Six Sigma And Lean Foundations And Principles Quizlet
Breaking News Today
Mar 18, 2025 · 6 min read
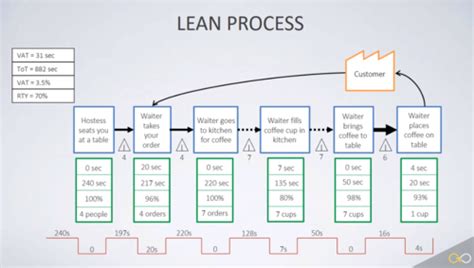
Table of Contents
Six Sigma and Lean Foundations and Principles Quizlet: A Comprehensive Guide
This article delves into the core principles of Six Sigma and Lean methodologies, providing a detailed overview that surpasses the typical Quizlet study guide. We'll explore their individual strengths, highlight their synergistic potential when combined, and discuss their practical applications across various industries. This in-depth exploration will equip you with a comprehensive understanding, far exceeding a simple quizlet review.
Understanding Six Sigma: A Deep Dive
Six Sigma is a data-driven methodology aimed at minimizing defects and variability in any process. Its core focus is on improving quality and efficiency by identifying and eliminating sources of error. This involves a structured approach using statistical methods and a defined set of tools and techniques.
Key Principles of Six Sigma:
-
DMAIC Cycle: This is the backbone of Six Sigma projects. It stands for Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control. This cyclical approach ensures a structured and systematic improvement process.
- Define: Clearly define the problem, project goals, and customer requirements. This stage sets the stage for the entire project and ensures everyone is on the same page.
- Measure: Collect data to quantify the current process performance and identify key metrics. This involves selecting appropriate data collection methods and analyzing the collected data to understand the current state.
- Analyze: Analyze the collected data to identify the root causes of the defects or variations. This stage often involves using statistical tools like Pareto charts, fishbone diagrams, and process capability analysis.
- Improve: Develop and implement solutions to address the root causes identified in the analysis phase. This might involve process redesign, training, or technology upgrades.
- Control: Implement controls to sustain the improvements achieved and prevent regression to the previous state. This often includes monitoring key metrics and developing a plan to address any deviations from the desired performance.
-
Focus on Data and Statistical Analysis: Six Sigma heavily relies on data to make informed decisions. Statistical tools are used throughout the DMAIC cycle to analyze process performance, identify root causes, and measure the impact of improvements.
-
Customer Focus: Ultimately, Six Sigma aims to improve customer satisfaction by delivering high-quality products and services consistently. Customer needs and expectations are central to the process.
-
Continuous Improvement: Six Sigma is not a one-time fix but rather a continuous improvement philosophy. Even after achieving significant improvements, the process should be continuously monitored and refined to maintain high performance.
Understanding Lean: Streamlining for Efficiency
Lean manufacturing, often simplified to just "Lean," is a systematic method for identifying and eliminating waste (Muda) within a manufacturing process. While originating in manufacturing, its principles are universally applicable across various industries and sectors.
Core Principles of Lean:
-
Value Stream Mapping: This technique visually maps the entire process flow, identifying all steps involved in delivering a product or service to the customer. It highlights areas of waste and inefficiency.
-
Waste Elimination (Muda): Lean focuses on identifying and eliminating seven types of waste (often expanded to eight):
- Transportation: Unnecessary movement of materials or information.
- Inventory: Excess inventory that ties up capital and hides problems.
- Motion: Unnecessary movement of people or equipment.
- Waiting: Delays in the process that cause idle time.
- Overproduction: Producing more than is needed or before it is needed.
- Over-processing: Performing more work than necessary to meet customer requirements.
- Defects: Errors or imperfections that require rework or scrap.
- Non-Utilized Talent: Failing to utilize the skills and knowledge of employees fully.
-
Just-in-Time (JIT) Inventory: A key principle of Lean is to minimize inventory by only producing what is needed, when it is needed. This reduces storage costs and waste.
-
Continuous Flow: Lean aims to create a smooth and continuous flow of materials and information through the process, minimizing interruptions and delays.
-
Pull System: Instead of pushing products through the process, a pull system allows downstream processes to pull materials and information from upstream processes only when needed.
-
Kaizen (Continuous Improvement): Like Six Sigma, Lean emphasizes continuous improvement through small, incremental changes. Kaizen encourages employee involvement and empowers them to identify and implement improvements.
Six Sigma and Lean: A Synergistic Combination
While distinct methodologies, Six Sigma and Lean are highly complementary and can be synergistically combined to achieve superior results. Their combined application leads to significant improvements in quality, efficiency, and customer satisfaction.
Combining Six Sigma and Lean:
-
Enhanced Problem Solving: Lean's focus on identifying and eliminating waste complements Six Sigma's data-driven approach to problem-solving. Combining both allows for a more comprehensive and effective approach to process improvement.
-
Improved Process Efficiency: Lean’s focus on streamlining processes directly addresses the variability that Six Sigma seeks to reduce. Together they create efficient and consistent processes.
-
Reduced Costs: Eliminating waste (Lean) and reducing defects (Six Sigma) both contribute to significant cost savings.
-
Increased Customer Satisfaction: Improving quality and efficiency leads to better products and services, ultimately increasing customer satisfaction.
Practical Applications Across Industries
The principles of Six Sigma and Lean are not limited to manufacturing. They have been successfully implemented across a wide range of industries, including:
- Healthcare: Improving patient care, reducing wait times, and minimizing medical errors.
- Finance: Streamlining processes, reducing operational costs, and improving customer service.
- IT: Enhancing software development processes, reducing bugs, and improving system performance.
- Government: Improving public services, reducing bureaucracy, and increasing efficiency.
Case Studies: Real-World Examples
Numerous companies have successfully implemented Six Sigma and Lean methodologies to achieve significant improvements. While specific details of proprietary projects are often confidential, the general principles and outcomes are widely documented:
-
Manufacturing: Many manufacturing companies have reduced defect rates, improved production efficiency, and lowered costs by implementing Six Sigma and Lean principles. These improvements often result in increased profitability and market competitiveness.
-
Service Industries: Companies in service industries, such as banking and telecommunications, have used Six Sigma and Lean to reduce wait times, improve customer service, and enhance operational efficiency.
-
Healthcare: Hospitals and healthcare systems have applied Six Sigma and Lean to improve patient care, reduce medical errors, and enhance the overall patient experience.
Conclusion: Beyond the Quizlet
This comprehensive overview extends far beyond a simple Six Sigma and Lean Quizlet study guide. It provides a nuanced understanding of the methodologies, their underlying principles, and their synergistic potential. Remember, mastering these methodologies isn't about memorizing definitions; it's about applying the principles to solve real-world problems and drive continuous improvement within your organization or field of study. The true value lies in understanding the "why" behind the "what," enabling you to effectively apply these powerful tools in any context. By grasping the fundamental principles and their interrelation, you equip yourself with a powerful toolkit for process optimization and achieving exceptional results. This deep understanding will translate to success far beyond any simple quiz.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
True Or False Professional And Technical Communication Is Research Oriented
Mar 18, 2025
-
Which Best Describes The Terrorist Planning Cycle
Mar 18, 2025
-
Cdl Combination Test Questions And Answers Pdf
Mar 18, 2025
-
Life Insurance Exam Questions And Answers Pdf
Mar 18, 2025
-
The Direct Carry Is Used To Transfer A Patient
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Six Sigma And Lean Foundations And Principles Quizlet . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
