Compare And Contrast Indentured Servanthood And Slavery.
Breaking News Today
Mar 31, 2025 · 5 min read
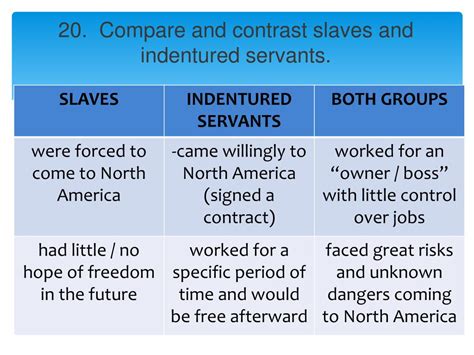
Table of Contents
Indentured Servitude vs. Slavery: A Comparative Analysis
Indentured servitude and slavery, while both involving forms of coerced labor, differ significantly in their origins, legal frameworks, and social implications. Understanding these differences is crucial to comprehending the complex history of forced labor and its lasting impact on societies worldwide. This in-depth analysis will delve into the key distinctions and similarities between these two systems, examining their historical contexts, legal structures, and social consequences.
Defining the Terms: Indentured Servitude and Slavery
Indentured servitude was a system where individuals voluntarily bound themselves to a master for a specified period, typically several years, in exchange for passage to a new land, food, shelter, and sometimes, a small sum of money. Upon completion of their contract, indentured servants were legally free. This system was prevalent in colonial America and other parts of the world during the 17th and 18th centuries.
Slavery, on the other hand, was a system of forced labor based on the ownership of human beings. Slaves were considered property, with no legal rights or protections. They were subject to the absolute control of their owners, who could buy, sell, or punish them at will. This system existed across various cultures and historical periods, with the transatlantic slave trade being a particularly brutal and exploitative example.
Key Differences: A Comparative Overview
The fundamental difference between indentured servitude and slavery lies in the nature of the contract and the legal status of the individual.
1. Contractual Agreement vs. Property Ownership:
- Indentured servitude: Was based on a voluntary (although often coerced by economic circumstances) contract with a defined duration. The servant had a legal expectation of freedom at the end of their term.
- Slavery: Involved the complete subjugation and ownership of an individual, with no expectation of freedom. Slaves were treated as commodities, bought, sold, and inherited like any other form of property.
2. Duration of Service:
- Indentured servitude: Had a specified term, usually lasting several years. This term was clearly defined within the contract.
- Slavery: Was typically lifelong, inheritable through generations, and without a predetermined end. Children born to enslaved mothers were automatically enslaved.
3. Legal Rights and Protections:
- Indentured servitude: While lacking many rights enjoyed by free individuals, indentured servants did possess some legal protections. For example, laws existed to prevent the most egregious forms of abuse. Furthermore, they could appeal to authorities in case of contract violations.
- Slavery: Denied virtually all legal rights and protections. Slaves were considered legally dead, incapable of owning property, testifying in court, or entering into contracts.
4. Social Mobility and Opportunity:
- Indentured servitude: Offered the potential for social mobility and upward economic advancement upon completion of the contract. Many indentured servants were able to acquire land, establish businesses, and build successful lives.
- Slavery: Offered no opportunity for social mobility or economic advancement. Slaves were permanently relegated to the bottom of the social hierarchy.
5. Violence and Brutality:
- Indentured servitude: While certainly subject to abuse and harsh treatment, the level of violence and brutality inflicted upon indentured servants was generally less systematic and extreme than that experienced by enslaved individuals.
- Slavery: Characterized by routine and widespread physical violence, sexual abuse, and psychological torture. The constant threat of violence was inherent in the system.
Similarities: Overlapping Characteristics
Despite their stark differences, indentured servitude and slavery share some important similarities:
1. Coerced Labor:
Both systems involved forms of coerced labor, stripping individuals of their autonomy and forcing them to work against their will. While indentured servants initially agreed to the terms, the circumstances surrounding their decisions often involved limited choices.
2. Economic Exploitation:
Both indentured servitude and slavery were economically exploitative systems, benefitting the masters or owners at the expense of the laborers. The work performed was often arduous, and the compensation (or lack thereof) was grossly disproportionate to the value of the labor provided.
3. Social Hierarchy and Inequality:
Both systems reinforced social hierarchies and inequalities. They created a distinct class of unfree laborers, at the bottom of the social structure, serving the interests of those who held power and wealth.
4. Dehumanization:
While the extent varied, both systems involved elements of dehumanization. Indentured servants were often stripped of their dignity and personhood, while the dehumanization of slaves was far more systematic and brutal.
Historical Contexts and Geographic Variations
The historical contexts of indentured servitude and slavery differed considerably. Indentured servitude was largely a feature of early colonial societies, where a labor shortage was met by offering passage and contract opportunities to European migrants. This contrasts with the transatlantic slave trade, which was driven by the insatiable demand for labor in the plantation economies of the Americas and was intrinsically linked to the racialization of African people. The geographic distribution of these systems also varied significantly; indentured servitude was more widespread in colonial North America, while chattel slavery dominated the Caribbean and Southern United States.
The Legacy of Indentured Servitude and Slavery
Both indentured servitude and slavery left a profound and lasting impact on societies. The legacy of slavery continues to manifest in the persistent racial inequalities, economic disparities, and social injustices experienced by descendants of enslaved people. The legacy of indentured servitude is less visible, yet the experiences of indentured servants significantly shaped early colonial demographics and laid the groundwork for the later development of racial hierarchies. Both systems serve as stark reminders of the human capacity for exploitation and oppression.
Conclusion: Distinguishing Features and Enduring Significance
In conclusion, while both indentured servitude and slavery involved coerced labor and economic exploitation, they differed fundamentally in their legal structures, social implications, and moral character. Indentured servitude, though exploitative, contained elements of contractual agreement and the possibility of eventual freedom, while slavery represented the absolute denial of human rights and the brutal commodification of human beings. Understanding these distinctions is essential for comprehending the complexities of historical oppression and grappling with the continuing consequences of these systems in modern society. The comparison illuminates not only the specific differences between these forms of forced labor but also the broader themes of social inequality, economic exploitation, and the enduring struggle for human rights. The legacies of both systems continue to resonate, shaping social, economic, and political landscapes around the world, serving as potent reminders of the critical need for social justice and equality.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Create A Single Record Form From The Classes Table
Apr 01, 2025
-
Which Finding Would Have Disproved Virchows Hypothesis
Apr 01, 2025
-
Place The Muscle Under The Appropriate Action
Apr 01, 2025
-
True Or False Clients Authenticate Directly Against The Radius Server
Apr 01, 2025
-
The Child Is Unresponsive After You Tap His Shoulder
Apr 01, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Compare And Contrast Indentured Servanthood And Slavery. . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
