The Macroenvironment Is Also Known As The Blank______ Environment.
Breaking News Today
Mar 31, 2025 · 8 min read
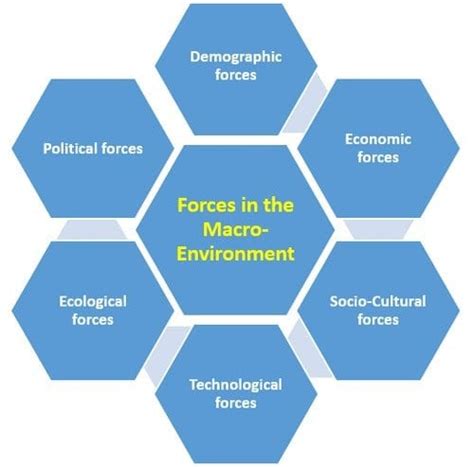
Table of Contents
The Macroenvironment: Also Known as the General Environment
The macroenvironment, also known as the general environment, encompasses the broad forces and factors that impact an organization's operations and performance. Understanding this environment is crucial for strategic planning and long-term success. Unlike the microenvironment, which focuses on stakeholders with direct interaction, the macroenvironment deals with larger, less controllable societal forces that shape the context in which businesses operate. Ignoring these forces can lead to missed opportunities, strategic miscalculations, and ultimately, failure. This comprehensive guide will delve into the key components of the macroenvironment, exploring their influence and providing practical examples.
The Six Key Components of the Macroenvironment
The macroenvironment is typically analyzed through six key segments: political, economic, socio-cultural, technological, environmental, and legal (PESTEL). Each segment presents unique challenges and opportunities, requiring businesses to adapt and innovate to remain competitive.
1. Political Environment
The political environment encompasses government policies, regulations, political stability, and the overall political climate. This segment significantly impacts businesses in several ways:
-
Government Regulations: Industries are subject to a wide array of regulations impacting everything from product safety and environmental standards to labor laws and taxation. Changes in these regulations can necessitate significant shifts in business practices and investment. For example, stricter emission standards for automobiles can force manufacturers to invest heavily in new technologies and redesign their production processes.
-
Political Stability: Political instability, such as civil unrest, coups, or corruption, can disrupt business operations, create uncertainty, and increase risk. Companies operating in politically unstable regions may face challenges securing resources, protecting assets, and maintaining a predictable business environment.
-
Trade Policies: International trade agreements, tariffs, and trade barriers directly impact businesses involved in global trade. Changes in trade policies can significantly alter import/export costs and market access.
-
Government Support: Government support in the form of subsidies, tax breaks, and grants can provide a significant advantage to businesses in certain industries. Understanding government priorities and accessing such support can be crucial for competitiveness.
Example: A change in government regulations regarding data privacy, like the implementation of GDPR in Europe, forced companies to overhaul their data handling processes and invest in compliance solutions.
2. Economic Environment
The economic environment reflects the overall state of the economy, encompassing factors like economic growth, inflation, interest rates, unemployment, and consumer spending. This segment significantly influences business decisions regarding investment, pricing, production, and market expansion.
-
Economic Growth: Strong economic growth typically translates to increased consumer spending and business investment, creating favorable conditions for expansion. Conversely, economic downturns can lead to reduced demand, higher unemployment, and cautious spending.
-
Inflation: High inflation erodes purchasing power, affecting consumer demand and input costs. Businesses must adapt to price increases and manage inflation's impact on profitability.
-
Interest Rates: Interest rates influence borrowing costs and investment decisions. High interest rates increase the cost of borrowing, potentially hindering expansion and investment projects.
-
Exchange Rates: Fluctuations in exchange rates impact businesses engaged in international trade. Favorable exchange rates can increase export competitiveness, while unfavorable rates can reduce profitability.
Example: During a recession, businesses might reduce production, cut costs, and focus on retaining existing customers rather than acquiring new ones.
3. Socio-Cultural Environment
The socio-cultural environment encompasses the societal values, beliefs, lifestyles, demographics, and cultural trends that shape consumer behavior and market demand. Understanding this segment is critical for product development, marketing strategies, and overall brand positioning.
-
Demographics: Changes in population size, age distribution, ethnicity, and education levels directly impact consumer preferences and market segmentation. Businesses need to adapt their products and services to cater to evolving demographic trends.
-
Lifestyles and Values: Shifting societal values, such as increasing environmental awareness or a preference for healthier lifestyles, can dramatically alter consumer choices and business opportunities.
-
Cultural Trends: Cultural trends, such as fashion, music, and entertainment, can influence consumer preferences and create new market demands. Businesses that are sensitive to these trends can capitalize on emerging opportunities.
-
Social Responsibility: Consumers are increasingly concerned about ethical and sustainable business practices. Companies that prioritize social responsibility and demonstrate a commitment to sustainability are often rewarded with enhanced brand reputation and customer loyalty.
Example: The growing popularity of veganism and vegetarianism has created new market opportunities for plant-based food products and related businesses.
4. Technological Environment
The technological environment encompasses technological advancements, innovations, and their impact on industries and businesses. Rapid technological change presents both opportunities and threats, demanding continuous adaptation and innovation.
-
Technological Advancements: New technologies can create new products, services, and production processes, leading to increased efficiency and competitiveness. Companies need to invest in research and development to stay ahead of the curve.
-
Automation and Robotics: Automation and robotics are transforming many industries, increasing efficiency and productivity while potentially displacing workers. Businesses must adapt to these changes by investing in retraining programs and exploring new business models.
-
Information Technology: Advances in information technology are transforming communication, data management, and customer engagement. Businesses must leverage these advancements to enhance efficiency, improve customer service, and gain a competitive edge.
-
Digital Transformation: The increasing reliance on digital technologies is reshaping industries and business models. Companies need to adapt to this shift by embracing digital transformation initiatives and building a strong digital presence.
Example: The rise of e-commerce has revolutionized retail, forcing brick-and-mortar stores to adapt by enhancing their online presence and developing integrated omnichannel strategies.
5. Environmental Environment
The environmental environment encompasses ecological concerns, sustainability, and the impact of business activities on the natural world. Growing environmental awareness and stricter regulations are forcing businesses to adopt more sustainable practices.
-
Climate Change: Climate change presents both risks and opportunities. Businesses must adapt to changing weather patterns and adopt sustainable practices to mitigate their environmental impact.
-
Resource Depletion: The depletion of natural resources is a growing concern, forcing businesses to find innovative solutions and adopt circular economy principles.
-
Pollution: Businesses must minimize pollution and adopt environmentally responsible practices to comply with regulations and maintain a positive brand image.
-
Sustainability: Consumers are increasingly demanding sustainable products and services. Businesses that demonstrate a commitment to sustainability can attract environmentally conscious consumers.
Example: Many companies are investing in renewable energy sources to reduce their carbon footprint and meet sustainability goals.
6. Legal Environment
The legal environment encompasses the laws, regulations, and legal frameworks that govern business activities. Compliance with these laws is essential to avoid penalties and maintain a positive reputation.
-
Labor Laws: Labor laws regulate employment practices, including wages, working conditions, and employee rights. Businesses must comply with these laws to avoid legal penalties and maintain positive employee relations.
-
Consumer Protection Laws: Consumer protection laws safeguard consumers' rights and protect them from unfair business practices. Businesses must comply with these laws to avoid legal issues and maintain consumer trust.
-
Intellectual Property Laws: Intellectual property laws protect businesses' inventions, brands, and creative works. Companies need to protect their intellectual property to maintain a competitive advantage.
-
Antitrust Laws: Antitrust laws prevent monopolies and promote competition. Businesses must comply with these laws to avoid legal penalties and maintain a fair and competitive market.
Example: The implementation of new data protection regulations requires businesses to adjust their data collection and handling practices to ensure compliance.
Analyzing the Macroenvironment: SWOT Analysis and More
Understanding the macroenvironment is not just about identifying the individual components; it's about analyzing their interplay and assessing their potential impact on your organization. Several analytical tools can help:
-
PESTEL Analysis: This systematic framework helps organize and analyze the key factors within each of the six segments.
-
SWOT Analysis: By integrating PESTEL findings into a SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) analysis, businesses can identify how macroenvironmental factors might affect their internal capabilities and competitive positioning. For example, a new technology (Technological environment) could present an opportunity (SWOT), but lack of internal expertise (Weakness) might hinder its exploitation.
-
Scenario Planning: This involves developing alternative future scenarios based on different combinations of macroenvironmental factors. This proactive approach helps businesses prepare for a range of potential outcomes and develop contingency plans.
-
Competitive Analysis: Understanding how competitors are responding to changes in the macroenvironment is crucial for developing effective strategies.
The Importance of Macroenvironmental Analysis
Ignoring the macroenvironment can have severe consequences:
-
Missed Opportunities: Failure to identify and capitalize on emerging trends can lead to lost market share and diminished profitability.
-
Strategic Miscalculations: Misunderstanding the macroenvironment can result in poorly conceived strategies that are ill-suited to the prevailing conditions.
-
Increased Risk: Ignoring potential risks associated with political instability, economic downturns, or technological disruption can expose businesses to significant financial losses.
-
Damage to Reputation: Failure to address environmental or social concerns can negatively impact brand reputation and customer loyalty.
In conclusion, the macroenvironment – the general environment – is a dynamic and influential force shaping the success or failure of organizations. By consistently monitoring and analyzing these external forces, businesses can anticipate challenges, identify opportunities, and develop robust strategies to navigate the complexities of the ever-changing business landscape. Proactive engagement with the macroenvironment is not just an option; it's a necessity for long-term sustainability and competitiveness.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Modifying Your Personal Action Plan Can Impede Personal Fitness Goals
Apr 02, 2025
-
If You Need To Download Something For A Class First
Apr 02, 2025
-
In Florida Deceptive Advertising Is Considered To Be
Apr 02, 2025
-
Indicate Which Muscle Is Highlighted In The Image
Apr 02, 2025
-
By Default Active Directory Adds New Computers To What Group
Apr 02, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Macroenvironment Is Also Known As The Blank______ Environment. . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
