An Interval Of An Ecg Is Quizlet
Breaking News Today
Mar 31, 2025 · 6 min read
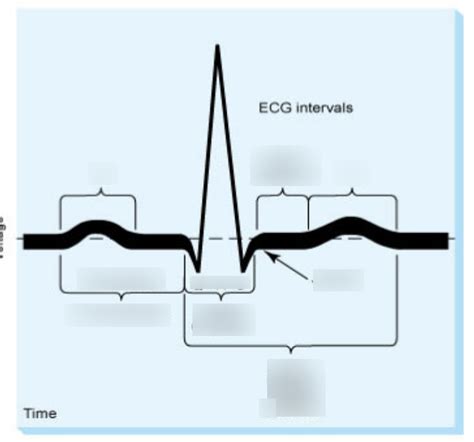
Table of Contents
An Interval of an ECG is Quizlet: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding electrocardiograms (ECGs or EKGs) is crucial for healthcare professionals. This article dives deep into ECG intervals, using a Quizlet-style approach to reinforce learning. We'll cover the key intervals, their significance in diagnosing cardiac conditions, and how to interpret them effectively.
What is an ECG?
An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a simple, non-invasive test that measures the electrical activity of your heart. It records the heart's rhythm and electrical impulses through electrodes placed on the skin. These electrical impulses cause your heart muscle to contract and pump blood. The ECG tracing shows these electrical activities as waves and intervals, providing valuable information about the heart's function.
Key ECG Intervals: A Quizlet-Style Breakdown
We'll explore the crucial ECG intervals using a question-and-answer format reminiscent of Quizlet, making the learning process engaging and memorable.
1. P-wave:
-
Question: What does the P-wave represent on an ECG?
-
Answer: The P-wave represents atrial depolarization. This is the electrical activation of the atria, leading to atrial contraction.
-
Clinical Significance: Changes in P-wave morphology (shape and size) can indicate atrial enlargement (e.g., left atrial enlargement in mitral stenosis) or other atrial abnormalities. Absence of a P-wave suggests atrial fibrillation.
2. PR Interval:
-
Question: Define the PR interval and its normal range.
-
Answer: The PR interval is the time from the beginning of the P-wave to the beginning of the QRS complex. The normal range is typically 0.12 to 0.20 seconds (3-5 small boxes on ECG paper).
-
Clinical Significance: A prolonged PR interval (longer than 0.20 seconds) suggests a first-degree atrioventricular (AV) block, indicating a delay in the conduction of electrical impulses from the atria to the ventricles. A shortened PR interval might indicate a pre-excitation syndrome like Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome.
3. QRS Complex:
-
Question: What does the QRS complex represent? What is its normal duration?
-
Answer: The QRS complex represents ventricular depolarization. This is the electrical activation of the ventricles, leading to ventricular contraction. The normal duration is 0.06 to 0.10 seconds (1.5-2.5 small boxes).
-
Clinical Significance: A widened QRS complex (longer than 0.10 seconds) suggests a delay in ventricular conduction, possibly due to a bundle branch block or other ventricular conduction abnormalities.
4. QT Interval:
-
Question: Explain the QT interval and its clinical importance.
-
Answer: The QT interval is the time from the beginning of the QRS complex to the end of the T-wave. It represents the total time for ventricular depolarization and repolarization. The normal duration varies depending on heart rate but is generally less than 0.44 seconds.
-
Clinical Significance: A prolonged QT interval (QT prolongation) increases the risk of developing torsades de pointes, a life-threatening type of ventricular tachycardia. Several medications and electrolyte imbalances can contribute to QT prolongation. A shortened QT interval is less common and may be associated with certain inherited conditions or hypercalcemia.
5. ST Segment:
-
Question: What is the ST segment, and what does its elevation or depression indicate?
-
Answer: The ST segment is the isoelectric (flat) line between the end of the QRS complex and the beginning of the T-wave. ST-segment elevation typically indicates acute myocardial infarction (heart attack), while ST-segment depression might suggest myocardial ischemia (reduced blood flow to the heart).
-
Clinical Significance: The precise location of ST-segment changes helps pinpoint the affected area of the heart. These changes are crucial for diagnosis and prompt intervention.
6. T-wave:
-
Question: What does the T-wave represent? What can changes in its morphology indicate?
-
Answer: The T-wave represents ventricular repolarization, the recovery phase of the ventricles. Changes in the T-wave's morphology (height, shape, inversion) can indicate various conditions, including electrolyte imbalances (e.g., hyperkalemia), myocardial ischemia, or myocardial infarction.
-
Clinical Significance: T-wave inversions are not always pathological and can sometimes be benign variations. However, their appearance in conjunction with other ECG changes is significant.
7. U-wave:
-
Question: What is a U-wave, and what might its presence signify?
-
Answer: The U-wave is a small, rounded wave that sometimes follows the T-wave. Its exact physiological origin is not fully understood, but it's thought to be related to repolarization of the Purkinje fibers. Prominent U-waves can sometimes be seen in hypokalemia (low potassium) or bradycardia (slow heart rate).
-
Clinical Significance: While often insignificant, prominent or unusual U-waves warrant further investigation to rule out underlying electrolyte disturbances or other cardiac issues.
Interpreting ECG Intervals: A Practical Approach
Analyzing ECG intervals requires careful attention to detail and systematic interpretation. Here's a structured approach:
- Heart Rate: Calculate the heart rate using appropriate methods (e.g., counting R-R intervals).
- Rhythm: Determine the regularity of the rhythm (regular or irregular).
- P-waves: Analyze the morphology, presence, and relationship to QRS complexes.
- PR Interval: Measure the PR interval and check for prolongation or shortening.
- QRS Complex: Measure the duration and assess for widening.
- ST Segment: Evaluate for elevation, depression, or other abnormalities.
- QT Interval: Measure the QT interval and consider the heart rate correction.
- T-waves: Analyze the morphology for any significant changes.
- U-waves: Note the presence, size, and any unusual characteristics.
Correlation with Clinical Findings: It is crucial to correlate ECG findings with the patient's clinical presentation, history, and other diagnostic tests. An ECG alone doesn't provide a complete diagnosis; it serves as a valuable tool in conjunction with other clinical data.
Common ECG Interval Abnormalities and Associated Conditions
This section briefly outlines some common ECG interval abnormalities and their associated conditions:
- Prolonged PR Interval: First-degree AV block, hyperkalemia, certain medications.
- Shortened PR Interval: Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome, junctional rhythms.
- Widened QRS Complex: Bundle branch blocks, ventricular hypertrophy, ventricular conduction delays.
- Prolonged QT Interval: Congenital long QT syndrome, acquired QT prolongation (due to medications or electrolyte imbalances).
- ST-segment Elevation: Acute myocardial infarction (STEMI), pericarditis.
- ST-segment Depression: Myocardial ischemia, angina pectoris.
- Inverted T-waves: Myocardial ischemia, electrolyte imbalances, left ventricular hypertrophy.
Advanced ECG Concepts and Further Learning
Beyond the basic intervals, ECG interpretation involves understanding more advanced concepts such as:
- Axis Deviation: The overall direction of the heart's electrical activity.
- Hypertrophy: Enlargement of the heart chambers.
- Bundle Branch Blocks: Delays or blocks in the conduction pathways within the ventricles.
- Atrial Fibrillation & Flutter: Irregular or rapid atrial rhythms.
- Ventricular Tachycardia & Fibrillation: Life-threatening rapid ventricular rhythms.
To further enhance your knowledge of ECG interpretation, you can explore resources such as:
- ECG textbooks and manuals: Many excellent resources are available for detailed study.
- Online ECG learning platforms: Several websites and apps provide interactive ECG interpretation practice.
- ECG workshops and courses: Hands-on training is highly beneficial.
Conclusion: Mastering ECG Intervals
Understanding ECG intervals is essential for healthcare professionals involved in cardiac care. This article provided a comprehensive overview of key intervals, their clinical significance, and a structured approach to interpretation. Regular practice, coupled with a thorough understanding of cardiac physiology, is crucial for mastering the art of ECG interpretation. Remember, the ECG is a valuable diagnostic tool, but its interpretation must always be considered in conjunction with the patient's overall clinical picture. Continuous learning and refinement of skills are vital for accurate and effective ECG analysis.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Exchange Rate And Purchasing Power Quick Check
Apr 02, 2025
-
Provide An Appropriate Article And Noun For Each Picture
Apr 02, 2025
-
Pablo Y Mercedes Al Aeropuerto En Autobus
Apr 02, 2025
-
The Greek Words Demos And Kratis Together Mean
Apr 02, 2025
-
Essentials Of Radiographic Physics And Imaging Chapter 1
Apr 02, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about An Interval Of An Ecg Is Quizlet . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
