In Contrast To A Cerebral Concussion A Cerebral Contusion
Breaking News Today
Mar 17, 2025 · 6 min read
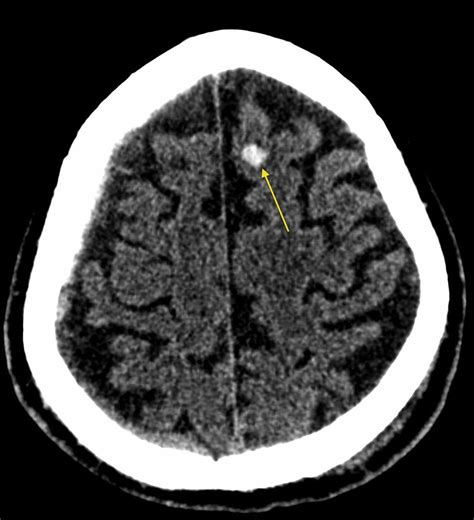
Table of Contents
Cerebral Concussion vs. Cerebral Contusion: Understanding the Differences
Brain injuries are a serious concern, and understanding the nuances between different types is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment. Two common types of brain injuries, often confused, are cerebral concussion and cerebral contusion. While both involve trauma to the brain, they differ significantly in their mechanisms, severity, and long-term effects. This comprehensive article delves into the distinct characteristics of each injury, highlighting their differences and emphasizing the importance of seeking immediate medical attention for any suspected brain injury.
What is a Cerebral Concussion?
A cerebral concussion, also known as a mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI), is a complex pathophysiological process affecting the brain, induced by biomechanical forces. It's characterized by a temporary disruption of brain function caused by a blow to the head, or a violent shaking of the head and body. Unlike a contusion, a concussion doesn't involve visible damage to the brain tissue itself; instead, it results in a functional disturbance. Think of it as a temporary glitch in the brain's intricate network. The symptoms are varied and can range from mild to severe, and the severity doesn't always correlate with the force of the impact.
Common Symptoms of a Concussion:
Concussion symptoms can manifest immediately after the injury or develop gradually over hours or days. They can include:
- Cognitive Symptoms: Headache, dizziness, difficulty concentrating, memory problems (both short-term and long-term), slowed processing speed, confusion, and difficulty with decision-making.
- Physical Symptoms: Nausea and vomiting, fatigue, balance problems, blurred vision, sensitivity to light and sound (photophobia and phonophobia), and sleep disturbances.
- Emotional Symptoms: Irritability, anxiety, sadness, emotional lability (rapid mood swings), and personality changes.
Diagnosis of a Concussion:
Diagnosing a concussion is challenging because there aren't any specific diagnostic tests. Doctors rely on a thorough neurological exam, assessing cognitive function, balance, and coordination. Neuropsychological testing may be used in some cases to evaluate cognitive deficits. Imaging techniques like CT scans and MRIs are typically normal in concussions, as the injury is functional rather than structural.
Treatment and Recovery from a Concussion:
Treatment for a concussion focuses on rest, both physical and cognitive. This involves avoiding strenuous activities, screen time, and mentally demanding tasks. Gradual return to activity is crucial, following a personalized plan guided by a healthcare professional. This phased approach helps prevent second-impact syndrome, a potentially life-threatening condition that can occur if another concussion is sustained before the brain has fully healed. In some cases, physical therapy, occupational therapy, and other rehabilitation strategies may be necessary to address persistent symptoms.
What is a Cerebral Contusion?
A cerebral contusion, in contrast to a concussion, is a bruise on the brain. It involves bleeding and swelling in the brain tissue caused by a direct impact or forceful acceleration-deceleration injury. This type of injury results in visible damage to brain cells and can range in severity from mild to severe, depending on the extent of the bleeding and swelling. The location and size of the contusion influence the specific symptoms experienced by the individual.
Common Symptoms of a Contusion:
Symptoms of a cerebral contusion are often more severe and persistent than those of a concussion. They can include:
- Loss of Consciousness: This is a common feature, often lasting from a few seconds to several minutes, and the duration can indicate the severity of the injury.
- Focal Neurological Deficits: Depending on the location of the contusion, individuals may experience weakness or paralysis on one side of the body (hemiparesis or hemiplegia), difficulty with speech (aphasia), visual disturbances, or changes in sensation.
- Seizures: Contusions can increase the risk of seizures, either immediately following the injury or later on.
- Cognitive Impairment: Similar to concussion, contusions can lead to cognitive difficulties, including memory problems, confusion, and difficulty with concentration. However, these impairments are often more pronounced and persistent in contusions.
- Increased Intracranial Pressure (ICP): The swelling and bleeding associated with a contusion can increase pressure within the skull, leading to further neurological damage. This is a serious complication requiring urgent medical attention.
Diagnosis of a Cerebral Contusion:
Unlike concussions, cerebral contusions are typically visible on brain imaging studies such as CT scans and MRIs. These scans show the location, size, and extent of the bleeding and swelling in the brain tissue. A thorough neurological examination is also essential for evaluating the patient's neurological status and identifying any focal deficits.
Treatment and Recovery from a Cerebral Contusion:
Treatment for a cerebral contusion depends on the severity of the injury. Individuals with mild contusions may be managed with close observation and supportive care. More severe contusions may require surgical intervention to reduce swelling or remove blood clots to relieve intracranial pressure. Medication may be used to manage pain, swelling, and seizures. Rehabilitation is often necessary, focusing on regaining lost function and improving cognitive skills. The recovery period can be lengthy and may involve months or even years of therapy.
Key Differences Summarized:
| Feature | Cerebral Concussion | Cerebral Contusion |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanism | Functional disruption; no visible brain damage | Bruising of brain tissue; visible bleeding and swelling |
| Brain Damage | No visible damage | Visible damage; tissue disruption |
| Loss of Consciousness | Usually absent; if present, brief | Often present; duration varies significantly |
| Imaging Findings | Typically normal on CT and MRI | Abnormalities visible on CT and MRI |
| Symptoms | Variable; often mild; may include headache, dizziness, cognitive difficulties | Can be severe; may include focal neurological deficits, loss of consciousness, seizures |
| Severity | Mild to moderate | Mild to severe |
| Recovery | Usually rapid; complete recovery expected | Can be prolonged; significant long-term effects possible |
Long-Term Effects:
Both concussions and contusions can have long-term effects, although the likelihood and severity differ. Post-concussion syndrome (PCS) is a condition that can develop after a concussion, characterized by persistent symptoms such as headaches, dizziness, fatigue, and cognitive difficulties. These symptoms can last for weeks, months, or even years. Similarly, cerebral contusions can lead to chronic neurological problems, including cognitive impairments, motor deficits, and seizures. The severity of long-term effects is related to the severity of the initial injury and the adequacy of treatment and rehabilitation.
Importance of Immediate Medical Attention:
Any suspected brain injury, whether concussion or contusion, requires immediate medical attention. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to minimizing the risk of complications and improving the chances of a full recovery. Delaying medical care can lead to irreversible brain damage.
Conclusion:
While both cerebral concussion and cerebral contusion are serious brain injuries, they differ significantly in their mechanisms, symptoms, and long-term prognosis. Concussions are characterized by a functional disruption of brain function without visible damage, while contusions involve bruising and visible damage to brain tissue. Understanding these differences is critical for appropriate diagnosis, treatment, and management of these injuries. Always seek immediate medical attention for any suspected brain injury to ensure optimal care and recovery. Early intervention can significantly impact the long-term outcome and quality of life for individuals suffering from these injuries. Continued research in the fields of neurotrauma and brain injury is essential to improve our understanding of these complex conditions and develop more effective treatments. The ongoing development of diagnostic tools and therapeutic interventions offers hope for improved outcomes for individuals facing these challenges. Patient education and awareness are paramount in ensuring individuals recognize the symptoms, seek timely medical assistance, and participate actively in their recovery process. Remember, early intervention can make a significant difference.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
High Levels Of Cholesterol Can First Lead Directly To
Mar 18, 2025
-
True Or False Professional And Technical Communication Is Research Oriented
Mar 18, 2025
-
Which Best Describes The Terrorist Planning Cycle
Mar 18, 2025
-
Cdl Combination Test Questions And Answers Pdf
Mar 18, 2025
-
Life Insurance Exam Questions And Answers Pdf
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about In Contrast To A Cerebral Concussion A Cerebral Contusion . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
