The Aztecs Controlled The Most Powerful Empire In
Breaking News Today
Mar 20, 2025 · 7 min read
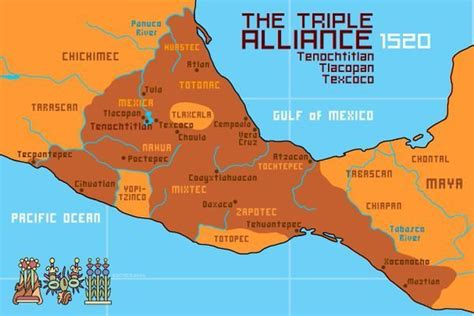
Table of Contents
The Aztecs: Masters of a Mighty Mesoamerican Empire
The Aztec Empire, a name synonymous with power, ritual sacrifice, and advanced civilization, dominated much of Mesoamerica in the 15th and early 16th centuries. While their reign was relatively short compared to some other ancient empires, the Aztecs achieved a level of political, economic, and military dominance that few others could match in their time. This article delves into the intricacies of their empire, exploring the factors that contributed to their rise, the mechanisms they used to maintain control, and the legacy they left behind.
The Rise of the Mexica: From Humble Beginnings to Imperial Power
The Aztecs, also known as the Mexica, weren't indigenous to the Valley of Mexico. They were a relatively small, nomadic group who migrated to the region sometime in the 13th century. Initially, they faced marginalization and hostility from established groups like the Tepanecs. Their ascent to power was a gradual, strategically calculated process built on several key elements:
Military Prowess and Strategic Alliances:
The Mexica were fierce warriors, developing sophisticated military tactics and organization. Their army, comprised of highly disciplined and trained soldiers, was pivotal in their expansion. Instead of simply conquering, they employed a strategy of forming alliances, incorporating conquered populations into their military structure and thereby swelling their ranks. This approach proved significantly more effective than brute force alone.
Harnessing the Power of Religion and Ideology:
Religion played a central role in Aztec society, shaping their worldview and providing a strong foundation for their political authority. The Mexica emperors were considered divinely appointed rulers, intermediaries between the gods and the people. This divine mandate strengthened their legitimacy and fostered loyalty among their subjects. The elaborate religious ceremonies, including the infamous human sacrifices, served not only to appease the gods but also to reinforce the power and authority of the ruling elite. While controversial and horrifying by modern standards, these practices were integral to their social and political structure.
Sophisticated Administrative Systems:
The Aztecs developed a complex administrative system to govern their sprawling empire. The empire wasn’t a unified, centralized state in the modern sense; rather, it was a network of tributary city-states, each retaining a degree of autonomy while paying tribute to the Mexica rulers. This system allowed for efficient resource extraction and control across vast distances. The capital city, Tenochtitlan, served as the central hub of the empire, a magnificent city built on an island in Lake Texcoco, showcasing the Aztec’s remarkable engineering skills and their ability to organize vast resources.
Maintaining Control: The Mechanisms of Aztec Power
The Aztecs’ ability to maintain control over such a diverse and extensive empire was a testament to their political acumen and organizational skills. Several key mechanisms were employed to ensure their dominance:
The Tribute System:
The tribute system was the cornerstone of the Aztec economy and a fundamental element of their power. Conquered city-states were obligated to pay regular tributes to the Mexica, which included a wide variety of goods: food, textiles, precious metals, feathers, and even human captives for sacrifice. This system ensured a constant flow of resources to Tenochtitlan and bolstered the empire's economic strength, while simultaneously reinforcing the Mexica’s authority. The highly organized nature of this system speaks volumes about the sophistication of their administration.
Provincial Governors and Military Garrisons:
To ensure compliance and prevent rebellion, the Aztecs established a system of provincial governors who were responsible for administering their assigned regions. These governors were often handpicked Aztec nobles or loyal allies, ensuring loyalty to the emperor. Military garrisons were stationed in key strategic locations throughout the empire, providing a constant show of force and serving as a swift response to any signs of unrest or rebellion. This combination of administrative and military control proved highly effective in maintaining order.
The Role of Ideology and Propaganda:
The Aztecs skillfully employed ideology and propaganda to consolidate their power. Religious beliefs and the divine right of the emperor were constantly reinforced through elaborate rituals, festivals, and artistic representations. The empire's propaganda machine portrayed the Mexica as divinely appointed rulers, deserving of obedience and tribute. This systematic dissemination of ideology helped to foster loyalty and suppress dissent among the diverse populations of the empire.
The Aztec Economy: A Thriving Network of Trade and Production
The Aztec economy was remarkably sophisticated for its time, built on a foundation of agriculture, trade, and skilled craftsmanship.
Agriculture and Resource Management:
The Aztecs developed advanced agricultural techniques, including chinampas (floating gardens) to maximize food production in the often-challenging environment of the Valley of Mexico. This efficient agriculture enabled them to support a large population and maintain a surplus to fund their military and administrative activities. Their understanding of water management and irrigation systems was crucial to their agricultural success and the prosperity of the empire.
Extensive Trade Networks:
The Aztecs controlled extensive trade networks that stretched across Mesoamerica. Goods were transported via land and water routes, connecting distant regions and facilitating the exchange of resources. The empire acted as a central hub, regulating trade and extracting significant economic benefits. The sophisticated organization of this trade system further exemplifies the advanced administrative capabilities of the Aztec empire. Markets were vital to this system, with major marketplaces acting as economic and social centers.
Specialized Crafts and Artistic Production:
The Aztecs were renowned for their skilled artisans and craftspeople. They produced high-quality textiles, ceramics, jewelry, and other luxury goods. These goods were not only used within the empire but also served as important trade items, generating wealth and prestige for the empire. The artistry and craftsmanship of the Aztecs remain a testament to their skill and creativity.
The Downfall of the Empire: Conquest and Collapse
Despite their impressive power and sophisticated organization, the Aztec empire ultimately succumbed to the Spanish conquistadors led by Hernán Cortés in 1521. Several factors contributed to their downfall:
Internal Divisions and Rebellions:
While the Aztec Empire seemed formidable from the outside, simmering tensions and resentments existed within. Many conquered groups harbored resentment towards the Mexica rulers and their heavy tribute demands. Cortés cleverly exploited these existing divisions, forming alliances with disgruntled tributary states who saw an opportunity to break free from Aztec rule. This strategy significantly weakened the Aztec’s ability to defend against the Spanish invaders.
Disease and Demographic Collapse:
The arrival of the Spanish also brought devastating diseases—smallpox, measles, and influenza—to which the indigenous population had no immunity. These diseases decimated the Aztec population, weakening their army and disrupting their society. The pandemic severely hampered their ability to effectively resist the Spanish conquest.
Superior Spanish Military Technology:
Cortés’s relatively small army had a decisive advantage in terms of weaponry and military technology. The Spanish possessed steel weapons, firearms, and horses, which gave them a distinct edge over the Aztec army's obsidian weapons and primitive defenses. This technological disparity played a significant role in the eventual Spanish victory.
The Legacy of the Aztec Empire
The Aztec Empire, though short-lived, left an indelible mark on history. Their achievements in urban planning, agriculture, art, and administration were remarkable. The ruins of Tenochtitlan, now submerged beneath Mexico City, stand as a silent testament to their power and sophisticated civilization. The study of their intricate social structures, complex religious beliefs, and sophisticated political organization continues to fascinate and inform historians and anthropologists. While the brutal aspects of their empire cannot be ignored, understanding their achievements provides a crucial perspective on the richness and complexity of pre-Columbian Mesoamerica.
The legacy of the Aztecs continues to resonate today. Their impact on the culture, language, and even the very landscape of Mexico is undeniable. The modern nation of Mexico is a product of its history, and the Aztec Empire represents a crucial chapter in that history, a testament to human ingenuity and ambition, a reminder of the rise and fall of empires, and a source of ongoing fascination for those who study the past. Their intricate political and social systems, remarkable engineering feats, and contributions to art and culture remain sources of inspiration and wonder, ensuring that the Aztecs maintain a prominent place in history. The remnants of their incredible civilization, scattered throughout modern-day Mexico, serve as a powerful reminder of their once formidable presence, a compelling story of a society that rose to unprecedented power and then ultimately fell to a combination of internal and external pressures. Their story provides a valuable lesson on the complexities of empire building, the fragility of power, and the enduring legacy of civilizations past.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Best Definition Of The Term Characterization
Mar 20, 2025
-
Match Each Picture With The Correct Stage Of Mitosis
Mar 20, 2025
-
Amazon Day 1 Final Exam Answers Pdf
Mar 20, 2025
-
Quote Two Idioms In Romeo And Juliet
Mar 20, 2025
-
The Sampling Distribution Of The Difference Helps Us Determine
Mar 20, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Aztecs Controlled The Most Powerful Empire In . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
