How Are Future Values Affected By Changes In Interest Rates
Breaking News Today
Mar 28, 2025 · 6 min read
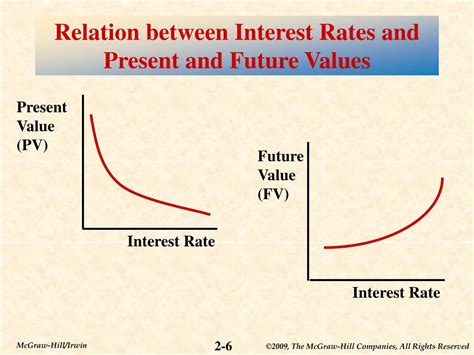
Table of Contents
How Are Future Values Affected by Changes in Interest Rates?
Interest rates are a cornerstone of modern finance, influencing everything from borrowing costs to investment returns. Understanding how changes in interest rates affect future values is crucial for individuals, businesses, and policymakers alike. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricate relationship between interest rate fluctuations and the future worth of money, exploring various scenarios and providing practical insights.
The Fundamental Relationship: Time, Money, and Interest
The core concept lies in the time value of money. A dollar today is worth more than a dollar tomorrow, simply because today's dollar can be invested to earn interest, generating a larger sum in the future. This future value is directly influenced by the prevailing interest rate.
The basic formula for calculating future value (FV) is:
FV = PV * (1 + r)^n
Where:
- FV = Future Value
- PV = Present Value (the initial amount of money)
- r = Interest rate (expressed as a decimal)
- n = Number of periods (e.g., years, months)
This formula demonstrates a direct relationship: higher interest rates lead to higher future values, assuming all other factors remain constant. Conversely, lower interest rates result in lower future values.
Interest Rate Changes and Their Impact on Future Value
The impact of interest rate changes on future value is multifaceted and depends on several factors, including:
- The type of investment: Different investments react differently to interest rate changes. For instance, the value of fixed-income securities like bonds is inversely related to interest rates (rising rates lower bond prices), while the impact on equities is more complex and depends on various macroeconomic factors.
- The duration of the investment: Longer-term investments are more sensitive to interest rate changes than shorter-term investments. A small change in interest rates can significantly impact the future value of a long-term investment.
- The frequency of compounding: The more frequently interest is compounded (e.g., daily, monthly, annually), the faster the future value grows. This compounding effect is amplified by higher interest rates.
- The direction of the change: A rise in interest rates increases the future value of investments that earn interest, but it might decrease the present value of fixed-income assets. Conversely, a decrease in interest rates has the opposite effect.
Scenario 1: Rising Interest Rates
When interest rates rise, several implications arise:
- Increased future value of savings and investments: Investors who deposit their money in interest-bearing accounts or invest in instruments like certificates of deposit (CDs) or bonds will see their future value increase. This is because they earn a higher return on their invested capital.
- Higher borrowing costs: Businesses and individuals will face higher costs when borrowing money, as lenders will demand higher interest rates to compensate for the increased risk and inflation. This can reduce investment and economic growth.
- Reduced present value of fixed-income securities: Existing bonds and other fixed-income securities will see their market value decline as newer bonds are issued with higher interest rates. This is because investors will demand a higher yield for comparable risk.
- Impact on inflation: Rising interest rates are often implemented by central banks to combat inflation. While higher interest rates can curb inflation, they can also slow down economic growth.
Scenario 2: Falling Interest Rates
Conversely, when interest rates fall:
- Decreased future value of savings and investments: The return on savings and investments decreases, resulting in a lower future value compared to a scenario with higher interest rates.
- Lower borrowing costs: Businesses and individuals find it cheaper to borrow money, stimulating investment and economic activity. Lower borrowing costs can also lead to increased consumer spending.
- Increased present value of fixed-income securities: The market value of existing bonds and other fixed-income securities rises, making them more attractive to investors seeking higher yields in a low-interest-rate environment.
- Potential for inflation: Lower interest rates can fuel inflation, as they encourage borrowing and spending, increasing demand without a corresponding increase in supply.
Specific Examples and Calculations
Let's illustrate the impact with numerical examples:
Example 1: Impact of Rising Rates
Suppose you invest $10,000 for 5 years.
- Scenario A: Interest rate of 3%: FV = $10,000 * (1 + 0.03)^5 = $11,592.74
- Scenario B: Interest rate of 5%: FV = $10,000 * (1 + 0.05)^5 = $12,762.82
The increase in the interest rate from 3% to 5% results in a higher future value of $1,160.08.
Example 2: Impact of Falling Rates
Consider the same $10,000 investment over 5 years.
- Scenario A: Interest rate of 5%: FV = $10,000 * (1 + 0.05)^5 = $12,762.82
- Scenario B: Interest rate of 2%: FV = $10,000 * (1 + 0.02)^5 = $11,040.81
The decrease in the interest rate from 5% to 2% leads to a lower future value of $1,722.01.
These examples highlight the significant impact even small changes in interest rates can have on future values, particularly over longer investment horizons.
Beyond Simple Interest: The Role of Compounding
The calculations above assume simple annual compounding. In reality, interest is often compounded more frequently (monthly, quarterly, or daily). This increases the future value significantly.
The formula for future value with compound interest is:
FV = PV * (1 + r/m)^(m*n)
Where:
- m = Number of compounding periods per year
For example, if interest is compounded monthly (m = 12), the future value will be higher than with annual compounding. The more frequent the compounding, the greater the impact of interest rate changes on the future value.
Factors Influencing Interest Rate Changes
Understanding the factors that drive interest rate changes is critical to anticipating their impact on future values. These include:
- Inflation: Central banks often raise interest rates to combat inflation, as higher rates curb borrowing and spending, thus reducing demand and inflationary pressure.
- Economic growth: Strong economic growth can lead to higher interest rates, as increased demand for credit pushes up borrowing costs.
- Government policy: Fiscal and monetary policies implemented by governments and central banks significantly influence interest rates.
- Global economic conditions: International events and economic conditions can impact interest rates in a country.
- Market forces: Supply and demand for credit also play a crucial role in determining interest rates.
Strategies for Managing Interest Rate Risk
Understanding how interest rate changes affect future values allows individuals and businesses to develop strategies for managing interest rate risk:
- Diversification: Diversifying investments across different asset classes (e.g., stocks, bonds, real estate) can help mitigate the impact of interest rate fluctuations.
- Matching maturities: Matching the maturity of investments to your financial goals can help minimize interest rate risk.
- Hedging: Financial instruments like interest rate swaps or futures contracts can be used to hedge against interest rate risk.
- Adjustable-rate vs. fixed-rate loans: Choosing between adjustable-rate and fixed-rate loans depends on your risk tolerance and expectations about future interest rate movements.
Conclusion
The relationship between interest rates and future values is fundamental to financial planning and investment decision-making. Understanding this relationship, along with the factors that influence interest rate changes, is vital for making informed decisions and mitigating the risks associated with interest rate volatility. By carefully analyzing the potential impacts of interest rate fluctuations, individuals and businesses can optimize their financial strategies and secure a more favorable future value for their assets. Continuous monitoring of economic indicators and interest rate movements is crucial for adapting to the ever-changing financial landscape.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Macroenvironment Is Also Known As The Blank Environment
Mar 31, 2025
-
A Competitive Market Is A Market In Which Quizlet
Mar 31, 2025
-
A Company Bought A Computer For 1500 Quizlet
Mar 31, 2025
-
Eggs Pox Sole I Ve Gibberish Meaning Quizlet
Mar 31, 2025
-
The Sarbanes Oxley Act Seeks To Increase Blank Independence
Mar 31, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Are Future Values Affected By Changes In Interest Rates . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
