Reducing Speed Increases A Driver's Total Stopping Distance.
Breaking News Today
Mar 24, 2025 · 5 min read
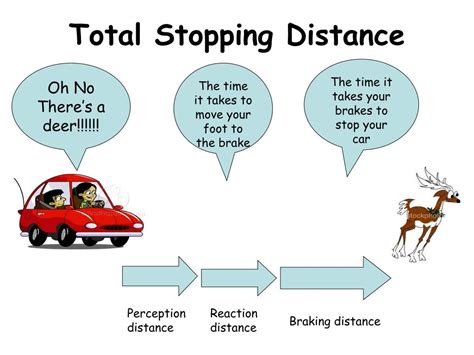
Table of Contents
Reducing Speed Increases a Driver's Total Stopping Distance: A Myth Debunked
The statement "reducing speed increases a driver's total stopping distance" is a common misconception. It's crucial to understand that while reducing speed inherently decreases the distance traveled during braking, it significantly reduces the overall stopping distance. This article will delve into the physics behind braking, explore the factors influencing stopping distance, and ultimately debunk this prevalent myth.
Understanding the Physics of Braking
Before we tackle the myth, let's establish a fundamental understanding of the physics governing braking. Stopping distance is primarily determined by two key components:
1. Reaction Distance: The Time Before Braking
This is the distance your vehicle travels from the moment you perceive a hazard until you actually apply the brakes. Reaction time is influenced by several factors, including:
- Driver alertness and fatigue: A tired or distracted driver will have a significantly longer reaction time.
- Alcohol and drug impairment: Substance abuse severely impairs reaction time, leading to increased stopping distances.
- Visibility conditions: Poor visibility due to fog, rain, or darkness extends reaction time.
- Vehicle condition: A vehicle with a delayed braking response system adds to reaction time.
Crucially, speed directly impacts reaction distance. At higher speeds, the vehicle covers more ground during the reaction time, even if the reaction time itself remains constant. Reducing speed inherently minimizes the distance covered during this crucial pre-braking phase.
2. Braking Distance: The Distance During Braking
This is the distance your vehicle travels from the moment you apply the brakes until it comes to a complete stop. Several factors determine braking distance:
- Vehicle speed: This is the most significant factor. The higher the speed, the longer the braking distance. The relationship is not linear; doubling the speed increases the braking distance by a factor greater than two. This is due to the kinetic energy of the vehicle, which increases proportionally to the square of its velocity.
- Road surface conditions: A dry, smooth surface provides optimal grip, while wet, icy, or loose surfaces dramatically reduce traction, increasing braking distance.
- Tire condition: Worn or damaged tires have significantly reduced grip, leading to increased braking distance.
- Brake system condition: Well-maintained brakes are essential for efficient stopping. Faulty brakes or inadequate brake fluid can significantly extend braking distance.
- Gradient of the road: Driving downhill increases braking distance, while uphill driving decreases it.
- Vehicle weight: Heavier vehicles generally require a longer braking distance.
Reducing speed drastically reduces braking distance. This is because the kinetic energy – the energy of motion – of the vehicle is directly related to its speed. Lower speed means lower kinetic energy, and hence, less distance needed to dissipate that energy through braking.
Debunking the Myth: Why Slower is Safer
The misconception that reducing speed increases total stopping distance arises from a misunderstanding of the relationship between speed, reaction distance, and braking distance. While reducing speed might seem to increase the overall time to stop, it dramatically decreases the total distance required to stop.
Consider this scenario:
-
Scenario 1: High Speed – A car traveling at 60 mph has a longer reaction distance and a significantly longer braking distance compared to a car traveling at 30 mph. The total stopping distance will be substantially greater.
-
Scenario 2: Lower Speed – A car traveling at 30 mph will have a shorter reaction distance and a much shorter braking distance. The total stopping distance will be significantly shorter.
The difference in total stopping distance between these two scenarios is substantial, making the lower speed option demonstrably safer.
The Importance of Safe Following Distance
Maintaining a safe following distance is paramount to preventing accidents. This distance should be sufficient to allow you to stop safely if the vehicle in front brakes suddenly. A common guideline is the "3-second rule," which involves selecting a stationary object and counting three seconds after the vehicle ahead passes it. If you reach the object before you finish counting, you're following too closely.
Reducing speed directly contributes to maintaining a safe following distance. At lower speeds, you have more time to react and a shorter stopping distance, significantly reducing the risk of rear-end collisions.
Other Factors Affecting Stopping Distance
Beyond speed, numerous other factors contribute to stopping distance, including:
- Driver experience: Experienced drivers tend to have shorter reaction times and better braking techniques.
- Vehicle maintenance: Regular vehicle maintenance, including brake checks and tire rotations, is essential for optimal stopping performance.
- Road conditions: Adverse weather conditions such as rain, snow, or ice significantly increase stopping distance.
- Load: Carrying a heavy load increases the vehicle's weight and inertia, extending braking distance.
Conclusion: Speed Reduction is Crucial for Safety
The notion that reducing speed increases total stopping distance is fundamentally flawed. While the time to stop might increase slightly at lower speeds, the distance required to stop is dramatically reduced. This reduction in stopping distance is critical for safety, significantly lowering the risk of accidents. Responsible driving involves maintaining a safe speed, adjusting to road and weather conditions, and consistently practicing safe driving habits. By understanding the factors influencing stopping distance and prioritizing safe driving practices, you can significantly improve your road safety and the safety of others. Remember, speed reduction is not just about following traffic laws; it's a crucial element of responsible and defensive driving. Prioritizing safety should always outweigh any perceived inconvenience caused by driving at a lower speed. The potential consequences of an accident far outweigh the time saved by driving at excessive speeds.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Post Test Mental Health And Community Health Issues
Mar 29, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Events Occurs During Metaphase Of Mitosis
Mar 29, 2025
-
Which Feature Is Most Closely Associated With Modernist Poetry
Mar 29, 2025
-
Food Handlers Who Scrub Their Hands And Arms With Soap
Mar 29, 2025
-
The Practice Of Statistics 6th Edition Answers
Mar 29, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Reducing Speed Increases A Driver's Total Stopping Distance. . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
