braking Takes More Time Than Hydraulic Braking Because Air
Breaking News Today
Mar 19, 2025 · 5 min read
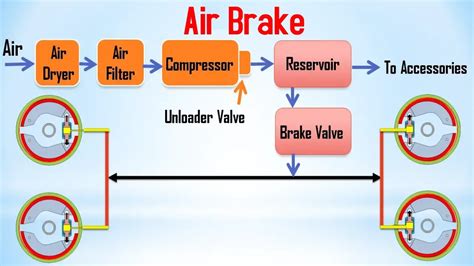
Table of Contents
Air Braking Takes More Time Than Hydraulic Braking Because Air…
Air brakes, while incredibly reliable and powerful, demonstrably take longer to react and fully engage compared to hydraulic braking systems. This difference in response time is a critical factor in vehicle safety, especially in high-speed applications like heavy-duty trucking and train operations. Understanding why air brakes are slower boils down to the fundamental properties of air itself, compared to the near-incompressible nature of hydraulic fluid.
The Physics of Pneumatic vs. Hydraulic Braking
The core difference lies in the compressibility of the mediums used. Hydraulic systems employ incompressible fluids, meaning their volume essentially remains constant under pressure. When the brake pedal is pressed, the pressure change is transmitted almost instantaneously throughout the system, resulting in near-immediate brake pad engagement.
Air, on the other hand, is highly compressible. This compressibility introduces several factors that contribute to the increased response time of air braking systems:
1. Air Compression and Response Time Lag
When the brake pedal is depressed in an air brake system, the compressed air must travel through a network of pipes and valves. Before the pressure reaches the brake chambers, it must compress the air already present within the lines. This compression takes time, resulting in a noticeable delay between pedal application and brake engagement. The longer the air lines, the more pronounced this lag becomes. This delay is magnified in large vehicles with extensive braking systems, such as articulated lorries or long freight trains.
2. The Role of Air Pressure and Volume
The effective braking force is directly proportional to the air pressure in the brake chambers. Building up sufficient pressure requires time, especially in larger systems with larger volumes of air to pressurize. This pressure buildup is not instantaneous; it's a gradual process influenced by the compressor's capacity, the size of the air reservoirs, and the length of the air lines.
Imagine trying to inflate a large balloon quickly – you can't simply fill it instantly. Similarly, filling a network of air lines and brake chambers to the necessary pressure for effective braking takes time.
3. System Leaks and Pressure Loss
Air brake systems are inherently susceptible to leaks. Even small leaks can significantly affect braking performance by reducing the available air pressure. This pressure loss necessitates longer braking distances and increases response time as the system struggles to maintain sufficient pressure to fully engage the brakes. Regular maintenance and leak checks are vital to ensure optimal braking efficiency and safety.
4. Temperature Effects on Air Pressure
Air pressure is highly sensitive to temperature fluctuations. Cold temperatures reduce air pressure, potentially leading to decreased braking power and longer stopping distances. Conversely, extremely high temperatures can increase pressure, but excessive pressure can damage system components. The air brake system must accommodate these temperature variations, introducing another factor influencing response time and overall braking performance.
Comparing Response Times: A Detailed Analysis
Quantifying the exact difference in response times between hydraulic and air brakes is difficult, as it depends on several factors, including:
- System size and complexity: Larger vehicles with more extensive air line networks inherently experience longer response times.
- Air compressor capacity: A more powerful compressor can reduce the time needed to build up sufficient pressure.
- Air reservoir size: Larger reservoirs provide a greater supply of compressed air, leading to faster response times.
- Maintenance status: A well-maintained system with minimal leaks will offer a faster response compared to a neglected system.
- Ambient temperature: Cold weather significantly increases response times due to reduced air pressure.
However, anecdotal evidence and practical experience consistently demonstrate that air brakes exhibit a noticeable delay, typically ranging from 0.2 to 0.5 seconds or even longer compared to hydraulic systems under identical conditions. While this may seem insignificant in isolation, this delay can be crucial in emergency braking scenarios. This lag can translate into several additional feet, or even tens of feet, of braking distance, especially at higher speeds.
Safety Implications of Slower Response Times
The extended response time of air brakes necessitates a more cautious driving style, particularly in situations requiring quick reactions. Heavy vehicle operators must compensate for this inherent lag by maintaining increased following distances and anticipating potential hazards. Driver training and awareness of the system's limitations are crucial for safe operation.
This response time difference also poses significant challenges in:
- Emergency braking situations: The delay can be critical in avoiding accidents, especially in scenarios requiring rapid deceleration.
- Gradient braking: Maintaining speed on steep inclines relies heavily on consistent braking power. The delay in response can make it harder to control speed and increase the risk of runaway situations.
- Adverse weather conditions: Reduced traction in wet or icy conditions necessitates even more cautious braking, and the longer response time of air brakes exacerbates this challenge.
Technological Advancements to Mitigate the Delay
While the fundamental physics of air compressibility can't be altered, several technological advancements aim to minimize the response time delay in air braking systems:
- Improved air compressor designs: More efficient compressors with higher output can reduce the time needed to build up sufficient pressure.
- Optimized air line routing: Shorter, less convoluted air lines reduce the distance the compressed air must travel.
- Advanced valve technology: Faster-acting valves can enhance the speed of air distribution throughout the system.
- Electronic braking systems (EBS): These systems incorporate electronic controls to monitor and adjust braking pressure, resulting in a more responsive and efficient system. EBS often include features such as anti-lock braking (ABS) and electronic stability control (ESC) to further improve safety.
These technological advancements are continuously improving the performance and response time of air braking systems, bringing them closer to the speed and efficiency of hydraulic systems, although the fundamental physical differences will always exist.
Conclusion: Understanding and Managing the Limitations
The increased response time of air brakes compared to hydraulic brakes is an inherent consequence of the compressibility of air. This difference necessitates a heightened awareness among operators of heavy vehicles and other equipment utilizing air braking systems. While technological advancements are constantly improving response times, the fundamental physical properties remain, requiring careful consideration and proactive driving strategies to compensate for this critical difference. Understanding this fundamental limitation is vital for ensuring the safe and effective operation of vehicles equipped with air braking systems. Continuous maintenance, driver training, and the incorporation of newer technological advancements are all crucial factors in maximizing safety and minimizing the inherent limitations of air braking technology.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Double Take Dual Court System Answer Key
Mar 19, 2025
-
What Reasoning Does Machiavelli Use In This Passage
Mar 19, 2025
-
Individuals Considered Members Of The Same Social Category Or Group
Mar 19, 2025
-
The Age Of Exploration Paved The Way For
Mar 19, 2025
-
Assessment Of A Patient With Hypoglycemia Will Most Likely Reveal
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Air Braking Takes More Time Than Hydraulic Braking Because Air . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
