Erythropoietin Is Produced By The Kidneys To Quizlet
Breaking News Today
Mar 18, 2025 · 6 min read
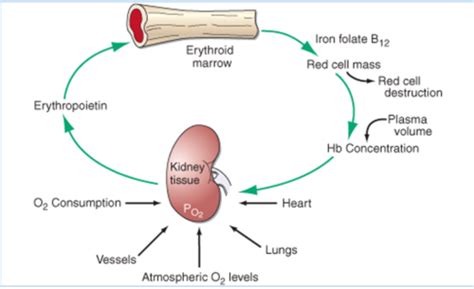
Table of Contents
Erythropoietin: Renal Production and Beyond
Erythropoietin (EPO) is a vital hormone primarily produced by the kidneys, playing a crucial role in regulating red blood cell production. Understanding its production, function, and clinical significance is essential for comprehending various physiological processes and associated pathologies. This comprehensive article delves into the intricate details of erythropoietin production, focusing specifically on its renal origins, its regulation, and its broader implications for health and disease.
The Kidney's Crucial Role in Erythropoietin Production
The kidneys are the primary site of erythropoietin synthesis in adults. While the liver produces EPO during fetal development, its production significantly diminishes after birth, with the kidneys taking over as the major producer. This renal production occurs predominantly in specialized interstitial cells located within the peritubular capillaries of the cortex and outer medulla. These cells, highly sensitive to oxygen levels, are termed peritubular fibroblasts or interstitial fibroblasts. They possess the unique ability to detect changes in oxygen tension (pO2) and respond accordingly by increasing or decreasing EPO synthesis.
The Oxygen-Sensing Mechanism: A Critical Regulatory Step
The process begins with the detection of low oxygen levels (hypoxia) within the kidney. This hypoxia triggers a complex cascade of events leading to increased EPO production. Specifically, hypoxia inhibits the activity of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1), a transcription factor crucial for EPO gene expression. Under normal oxygen levels, HIF-1 is rapidly degraded. However, during hypoxia, HIF-1 stabilizes and translocates to the nucleus, where it binds to specific DNA sequences in the EPO gene promoter region. This binding initiates the transcription and subsequent translation of the EPO gene, resulting in increased EPO synthesis and release into the bloodstream.
Factors Influencing Renal EPO Production
Several factors beyond oxygen tension influence renal EPO production. These include:
- Androgens: Testosterone and other androgens stimulate EPO production, contributing to the higher hematocrit levels observed in males.
- Growth hormone: Growth hormone indirectly stimulates EPO production, possibly through its effects on erythroid progenitor cells.
- Iron levels: Adequate iron stores are crucial for hemoglobin synthesis. Low iron levels can limit EPO's effectiveness, even if EPO production is normal. This highlights the interconnectedness of various factors in maintaining optimal red blood cell production.
- Inflammation: Inflammatory cytokines, such as interleukin-6, can either stimulate or inhibit EPO production, depending on the context and severity of the inflammation. This complex interplay underscores the importance of considering the overall physiological state when assessing EPO levels.
- Kidney disease: Chronic kidney disease (CKD) significantly impairs EPO production, leading to anemia. This is because damaged kidney tissue is less capable of producing EPO, resulting in insufficient stimulation of red blood cell formation. This is a major clinical concern in CKD management.
Erythropoietin's Action: Stimulating Red Blood Cell Production
EPO, once released into the circulation, travels to the bone marrow, the primary site of red blood cell production (erythropoiesis). In the bone marrow, EPO binds to specific receptors (EPO receptors) located on the surface of erythroid progenitor cells (committed precursor cells that will become red blood cells). This binding initiates a signaling cascade leading to increased erythroid progenitor cell proliferation, differentiation, and ultimately, increased red blood cell production.
Erythropoiesis: A Multi-Step Process Enhanced by EPO
Erythropoiesis is a complex and tightly regulated process involving multiple stages of cell division and differentiation. EPO primarily acts on erythroid progenitor cells in the later stages of differentiation, accelerating their maturation into reticulocytes (immature red blood cells) and ultimately, mature erythrocytes (red blood cells). This accelerated maturation significantly increases the number of circulating red blood cells, improving oxygen-carrying capacity.
The Importance of Maintaining Optimal Red Blood Cell Mass
Maintaining an optimal red blood cell mass is critical for delivering sufficient oxygen to tissues throughout the body. This oxygen delivery is essential for cellular respiration, energy production, and overall physiological function. EPO's role in regulating red blood cell production is thus crucial for maintaining tissue oxygenation and overall health. Inadequate EPO production or impaired EPO receptor function can lead to anemia, characterized by a decreased number of red blood cells and reduced oxygen-carrying capacity.
Clinical Significance of Erythropoietin
The clinical significance of erythropoietin extends to various medical conditions and therapeutic applications. Understanding its role in health and disease is essential for effective diagnosis and management.
Anemia of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
As mentioned earlier, CKD is a significant cause of anemia due to impaired renal EPO production. The resulting anemia can lead to fatigue, weakness, and reduced quality of life. Recombinant human erythropoietin (rHuEPO), a synthetic form of EPO, is commonly used to treat anemia in CKD patients, stimulating red blood cell production and improving symptoms.
Anemia in Other Conditions
EPO deficiency or resistance can also contribute to anemia in other conditions, including:
- Anemia of inflammation: Inflammatory diseases can impair EPO production or its effectiveness.
- Cancer-related anemia: Cancer treatment and the cancer itself can suppress red blood cell production.
- Nutritional deficiencies: Deficiencies in iron, vitamin B12, or folate can impact red blood cell formation.
Doping in Sports: An Ethical Concern
EPO's ability to enhance red blood cell production has led to its misuse as a performance-enhancing drug in sports. Increased red blood cell count improves oxygen delivery to muscles, enhancing endurance and performance. However, the use of EPO in sports is strictly prohibited due to its potential health risks, including increased blood viscosity and the risk of blood clots. Detection methods are continuously improving to combat this unethical practice.
Future Directions and Research
Research continues to explore the nuances of EPO production, regulation, and its therapeutic potential. Areas of ongoing investigation include:
- Novel EPO analogs: Development of EPO analogs with improved efficacy and reduced side effects.
- Targeted therapies: Development of therapies that specifically target EPO production or receptor function to treat various anemias.
- Understanding the role of EPO in other physiological processes: EPO's role beyond red blood cell production is becoming increasingly appreciated. Research is exploring its potential effects on other systems, including the cardiovascular and nervous systems.
Conclusion: Erythropoietin - A Cornerstone of Red Blood Cell Regulation
Erythropoietin, primarily produced by the kidneys in response to hypoxia, plays a pivotal role in regulating red blood cell production. Its precise control over erythropoiesis is essential for maintaining adequate tissue oxygenation and overall health. Dysregulation of EPO production or function can lead to various forms of anemia, highlighting its clinical significance. The development of recombinant EPO and ongoing research into its broader physiological roles continues to shape our understanding and management of related conditions. Understanding the intricate processes involved in EPO production and its multifaceted effects underscores its vital contribution to human physiology. Future research promises further advances in diagnosing, treating, and preventing conditions linked to EPO deficiency or dysfunction.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Best Describes The Terrorist Planning Cycle
Mar 18, 2025
-
Cdl Combination Test Questions And Answers Pdf
Mar 18, 2025
-
Life Insurance Exam Questions And Answers Pdf
Mar 18, 2025
-
The Direct Carry Is Used To Transfer A Patient
Mar 18, 2025
-
The Emancipation Proclamation Of January 1 1863 Quizlet
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Erythropoietin Is Produced By The Kidneys To Quizlet . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
