Signs And Symptoms Of Congestive Heart Failure Quizlet
Breaking News Today
Mar 17, 2025 · 6 min read
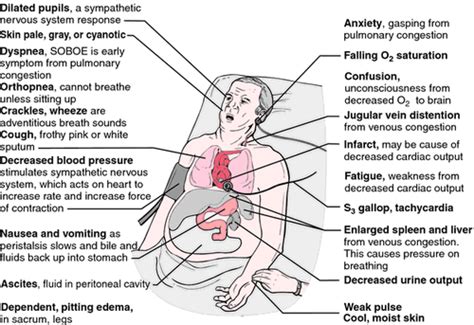
Table of Contents
Decoding the Signs and Symptoms of Congestive Heart Failure: A Comprehensive Guide
Congestive heart failure (CHF), also known as heart failure, is a serious condition where the heart can't pump enough blood to meet the body's needs. Understanding its signs and symptoms is crucial for early diagnosis and management. This comprehensive guide delves into the various manifestations of CHF, providing a detailed overview suitable for both healthcare professionals and individuals seeking to learn more about this prevalent condition. We'll explore common and less common symptoms, differentiating between left-sided and right-sided heart failure, and highlight the importance of prompt medical attention.
Understanding the Mechanics of Congestive Heart Failure
Before diving into the symptoms, it's essential to grasp the underlying mechanisms of CHF. The heart, a tireless muscle, works relentlessly to pump oxygen-rich blood throughout the body. In CHF, this vital function becomes impaired. This impairment can stem from various causes, including:
- Coronary artery disease: Narrowed arteries restrict blood flow to the heart muscle, weakening its ability to pump.
- High blood pressure (hypertension): Chronically elevated blood pressure forces the heart to work harder, leading to eventual weakening.
- Valve disease: Damaged heart valves disrupt the smooth flow of blood, increasing the heart's workload.
- Cardiomyopathy: Diseases affecting the heart muscle itself, compromising its pumping ability.
- Congenital heart defects: Birth defects affecting the heart's structure can contribute to CHF.
The inability of the heart to pump efficiently leads to a buildup of fluid in the lungs (pulmonary edema) and/or other parts of the body (peripheral edema), a hallmark characteristic of congestive heart failure. This fluid buildup further exacerbates the heart's struggle, creating a vicious cycle.
Common Signs and Symptoms of Congestive Heart Failure: A Detailed Breakdown
The symptoms of CHF are highly variable, depending on the severity and location of the fluid buildup. However, some common indicators include:
Left-Sided Heart Failure Symptoms:
Left-sided heart failure primarily affects the left ventricle, the chamber responsible for pumping oxygenated blood to the body. Common symptoms include:
-
Shortness of breath (dyspnea): This is often the most prominent symptom, appearing initially during exertion and progressing to rest. It can manifest as breathlessness while lying down (orthopnea) or waking up gasping for air at night (paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea). Dyspnea is a crucial indicator requiring immediate medical attention.
-
Wheezing and coughing: Fluid buildup in the lungs can cause wheezing and a persistent, often dry, cough. The cough might produce frothy or blood-tinged sputum in severe cases.
-
Fatigue and weakness: The reduced blood flow to the body deprives organs of oxygen, leading to pronounced fatigue and overall weakness.
-
Rapid or irregular heartbeat (palpitations): The heart attempts to compensate for its reduced pumping efficiency by beating faster, leading to palpitations.
Right-Sided Heart Failure Symptoms:
Right-sided heart failure primarily impacts the right ventricle, responsible for pumping deoxygenated blood to the lungs. Symptoms often include:
-
Swelling in the legs, ankles, and feet (peripheral edema): This is a common manifestation due to fluid buildup in the lower extremities.
-
Swelling in the abdomen (ascites): Fluid accumulation in the abdominal cavity can cause significant abdominal distension.
-
Swollen veins in the neck (jugular venous distension): Increased pressure in the veins can cause them to bulge prominently in the neck.
-
Weight gain: The retention of excess fluid contributes to a noticeable and often rapid weight gain.
-
Reduced urine output: The kidneys may be less efficient in removing excess fluid, resulting in decreased urination.
Less Common, but Significant, Symptoms:
Beyond the common symptoms, some less frequent indicators can also point towards CHF:
-
Persistent dry cough: A dry cough, unrelated to respiratory infections, can be a subtle yet important sign.
-
Nausea and loss of appetite: Reduced blood flow to the digestive system can cause digestive upset.
-
Confusion or memory problems: In severe cases, inadequate oxygen supply to the brain can lead to cognitive impairment.
-
Chest pain: Although not always directly related to CHF, chest pain can sometimes indicate underlying cardiac issues that contribute to heart failure.
Differentiating CHF from Other Conditions: The Importance of Accurate Diagnosis
Many conditions share symptoms with CHF, making accurate diagnosis critical. Conditions like pneumonia, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and anxiety can mimic some of CHF's symptoms. Only a thorough medical evaluation, including a physical exam, blood tests (e.g., BNP levels), chest X-rays, echocardiogram, and possibly electrocardiogram (ECG), can confirm a diagnosis of CHF.
The Significance of Early Detection and Management: Improving Quality of Life
Early detection of CHF is paramount. Prompt diagnosis and treatment significantly improve the patient's quality of life and prognosis. Treatment strategies focus on managing underlying conditions, optimizing heart function, and alleviating symptoms. This often involves lifestyle modifications (diet, exercise, stress management), medications (diuretics, ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers, etc.), and in severe cases, surgery or device implantation (pacemakers, implantable cardioverter-defibrillators – ICDs).
CHF and Lifestyle Modifications: A Collaborative Approach to Wellness
Beyond medical interventions, lifestyle modifications play a critical role in managing CHF. These modifications contribute to slowing disease progression and improving overall well-being. Key lifestyle adjustments include:
-
Dietary changes: Following a low-sodium diet is essential to reduce fluid retention. Limiting saturated and trans fats, and choosing lean protein sources are also beneficial.
-
Regular exercise: Moderate physical activity, tailored to individual capabilities, strengthens the heart and improves overall cardiovascular health. Consult your physician before starting any new exercise program.
-
Stress management: Chronic stress exacerbates cardiovascular problems. Implementing stress-reduction techniques like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises can significantly improve heart health.
-
Weight management: Maintaining a healthy weight reduces strain on the heart. Losing excess weight can improve overall cardiovascular function and lessen the symptoms of CHF.
-
Quitting smoking: Smoking significantly damages the cardiovascular system. Quitting is crucial for improving heart health and reducing the risk of complications.
-
Limiting alcohol consumption: Excessive alcohol intake can worsen heart failure. Moderation or abstinence, as advised by your physician, is essential.
Prognosis and Long-Term Outlook: Navigating the Journey with CHF
The prognosis for CHF varies greatly depending on several factors, including the severity of the condition, the presence of other medical issues, and the effectiveness of treatment. While CHF is a chronic condition, adherence to treatment plans and lifestyle modifications can significantly improve the long-term outlook. Regular medical follow-ups and open communication with your healthcare team are crucial for effective management and maintaining a good quality of life.
Conclusion: Empowering Individuals Through Knowledge and Action
Understanding the signs and symptoms of congestive heart failure is the first step in proactive health management. Recognizing the early warning signals allows for timely medical intervention, potentially preventing severe complications and improving overall prognosis. By combining medical treatment with lifestyle modifications, individuals with CHF can navigate the journey with improved quality of life and a greater sense of empowerment. Remember, prompt medical attention is crucial if you suspect you or someone you know might be experiencing symptoms of CHF. Early intervention is key to a positive outcome.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
True Or False Professional And Technical Communication Is Research Oriented
Mar 18, 2025
-
Which Best Describes The Terrorist Planning Cycle
Mar 18, 2025
-
Cdl Combination Test Questions And Answers Pdf
Mar 18, 2025
-
Life Insurance Exam Questions And Answers Pdf
Mar 18, 2025
-
The Direct Carry Is Used To Transfer A Patient
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Signs And Symptoms Of Congestive Heart Failure Quizlet . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
