States That Have Adopted Right-to-work Laws: Quizlet
Breaking News Today
Mar 17, 2025 · 5 min read
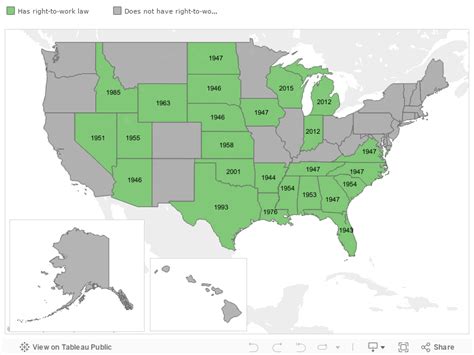
Table of Contents
States That Have Adopted Right-to-Work Laws: A Comprehensive Overview
Right-to-work (RTW) laws have been a significant point of contention in the United States, sparking debates about their impact on workers' rights, unions, and the overall economy. Understanding which states have adopted these laws is crucial for anyone interested in labor relations, economics, or political science. This comprehensive guide will not only list the states with RTW laws but also delve into the history, implications, and ongoing controversies surrounding them. We'll also explore the arguments for and against RTW legislation, providing a balanced perspective on this complex issue.
What are Right-to-Work Laws?
Right-to-work laws prohibit union security agreements, meaning that employers cannot require employees to pay union dues or fees as a condition of employment, even if the majority of workers in a workplace have voted to be represented by a union. This contrasts with "union shop" agreements, common in states without RTW laws, where union membership or dues payment is often a requirement for employment.
The Key Argument: Freedom of Association vs. Fair Share
The core debate revolves around the concepts of freedom of association and fair share. Proponents of RTW laws argue they uphold individual freedom by preventing mandatory union membership or financial contributions. They contend that workers shouldn't be forced to support a union, even if it represents them, if they disagree with its policies or goals.
Opponents, however, argue that RTW laws weaken unions and ultimately harm workers. They contend that RTW laws allow "free riders"—employees who benefit from union negotiations and protections without contributing financially—which undermines the union's ability to effectively bargain for better wages, benefits, and working conditions. The argument is that a strong union needs the financial support of all its members to be truly effective.
The List: States with Right-to-Work Laws
Currently, 27 states have enacted right-to-work laws. These states are:
- Alabama
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- Florida
- Georgia
- Idaho
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Mississippi
- Montana (partial right-to-work; see below for clarification)
- Nebraska
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Oklahoma
- Right-to-work South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming
Montana's Unique Status:
Montana deserves special mention. While it is often included in lists of RTW states, its law is somewhat unique. Montana doesn't have a comprehensive RTW law prohibiting all union security agreements. Instead, it has a law that restricts the use of union security clauses in certain situations, effectively limiting their applicability. This makes Montana's status as a "right-to-work" state a subject of debate among legal experts and labor activists.
Historical Context and the Evolution of RTW Laws
The passage of RTW laws wasn't a uniform or simultaneous event. The first RTW law was passed in 1947 in Virginia, spurred by a post-World War II pushback against organized labor. The legislative momentum for RTW laws intensified in the latter half of the 20th century, with many southern states enacting these laws in an effort to attract businesses and deter unionization.
The spread of RTW laws has been closely tied to political shifts and economic considerations. Conservative political movements have strongly supported RTW legislation, viewing it as a way to limit the power of unions and promote a more business-friendly environment.
Economic Impact: A Contentious Debate
The economic effects of RTW laws remain a highly debated topic. Proponents claim that these laws attract businesses, stimulate economic growth, and create jobs by lowering labor costs. They argue that the reduced costs of employing unionized workers make these states more competitive.
Critics, however, argue that RTW laws suppress wages, reduce benefits, and harm overall worker well-being. They point to studies suggesting that RTW states often have lower wages, fewer benefits, and a greater income inequality compared to non-RTW states. The debate is further complicated by the numerous other factors—like education levels, industry composition, and overall economic conditions—that influence a state's economic performance.
Social Implications: Union Density and Worker Representation
The impact of RTW laws on union density is undeniable. States with RTW laws consistently show significantly lower union membership rates compared to non-RTW states. This decline in union membership can have broader social implications, affecting workers' collective bargaining power, their ability to advocate for better conditions, and the overall balance of power between labor and management.
The reduction in union membership can also lead to a decline in worker representation and participation in the political process. Unions often play a critical role in advocating for workers' rights and improving social and economic conditions.
Political Ramifications: A Divisive Issue
RTW laws remain a highly divisive political issue. The debate often aligns with broader ideological divides, pitting proponents of limited government regulation and free-market principles against those who emphasize the importance of workers' rights and collective bargaining. The fight over RTW laws reflects a larger struggle over the role of labor unions in society and the balance of power between employers and employees.
The Future of Right-to-Work Legislation
While the current distribution of RTW laws is relatively stable, the possibility of future changes remains. Political shifts, economic pressures, and ongoing debates over labor rights could all influence the future landscape of RTW legislation. The ongoing discussion highlights the importance of continuing to examine the impact of RTW laws on workers, businesses, and the overall economy.
Conclusion: A Multifaceted Issue Requiring Deeper Understanding
The issue of right-to-work laws is far from simple. It's a complex, multifaceted issue with economic, social, and political implications. While this article provides a comprehensive overview, it's crucial to engage in further research and critical analysis to form your own informed opinion on this enduring debate. By understanding the arguments for and against RTW laws, the historical context of their adoption, and their potential impacts, we can contribute to a more nuanced discussion of this significant aspect of labor relations in the United States. It is also vital to consider the various academic studies and research papers available on this topic to gain a more complete understanding of the complexities involved. This allows for a more robust and well-informed discussion and decision-making process when considering the impact of right-to-work laws.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Best Describes The Terrorist Planning Cycle
Mar 18, 2025
-
Cdl Combination Test Questions And Answers Pdf
Mar 18, 2025
-
Life Insurance Exam Questions And Answers Pdf
Mar 18, 2025
-
The Direct Carry Is Used To Transfer A Patient
Mar 18, 2025
-
The Emancipation Proclamation Of January 1 1863 Quizlet
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about States That Have Adopted Right-to-work Laws: Quizlet . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
