In Contrast To An Automated Implanted Cardioverter
Breaking News Today
Mar 16, 2025 · 6 min read
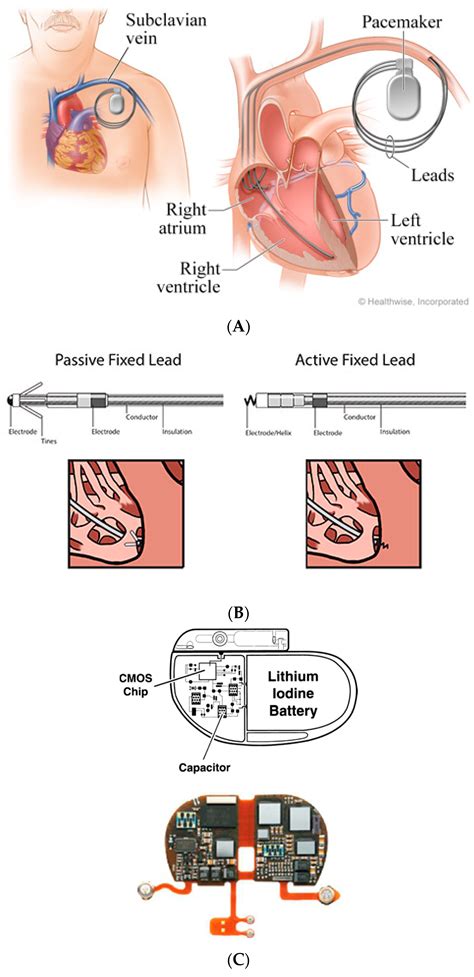
Table of Contents
In Contrast to an Automated Implanted Cardioverter-Defibrillator (AICD): Exploring Alternative Treatments for Cardiac Arrhythmias
The automated implanted cardioverter-defibrillator (AICD), also known as an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD), is a life-saving device for individuals at high risk of sudden cardiac death due to life-threatening arrhythmias like ventricular tachycardia (VT) or ventricular fibrillation (VF). However, AICDs are not without their drawbacks. This article explores alternative treatments for cardiac arrhythmias, contrasting them with AICDs in terms of invasiveness, efficacy, complications, and suitability for different patient populations. Understanding these alternatives empowers both patients and healthcare professionals to make informed decisions about the best course of action for managing arrhythmias.
Understanding the Role of an AICD
Before delving into alternatives, it's crucial to understand the function of an AICD. This small, battery-powered device is implanted surgically under the skin, usually in the chest area. It continuously monitors the heart's rhythm and detects potentially fatal arrhythmias. If a dangerous rhythm is detected, the AICD delivers a therapeutic shock to restore a normal heartbeat. This shock, while potentially uncomfortable, can be life-saving.
AICD's Key Functions:
- Rhythm Monitoring: Continuous monitoring of the heart's electrical activity.
- Shock Delivery: Delivery of electrical shocks to correct life-threatening arrhythmias.
- Pacing: Some AICDs also have pacing capabilities to help regulate slow heart rates (bradycardia).
Alternatives to AICDs: A Comparative Analysis
While AICDs are a cornerstone of arrhythmia management, several alternative therapies exist, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. The choice of treatment depends on several factors, including the type and severity of the arrhythmia, the patient's overall health, and individual preferences.
1. Medications (Antiarrhythmic Drugs)
Antiarrhythmic drugs are a common first-line treatment for many types of arrhythmias. These medications work by altering the electrical activity of the heart, helping to regulate heart rhythm.
Advantages:
- Non-invasive: Medication is administered orally or intravenously, avoiding the need for surgery.
- Cost-effective: Generally less expensive than AICDs.
- Adjustability: Dosage can be adjusted based on the patient's response.
Disadvantages:
- Side effects: Antiarrhythmic drugs can have a range of side effects, some of which can be serious.
- Variable efficacy: The effectiveness of these drugs can vary significantly between individuals.
- May not be suitable for all arrhythmias: Some arrhythmias are unresponsive to medication.
2. Catheter Ablation
Catheter ablation is a minimally invasive procedure used to treat certain types of arrhythmias. A thin, flexible tube (catheter) is inserted into a vein and guided to the heart. Radiofrequency energy or cryoablation (freezing) is then used to destroy the abnormal heart tissue causing the arrhythmia.
Advantages:
- Minimally invasive: Less invasive than AICD implantation.
- High success rate: Catheter ablation can be highly effective in treating certain arrhythmias.
- Potential for cure: In some cases, catheter ablation can lead to a complete resolution of the arrhythmia.
Disadvantages:
- Risks of complications: Like any procedure, there are risks associated with catheter ablation, including bleeding, infection, and blood clots.
- Not suitable for all arrhythmias: Not all arrhythmias are amenable to catheter ablation.
- May require multiple procedures: Sometimes, more than one ablation procedure is needed to achieve optimal results.
3. Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy (CRT)
CRT is a therapy used for patients with heart failure and conduction abnormalities. It involves implanting a device similar to an AICD, but its primary function is to resynchronize the heart's contractions, improving the heart's pumping efficiency. Some CRT devices also include defibrillation capabilities.
Advantages:
- Improves heart function: CRT can significantly improve heart function and symptoms in eligible patients.
- Reduces hospitalization: Can lead to a reduction in hospitalizations due to worsening heart failure.
- Can improve quality of life: Can improve exercise tolerance and overall quality of life.
Disadvantages:
- Invasive procedure: Requires implantation surgery.
- Specific patient criteria: CRT is only suitable for patients who meet specific criteria.
- Potential complications: Similar to AICD implantation, there are potential complications.
4. Lifestyle Modifications
For some individuals with mild arrhythmias, lifestyle modifications can be an effective management strategy. These modifications may include:
- Dietary changes: A balanced diet low in sodium and saturated fats.
- Regular exercise: Moderate-intensity aerobic exercise.
- Stress reduction techniques: Yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises.
- Smoking cessation: Quitting smoking is crucial for heart health.
- Alcohol moderation: Limiting alcohol consumption.
Advantages:
- Non-invasive: No medical interventions are required.
- Cost-effective: Generally inexpensive.
- Improved overall health: Beneficial for overall health, not just arrhythmia management.
Disadvantages:
- May not be sufficient for all arrhythmias: Lifestyle modifications alone may not be enough for severe arrhythmias.
- Requires commitment: Requires consistent effort and adherence.
- Slow effect: May take time to see noticeable improvements.
Choosing the Right Treatment: A Multifaceted Decision
The selection of the optimal treatment for a cardiac arrhythmia is a complex decision that requires careful consideration of several factors:
- Type and Severity of Arrhythmia: The specific type and severity of the arrhythmia will significantly influence the choice of treatment.
- Patient's Overall Health: The patient's overall health status and the presence of other medical conditions will affect treatment options.
- Risk of Sudden Cardiac Death: The patient's risk of sudden cardiac death is a crucial factor in deciding whether an AICD is necessary.
- Patient Preferences: Patient preferences and values play a significant role in shared decision-making.
A collaborative approach between the patient and the healthcare team, including cardiologists and electrophysiologists, is essential for determining the best treatment strategy. This involves a thorough evaluation of the patient's condition, a discussion of the risks and benefits of each treatment option, and the development of a personalized treatment plan.
Long-Term Management and Follow-Up
Regardless of the chosen treatment, long-term management and follow-up are critical for successful arrhythmia management. This includes:
- Regular check-ups: Regular visits to the cardiologist for monitoring and assessment.
- Medication adherence: Careful adherence to prescribed medication regimens.
- Lifestyle adjustments: Continued adherence to lifestyle modifications.
- Device monitoring (if applicable): Regular monitoring of AICD or CRT devices.
- Prompt attention to symptoms: Seeking immediate medical attention if new or worsening symptoms occur.
Conclusion: A Personalized Approach to Arrhythmia Management
In contrast to the life-saving intervention provided by an AICD, alternative treatments offer a range of options for managing cardiac arrhythmias. The decision regarding the most appropriate approach is highly individualized and depends on numerous patient-specific factors. A comprehensive understanding of the benefits and drawbacks of each therapy, combined with a collaborative dialogue between the patient and the healthcare team, ensures the selection of the most effective and safe treatment strategy, ultimately improving the patient's quality of life and long-term prognosis. This personalized approach is paramount in the evolving landscape of cardiac arrhythmia management. Continuous research and advancements in technology promise even more refined and effective treatment options in the future.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Best Describes The Terrorist Planning Cycle
Mar 18, 2025
-
Cdl Combination Test Questions And Answers Pdf
Mar 18, 2025
-
Life Insurance Exam Questions And Answers Pdf
Mar 18, 2025
-
The Direct Carry Is Used To Transfer A Patient
Mar 18, 2025
-
The Emancipation Proclamation Of January 1 1863 Quizlet
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about In Contrast To An Automated Implanted Cardioverter . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
