Pharmacology Made Easy 5.0 Pain And Inflammation Test
Breaking News Today
Mar 17, 2025 · 5 min read
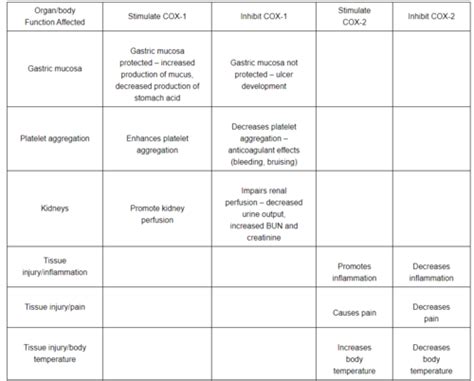
Table of Contents
Pharmacology Made Easy 5.0: Pain and Inflammation Test - A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding pain and inflammation is crucial for anyone studying pharmacology. This comprehensive guide delves into the complexities of these physiological processes, exploring the mechanisms of action of various drugs used in their management. We'll break down the key concepts to make pharmacology more accessible and prepare you for any pain and inflammation test, particularly focusing on the potential content of a "Pharmacology Made Easy 5.0" examination.
Understanding Pain: Nociception and Beyond
Pain, a subjective sensory and emotional experience, is far more than just a simple sensation. It's a complex interplay of physiological and psychological factors. Let's break down the process:
Nociception: The Physiological Basis of Pain
Nociception refers to the physiological process of detecting noxious stimuli. This involves specialized sensory neurons called nociceptors, located throughout the body in the skin, muscles, joints, and internal organs. Nociceptors are activated by various stimuli, including:
- Mechanical stimuli: Pressure, cutting, crushing.
- Thermal stimuli: Extreme heat or cold.
- Chemical stimuli: Acids, inflammatory mediators (like bradykinin, prostaglandins, and substance P).
Once activated, nociceptors transmit signals along nerve fibers to the spinal cord, and then up to the brain where pain perception occurs. This transmission involves different types of nerve fibers:
- A-delta fibers: Myelinated fibers that transmit sharp, well-localized pain signals rapidly.
- C fibers: Unmyelinated fibers that transmit dull, aching, and poorly localized pain signals more slowly.
Beyond Nociception: The Pain Experience
The perception of pain is influenced by numerous factors beyond the simple activation of nociceptors. These include:
- Psychological factors: Anxiety, depression, stress, and past experiences significantly modulate pain perception.
- Cognitive factors: Beliefs about pain, expectations, and attention to pain all play a role.
- Social factors: Cultural norms, social support, and the environment can impact how individuals experience and respond to pain.
Inflammation: The Body's Response to Injury
Inflammation is a complex biological response to tissue injury or infection. It's characterized by:
- Redness (rubor): Due to increased blood flow to the affected area.
- Swelling (tumor): Caused by fluid accumulation in the tissues.
- Heat (calor): Resulting from increased blood flow and metabolic activity.
- Pain (dolor): A consequence of nerve stimulation by inflammatory mediators.
- Loss of function (functio laesa): Caused by swelling, pain, and tissue damage.
Inflammatory Mediators: Key Players
Numerous chemical mediators contribute to the inflammatory process. Understanding their roles is crucial for comprehending how anti-inflammatory drugs work:
- Prostaglandins: Potent mediators involved in pain, fever, and inflammation. They sensitize nociceptors, making them more responsive to stimuli.
- Leukotrienes: Contributes to bronchoconstriction, vascular permeability, and chemotaxis (attraction of immune cells).
- Bradykinin: Causes vasodilation, increased vascular permeability, and pain.
- Histamine: Released by mast cells, it causes vasodilation, increased vascular permeability, and itching.
- Cytokines: Signaling molecules involved in cell communication during inflammation, some inducing pain and fever (like TNF-α and IL-1).
Pharmacotherapy of Pain and Inflammation: A Detailed Look
A wide array of pharmacological agents are used to manage pain and inflammation. Let’s examine some major drug classes:
Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
NSAIDs are widely used for their analgesic (pain-relieving), antipyretic (fever-reducing), and anti-inflammatory effects. They work primarily by inhibiting the enzyme cyclooxygenase (COX), which is responsible for the production of prostaglandins. There are two main COX isoforms:
- COX-1: Present in most tissues, involved in maintaining gastric mucosal protection and platelet aggregation.
- COX-2: Induced during inflammation, primarily responsible for the production of prostaglandins involved in pain and inflammation.
NSAIDs can be categorized into:
- Non-selective NSAIDs: Inhibit both COX-1 and COX-2, leading to both therapeutic benefits and side effects (e.g., ibuprofen, naproxen, diclofenac). These commonly cause gastrointestinal problems.
- COX-2 selective inhibitors (coxibs): Primarily inhibit COX-2, reducing gastrointestinal side effects but potentially increasing cardiovascular risks (e.g., celecoxib, rofecoxib – withdrawn due to cardiovascular risks).
Opioid Analgesics
Opioids are powerful analgesics used to manage moderate to severe pain. They act primarily by binding to opioid receptors in the central nervous system, reducing pain perception and causing euphoria. Important opioid receptor subtypes include:
- μ-receptors: Mediate analgesia, respiratory depression, and euphoria.
- κ-receptors: Involved in analgesia and sedation.
- δ-receptors: Contribute to analgesia.
Opioid analgesics include morphine, codeine, fentanyl, oxycodone, and tramadol. They can be associated with significant side effects, including respiratory depression, constipation, nausea, and addiction.
Acetaminophen (Paracetamol)
Acetaminophen is an effective analgesic and antipyretic, but its anti-inflammatory effects are minimal. Its exact mechanism of action isn't fully understood, but it's believed to involve inhibition of COX enzymes in the central nervous system.
Other Analgesic and Anti-inflammatory Agents
- Corticosteroids: Potent anti-inflammatory drugs used for severe inflammation. They inhibit the production of inflammatory mediators by suppressing immune responses. Their use is often limited by significant side effects.
- Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs): Used in the management of chronic inflammatory conditions like rheumatoid arthritis. They work by modifying the underlying immune response responsible for the disease.
Preparing for Your Pharmacology Made Easy 5.0 Pain and Inflammation Test
To excel in your exam, focus on these key areas:
- Mechanisms of pain and inflammation: Understand the physiological processes involved, including nociception and the roles of different inflammatory mediators.
- Drug classes: Know the mechanisms of action, indications, contraindications, side effects, and drug interactions of the major drug classes used to treat pain and inflammation (NSAIDs, opioids, acetaminophen, corticosteroids, DMARDs).
- Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics: Understand how these drugs are absorbed, distributed, metabolized, and excreted (pharmacokinetics) and how they exert their therapeutic effects (pharmacodynamics).
- Clinical applications: Be familiar with the appropriate use of these drugs in different pain and inflammatory conditions.
Practice Questions and Review
The best way to prepare for any exam is through consistent practice. Create flashcards for key concepts, practice multiple-choice questions, and review your notes regularly. Focus on understanding the underlying principles rather than simple memorization.
Conclusion: Mastering Pain and Inflammation Pharmacology
Mastering pain and inflammation pharmacology requires a thorough understanding of the physiological processes involved and the mechanisms of action of different drug classes. This detailed guide provides a solid foundation, equipping you with the knowledge needed to confidently tackle your "Pharmacology Made Easy 5.0" pain and inflammation test. Remember to focus on the core concepts, practice consistently, and review regularly to ensure success. Good luck!
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
True Or False Professional And Technical Communication Is Research Oriented
Mar 18, 2025
-
Which Best Describes The Terrorist Planning Cycle
Mar 18, 2025
-
Cdl Combination Test Questions And Answers Pdf
Mar 18, 2025
-
Life Insurance Exam Questions And Answers Pdf
Mar 18, 2025
-
The Direct Carry Is Used To Transfer A Patient
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Pharmacology Made Easy 5.0 Pain And Inflammation Test . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
