All Vehicles Require The Same Amount Of Stopping Distance.
Breaking News Today
Mar 17, 2025 · 6 min read
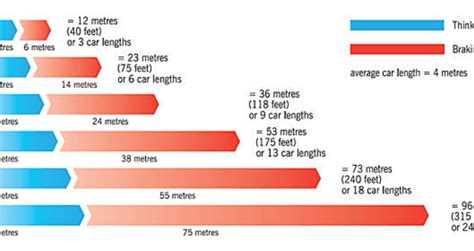
Table of Contents
The Great Myth of Uniform Stopping Distances: Why "All Vehicles Stop the Same" is Dangerously Wrong
The statement "all vehicles require the same amount of stopping distance" is a dangerous misconception. While seemingly simple, this false belief can lead to serious accidents and misunderstandings about road safety. The reality is far more complex, with numerous factors influencing how quickly a vehicle can come to a complete stop. This article will delve into the intricacies of stopping distance, debunking the myth and exploring the critical variables that contribute to safe braking.
Debunking the Myth: Why One Size Doesn't Fit All
The idea that all vehicles stop identically ignores a multitude of variables that significantly affect braking performance. These variables can be broadly categorized into vehicle-specific factors, driver-related factors, and environmental factors. Let's examine each:
Vehicle-Specific Factors: The Heart of the Matter
The most significant differences in stopping distance stem from variations in vehicle design and engineering. These include:
-
Braking System: Different vehicles utilize different braking systems. While most use disc brakes at the front and either disc or drum brakes at the rear, the size, material, and design of these components vary significantly. Larger brake rotors and calipers, for instance, offer superior braking power compared to smaller units. The efficiency of the anti-lock braking system (ABS) also plays a crucial role. ABS prevents wheel lockup, allowing for greater steering control during braking, but its effectiveness depends on its design and maintenance. Advanced systems like electronic stability control (ESC) further enhance braking performance by automatically applying brake pressure to individual wheels to maintain stability.
-
Tire Condition and Type: Tire condition is paramount. Worn tires, with reduced tread depth, offer significantly less grip, extending stopping distances drastically. The type of tire also matters. Summer tires, all-season tires, and winter tires all exhibit different braking characteristics, with winter tires offering superior grip on snow and ice. Tire pressure also plays a crucial role; under-inflated tires deform more under braking, reducing contact patch and braking efficiency.
-
Vehicle Weight and Mass: Heavier vehicles, naturally, require more force to stop. The greater momentum needs to be overcome, resulting in longer stopping distances. This difference is particularly pronounced when comparing a lightweight sports car to a heavy SUV or truck.
-
Aerodynamics: Aerodynamic drag contributes to braking, albeit to a lesser extent than other factors. More aerodynamic vehicles experience less air resistance, allowing for slightly shorter stopping distances, especially at higher speeds.
-
Vehicle Maintenance: Properly maintained vehicles will always stop more reliably and efficiently. Factors like brake fluid condition, brake pad wear, and overall mechanical soundness directly impact stopping performance. Neglecting routine maintenance can lead to significantly extended stopping distances and greatly increase the risk of accidents.
Driver-Related Factors: The Human Element
Driver actions and reactions significantly influence stopping distance. These factors include:
-
Reaction Time: The time it takes for a driver to perceive a hazard, react, and apply the brakes is crucial. This reaction time can vary depending on factors such as alertness, distractions (like using a mobile phone), and impairment (due to alcohol or drugs). Even a small increase in reaction time translates into a significant increase in stopping distance, especially at higher speeds.
-
Braking Technique: The way a driver applies the brakes also impacts stopping distance. Sudden, hard braking can lock the wheels, leading to loss of control and a longer stopping distance. Smooth, controlled braking, ideally utilizing ABS effectively, results in shorter stopping distances.
-
Driver Experience and Skill: Experienced drivers tend to have quicker reaction times and more refined braking techniques, resulting in shorter stopping distances compared to novice drivers.
-
Driver's Physical Condition: Physical limitations, such as impaired vision or reduced reflexes, can negatively impact reaction time and braking performance, leading to longer stopping distances.
Environmental Factors: The External Influences
Environmental conditions play a critical role in determining stopping distance. These include:
-
Road Surface: The condition of the road surface profoundly affects braking performance. Dry asphalt provides the best grip, whereas wet, icy, or snowy roads drastically reduce traction, significantly increasing stopping distances. Loose gravel or debris on the road further compromises traction and extends braking distances.
-
Weather Conditions: Adverse weather like rain, snow, ice, or fog significantly reduces visibility and tire grip, thus lengthening stopping distances. Reduced visibility can also increase reaction time, exacerbating the problem.
-
Grade of the Road: Driving uphill or downhill affects stopping distance. Going downhill increases speed, and gravity further extends the stopping distance. Going uphill slightly reduces stopping distance but does not negate the other factors.
-
Ambient Temperature: Extreme temperatures, both high and low, can affect tire performance and brake fluid efficiency, impacting stopping distance.
Calculating Stopping Distance: A Simplified Model
While a precise calculation requires considering all the variables mentioned above, a simplified model can illustrate the key components:
Total Stopping Distance = Perception Distance + Reaction Distance + Braking Distance
- Perception Distance: The distance the vehicle travels while the driver perceives the need to brake.
- Reaction Distance: The distance traveled from the moment the driver decides to brake until the brakes are actually applied.
- Braking Distance: The distance traveled from the moment the brakes are applied until the vehicle comes to a complete stop.
This simplified model highlights that stopping distance is not solely determined by braking performance but also by the driver's reaction time and perception.
The Importance of Safe Driving Practices
Understanding the complexities of stopping distance underscores the importance of safe driving practices. These include:
-
Maintaining a Safe Following Distance: Leaving ample space between your vehicle and the vehicle in front allows for sufficient time to react and brake safely. The "3-second rule" is a useful guideline.
-
Regular Vehicle Maintenance: Ensuring your vehicle's braking system, tires, and other components are in good working order is critical for safe braking performance.
-
Driving Defensively: Anticipating potential hazards and adjusting your driving accordingly can help prevent accidents and reduce the need for sudden braking.
-
Avoiding Distractions: Minimizing distractions while driving, such as using mobile phones or eating, is crucial for maintaining alertness and quick reaction times.
-
Driving Appropriately for Conditions: Adjusting speed and driving style to account for weather conditions, road surfaces, and traffic density is vital for safe driving.
Conclusion: Beyond the Myth
The myth that all vehicles require the same stopping distance is demonstrably false. Numerous factors, ranging from vehicle design and maintenance to driver behavior and environmental conditions, dramatically impact braking performance. Understanding these factors is essential for promoting road safety and preventing accidents. By embracing safe driving practices and acknowledging the inherent variability in stopping distances, we can significantly reduce the risk of collisions and create safer roads for everyone. Remember, responsible driving is not just about following traffic laws, but about actively mitigating risks and understanding the limitations of your vehicle and yourself. The next time you're on the road, take a moment to consider the many factors that contribute to safe stopping, and drive accordingly.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
High Levels Of Cholesterol Can First Lead Directly To
Mar 18, 2025
-
True Or False Professional And Technical Communication Is Research Oriented
Mar 18, 2025
-
Which Best Describes The Terrorist Planning Cycle
Mar 18, 2025
-
Cdl Combination Test Questions And Answers Pdf
Mar 18, 2025
-
Life Insurance Exam Questions And Answers Pdf
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about All Vehicles Require The Same Amount Of Stopping Distance. . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
