Holds That Our Behavior Is Determined By Internal Factors
Breaking News Today
Mar 17, 2025 · 6 min read
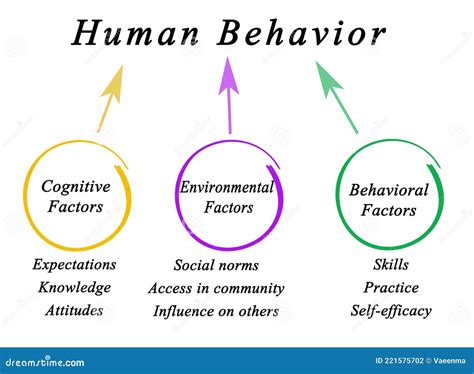
Table of Contents
Internal Factors: The Driving Force Behind Our Actions
The age-old debate of nature versus nurture continues to fascinate and challenge psychologists and philosophers alike. While environmental influences undoubtedly shape our behavior, a compelling argument holds that our actions are primarily determined by internal factors. This perspective, emphasizing the role of genetics, personality, and cognitive processes, provides a rich and nuanced understanding of human behavior. This article delves deep into this perspective, exploring the significant internal factors that drive our actions, examining their complexities, and acknowledging their interplay with external forces.
The Power of Genetics: The Blueprint of Behavior
Our genetic makeup, inherited from our parents, forms the foundational blueprint for our physical and behavioral characteristics. This isn't a deterministic claim suggesting genes dictate every action; rather, genes establish predispositions and probabilities. Genes influence temperament, personality traits, and even susceptibility to certain psychological disorders.
Temperament: The Innate Foundation
Temperament, the inherent behavioral style present from infancy, significantly influences our later behavior. Babies are born with varying temperaments: some are easygoing and adaptable, while others are more irritable and sensitive. These early tendencies, rooted in genetics, shape how we interact with the world and influence the development of our personality. Research consistently demonstrates a strong genetic component in temperament dimensions like reactivity, self-regulation, and sociability.
Personality Traits: A Genetic Underpinning
Personality traits, stable patterns of thinking, feeling, and behaving, also have a substantial genetic basis. Studies utilizing twin and adoption methods have consistently revealed a significant heritability for traits like extraversion, neuroticism, conscientiousness, agreeableness, and openness to experience – the "Big Five" personality factors. While environment plays a role in shaping these traits, genetic factors account for a substantial portion of the variance. This genetic influence manifests in various aspects of our behavior, from our social interactions and career choices to our responses to stress and challenges.
Predispositions to Psychological Disorders: The Genetic Link
Genetic factors play a crucial role in the development of many psychological disorders. While environmental stressors can trigger these disorders, genetic predispositions significantly increase the risk. For example, a family history of depression or anxiety substantially increases an individual's likelihood of developing these conditions. This doesn't mean that having a genetic predisposition guarantees the development of a disorder; rather, it indicates an increased vulnerability. Understanding these genetic predispositions allows for earlier intervention and targeted support.
The Role of Personality: Shaping Our Responses
Personality, encompassing our enduring patterns of thoughts, feelings, and behaviors, is a powerful internal factor determining our actions. It's not merely a collection of traits but a complex, interacting system that influences how we perceive and respond to the world.
Cognitive Processes: The Internal Interpretive Lens
Our cognitive processes, including perception, attention, memory, and thought patterns, significantly shape our behavior. How we interpret events and situations directly influences our emotional and behavioral responses. For example, two individuals might encounter the same stressful situation, but their different cognitive appraisals will lead to different emotional and behavioral reactions. One might view the situation as a challenge, leading to proactive problem-solving; the other might perceive it as a threat, resulting in anxiety and avoidance.
Motivations and Goals: Internal Drivers of Action
Our motivations and goals, largely shaped by personality and individual values, are powerful internal drivers of our behavior. We are driven by a wide array of needs and desires, both conscious and unconscious, which profoundly influence our actions. Understanding these internal motivations is crucial to understanding why we behave in certain ways. For example, someone motivated by achievement might consistently strive for excellence, while someone driven by affiliation might prioritize social connection and harmony.
The Influence of Cognitive Biases: Distorting Our Perceptions
Cognitive biases, systematic patterns of deviation from norm or rationality in judgment, significantly influence our decisions and actions. These biases, rooted in our cognitive processes, often operate unconsciously, distorting our perceptions and leading to suboptimal choices.
Confirmation Bias: Seeking Corroboration
Confirmation bias, the tendency to favor information confirming pre-existing beliefs, impacts how we process information and make decisions. We actively seek out information supporting our views and dismiss contradictory evidence, perpetuating our existing beliefs. This bias influences our behavior by reinforcing certain patterns of thinking and action, even when faced with conflicting evidence.
Availability Heuristic: The Impact of Recency and Vividness
The availability heuristic refers to our tendency to overestimate the likelihood of events that are easily recalled, often due to their recency or vividness. This cognitive shortcut can lead to distorted judgments and inappropriate actions. For example, following a highly publicized plane crash, individuals might overestimate the risk of air travel, even though statistically, it remains a very safe mode of transportation.
The Interplay of Internal and External Factors
While this article emphasizes internal factors, it's crucial to acknowledge the significant interplay between internal and external forces. Our genetic predispositions and personality traits interact dynamically with environmental influences, shaping our behavior in complex ways. Nature provides the blueprint, but nurture shapes the expression of that blueprint.
Gene-Environment Interaction: A Complex Dance
Gene-environment interaction highlights how our genes and environment interact to influence behavior. For example, individuals with a genetic predisposition to depression might only develop the disorder under conditions of significant environmental stress. Similarly, individuals with a genetic predisposition to resilience might thrive even in challenging environments. This interaction highlights the complexity of behavior and the limitations of simplistic nature versus nurture dichotomies.
Environmental Influences: Shaping the Expression of Internal Factors
Environmental factors, including upbringing, culture, social experiences, and life events, significantly influence the expression of our internal factors. For example, an individual with a genetically predisposed aggressive temperament might exhibit this aggression only in certain social contexts or under specific environmental triggers. Conversely, a supportive and nurturing environment could mitigate the expression of negative genetic predispositions.
Conclusion: A Holistic Understanding of Behavior
Understanding human behavior requires a holistic approach that acknowledges the significant role of internal factors. While environmental influences undoubtedly shape our lives, our genes, personality traits, cognitive processes, and motivations profoundly influence our actions. Recognizing the power of these internal factors enables a more nuanced and comprehensive understanding of ourselves and others.
This understanding has significant implications for various fields, including psychology, education, and even criminal justice. By appreciating the complex interplay between internal and external factors, we can develop more effective strategies for personal growth, conflict resolution, and social well-being. The journey to understanding human behavior is ongoing, but by focusing on the internal drivers of action, we gain valuable insight into the intricate mechanisms shaping our lives. Further research into the complexities of gene-environment interactions will continue to refine our understanding of this dynamic interplay and ultimately lead to a more holistic and comprehensive perspective on the determinants of human behavior.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
High Levels Of Cholesterol Can First Lead Directly To
Mar 18, 2025
-
True Or False Professional And Technical Communication Is Research Oriented
Mar 18, 2025
-
Which Best Describes The Terrorist Planning Cycle
Mar 18, 2025
-
Cdl Combination Test Questions And Answers Pdf
Mar 18, 2025
-
Life Insurance Exam Questions And Answers Pdf
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Holds That Our Behavior Is Determined By Internal Factors . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
